Difference between revisions of "Cathepsin B (Bos taurus)"
(→Reference) |
(→Reference) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| __TOC__ | | __TOC__ | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|CTSB|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P07688 P07688]|Bos taurus|Cys108|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00112 Peptidase C1 family]|[[:Category:Cathepsin B (Bos taurus)|Ligand list]]}} | + | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|CTSB|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P07688 P07688]|Bos taurus|Cys108|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00112 Peptidase C1 family]|[[:Category:Cathepsin B (Bos taurus)|Ligand list]]|Protease}} |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| − | Cys108 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin, which is very close to His278 and Asn298 in spcae. These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.<br/> | + | Cys108 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin B, which is very close to His278 and Asn298 in spcae. These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.<br/> |
* Hydrophobic property: | * Hydrophobic property: | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
:[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1QDQ 1QDQ], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1ITO 1ITO], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1SP4 1SP4], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2DC6 2DC6]<br/> | :[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1QDQ 1QDQ], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1ITO 1ITO], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1SP4 1SP4], [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2DC6 2DC6]<br/> | ||
| − | *Protein structure | + | *Protein structure: |
| − | [[483. | + | [[File:483.PNG|center|800px]] |
==Related Pathway== | ==Related Pathway== | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04142 Lysosome] <br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04142 Lysosome] <br/> | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04612 Antigen processing and presentation]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04612 Antigen processing and presentation]<br/> | ||
| + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04140 Autophagy] <br/> | ||
| + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04210 Apoptosis] <br/> | ||
| + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04621 NOD-like receptor signaling pathway] <br/> | ||
| + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04924 Renin secretion] <br/> | ||
==Experimental Evidence== | ==Experimental Evidence== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 47: | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| − | # Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Hara T, et al. '''Substrate specificity of bovine cathepsin B and its inhibition by CA074, based on crystal structure refinement of the complex[J].''' The Journal of Biochemistry, 2000, 127(4): 635-643 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10739956 10739956]<br/> | + | # Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Hara T, et al. '''Substrate specificity of bovine cathepsin B and its inhibition by CA074, based on crystal structure refinement of the complex[J].''' The Journal of Biochemistry, 2000, 127(4): 635-643. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10739956 10739956]<br/> |
# Smith R A, Copp L J, Coles P J, et al. '''New inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. Peptidyl acyloxymethyl ketones and the quiescent nucleofuge strategy[J].''' Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1988, 110(13): 4429-4431. DOI: 10.1021/ja00221a062 <br/> | # Smith R A, Copp L J, Coles P J, et al. '''New inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. Peptidyl acyloxymethyl ketones and the quiescent nucleofuge strategy[J].''' Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1988, 110(13): 4429-4431. DOI: 10.1021/ja00221a062 <br/> | ||
| − | # Štern I, Schaschke N, Moroder L, et al. '''Crystal structure of NS-134 in complex with bovine cathepsin B: a two-headed epoxysuccinyl inhibitor extends along the entire active-site cleft[J].''' Biochemical Journal, 2004, 381(2): 511-517.[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15084146 15084146]<br/> | + | # Štern I, Schaschke N, Moroder L, et al. '''Crystal structure of NS-134 in complex with bovine cathepsin B: a two-headed epoxysuccinyl inhibitor extends along the entire active-site cleft[J].''' Biochemical Journal, 2004, 381(2): 511-517. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15084146 15084146]<br/> |
# Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Matsugi K, et al. '''Structural basis for development of cathepsin B-specific noncovalent-type inhibitor: crystal structure of cathepsin B–E64c complex[J].''' Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2002, 1597(2): 244-251. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12044902 12044902]<br/> | # Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Matsugi K, et al. '''Structural basis for development of cathepsin B-specific noncovalent-type inhibitor: crystal structure of cathepsin B–E64c complex[J].''' Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2002, 1597(2): 244-251. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12044902 12044902]<br/> | ||
# Watanabe D, Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, et al. '''Quantitative evaluation of each catalytic subsite of cathepsin B for inhibitory activity based on inhibitory activity–binding mode relationship of epoxysuccinyl inhibitors by X-ray crystal structure analyses of complexes[J].''' Journal of molecular biology, 2006, 362(5): 979-993. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=16950396 16950396]<br/> | # Watanabe D, Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, et al. '''Quantitative evaluation of each catalytic subsite of cathepsin B for inhibitory activity based on inhibitory activity–binding mode relationship of epoxysuccinyl inhibitors by X-ray crystal structure analyses of complexes[J].''' Journal of molecular biology, 2006, 362(5): 979-993. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=16950396 16950396]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Bos taurus]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Protease]] |
| − | [[Category:Antigen processing and presentation | + | [[Category:Peptidase C1 family]] |
| + | [[Category:Lysosome]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Antigen processing and presentation]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Autophagy - animal]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Apoptosis]] | ||
| + | [[Category:NOD-like receptor signaling pathway]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Renin secretion]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:45, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CTSB |
| UNP ID | P07688 |
| Organism | Bos taurus |
| Cys Site | Cys108 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C1 family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
CTSB is a thiol protease which is believed to participate in intracellular degradation and turnover of proteins. It has also been implicated in tumor invasion and metastasis.
