Difference between revisions of "Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|Glun1, GRIN1, NMDA1|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q05586 Q05586]|Homo sapiens|Cys744, Cys798|Glutamate-gated...") |
(→Protein Function) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. This protein plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. It mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Is involved in the cell surface targeting of NMDA receptors. (From Uniprot)<br/> | NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. This protein plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. It mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Is involved in the cell surface targeting of NMDA receptors. (From Uniprot)<br/> | ||
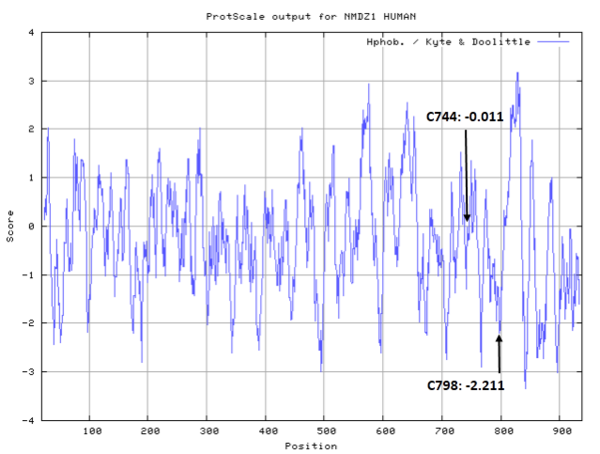
| − | [[File:549-function.png|center| | + | [[File:549-function.png|center|500px]] |
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
Revision as of 02:49, 10 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Glun1, GRIN1, NMDA1 |
| UNP ID | Q05586 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys744, Cys798 |
| Family/Domain |
Glutamate-gated ion channel family, NR1/GRIN1 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Ion channel |
Summary
Protein Function
NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. This protein plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. It mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Is involved in the cell surface targeting of NMDA receptors. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys744: Unknown
- Cys798: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MSTMRLLTLA LLFSCSVARA ACDPKIVNIG AVLSTRKHEQ MFREAVNQAN
KRHGSWKIQL NATSVTHKPN AIQMALSVCE DLISSQVYAI LVSHPPTPND
HFTPTPVSYT AGFYRIPVLG LTTRMSIYSD KSIHLSFLRT VPPYSHQSSV
WFEMMRVYSW NHIILLVSDD HEGRAAQKRL ETLLEERESK AEKVLQFDPG
TKNVTALLME AKELEARVII LSASEDDAAT VYRAAAMLNM TGSGYVWLVG
EREISGNALR YAPDGILGLQ LINGKNESAH ISDAVGVVAQ AVHELLEKEN
ITDPPRGCVG NTNIWKTGPL FKRVLMSSKY ADGVTGRVEF NEDGDRKFAN
YSIMNLQNRK LVQVGIYNGT HVIPNDRKII WPGGETEKPR GYQMSTRLKI
VTIHQEPFVY VKPTLSDGTC KEEFTVNGDP VKKVICTGPN DTSPGSPRHT
VPQCCYGFCI DLLIKLARTM NFTYEVHLVA DGKFGTQERV NNSNKKEWNG
MMGELLSGQA DMIVAPLTIN NERAQYIEFS KPFKYQGLTI LVKKEIPRST
LDSFMQPFQS TLWLLVGLSV HVVAVMLYLL DRFSPFGRFK VNSEEEEEDA
LTLSSAMWFS WGVLLNSGIG EGAPRSFSAR ILGMVWAGFA MIIVASYTAN
LAAFLVLDRP EERITGINDP RLRNPSDKFI YATVKQSSVD IYFRRQVELS
TMYRHMEKHN YESAAEAIQA VRDNKLHAFI WDSAVLEFEA SQKCDLVTTG
ELFFRSGFGI GMRKDSPWKQ NVSLSILKSH ENGFMEDLDK TWVRYQECDS
RSNAPATLTF ENMAGVFMLV AGGIVAGIFL IFIEIAYKRH KDARRKQMQL
AFAAVNVWRK NLQDRKSGRA EPDPKKKATF RAITSTLASS FKRRRSSKDT
STGGGRGALQ NQKDTVLPRR AIEREEGQLQ LCSRHRES
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Ras signaling pathway
- Rap1 signaling pathway
- Calcium signaling pathway
- cAMP signaling pathway
- Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
- Circadian entrainment
- Long-term potentiation
- Glutamatergic synapse
- Alzheimer disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Cocaine addiction
- Amphetamine addiction
- Nicotine addiction
- Alcoholism
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Kim W K, Choi Y B, Rayudu P V, et al. Attenuation of NMDA receptor activity and neurotoxicity by nitroxyl anion, NO−[J]. Neuron, 1999, 24(2): 461-469. 10571239
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Ion channel
- Glutamate-gated ion channel family
- NR1/GRIN1 subfamily
- Ras signaling pathway
- Rap1 signaling pathway
- Calcium signaling pathway
- CAMP signaling pathway
- Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
- Circadian entrainment
- Long-term potentiation
- Glutamatergic synapse
- Alzheimer disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Cocaine addiction
- Amphetamine addiction
- Nicotine addiction
- Alcoholism