Hydrolysis of proteins with broad specificity for peptide bonds. Preferentially cleaves -Arg-Arg-|-Xaa bonds in small molecule substrates (thus differing from cathepsin L). In addition to being an endopeptidase, shows peptidyl-dipeptidase activity, liberating C-terminal dipeptides.
Cys Function & Property
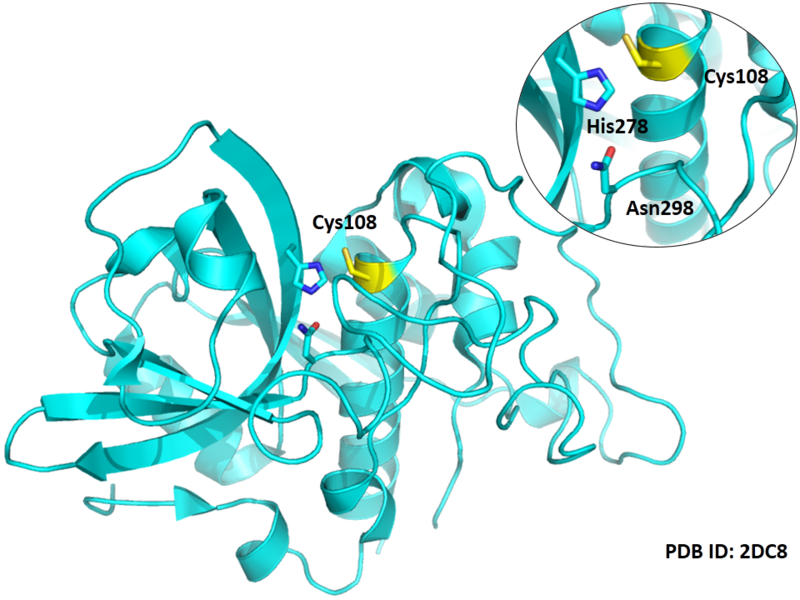
Cys108 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin B, which is very close to His278 and Asn298 in spcae. These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.
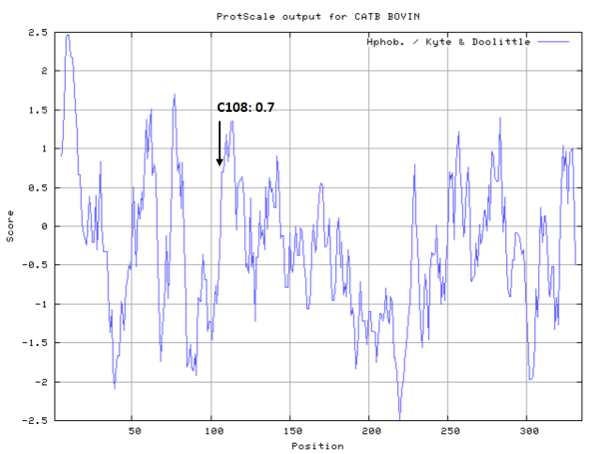
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys108: 4.137 A^2
Protein Sequence
MWRLLATLSC LLVLTSARSS LYFPPLSDEL VNFVNKQNTT WKAGHNFYNV
DLSYVKKLCG AILGGPKLPQ RDAFAADVVL PESFDAREQW PNCPTIKEIR
DQGSCGSCWA FGAVEAISDR ICIHSNGRVN VEVSAEDMLT CCGGECGDGC
NGGFPSGAWN FWTKKGLVSG GLYNSHVGCR PYSIPPCEHH VNGSRPPCTG
EGDTPKCSKT CEPGYSPSYK EDKHFGCSSY SVANNEKEIM AEIYKNGPVE
GAFSVYSDFL LYKSGVYQHV SGEIMGGHAI RILGWGVENG TPYWLVGNSW
NTDWGDNGFF KILRGQDHCG IESEIVAGMP CTHQY
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Lysosome
- Antigen processing and presentation
- Autophagy
- Apoptosis
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- Renin secretion
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Homologous Analysis of Sequence
Reference
- Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Hara T, et al. Substrate specificity of bovine cathepsin B and its inhibition by CA074, based on crystal structure refinement of the complex[J]. The Journal of Biochemistry, 2000, 127(4): 635-643. 10739956
- Smith R A, Copp L J, Coles P J, et al. New inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. Peptidyl acyloxymethyl ketones and the quiescent nucleofuge strategy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1988, 110(13): 4429-4431. DOI: 10.1021/ja00221a062
- Štern I, Schaschke N, Moroder L, et al. Crystal structure of NS-134 in complex with bovine cathepsin B: a two-headed epoxysuccinyl inhibitor extends along the entire active-site cleft[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2004, 381(2): 511-517. 15084146
- Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Matsugi K, et al. Structural basis for development of cathepsin B-specific noncovalent-type inhibitor: crystal structure of cathepsin B–E64c complex[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2002, 1597(2): 244-251. 12044902
- Watanabe D, Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, et al. Quantitative evaluation of each catalytic subsite of cathepsin B for inhibitory activity based on inhibitory activity–binding mode relationship of epoxysuccinyl inhibitors by X-ray crystal structure analyses of complexes[J]. Journal of molecular biology, 2006, 362(5): 979-993. 16950396