Difference between revisions of "Cathepsin L1"
(→Reference) |
(→Reference) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
# Torkar A, Lenarčič B, Lah T, et al. '''Identification of new peptide amides as selective cathepsin L inhibitors: The first step towards selective irreversible inhibitors?[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2013, 23(10): 2968-2973. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=23562595 23562595]<br/> | # Torkar A, Lenarčič B, Lah T, et al. '''Identification of new peptide amides as selective cathepsin L inhibitors: The first step towards selective irreversible inhibitors?[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2013, 23(10): 2968-2973. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=23562595 23562595]<br/> | ||
# Respondek T, Garner R N, Herroon M K, et al. '''Light activation of a cysteine protease inhibitor: caging of a peptidomimetic nitrile with Ru<sup>II</sup>(bpy)<sub>2</sub>[J].''' Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(43): 17164-17167. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21973207 21973207]<br/> | # Respondek T, Garner R N, Herroon M K, et al. '''Light activation of a cysteine protease inhibitor: caging of a peptidomimetic nitrile with Ru<sup>II</sup>(bpy)<sub>2</sub>[J].''' Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(43): 17164-17167. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21973207 21973207]<br/> | ||
| − | Falgueyret J P, Black W C, Cromlish W, et al. '''An activity-based probe for the determination of cysteine cathepsin protease activities in whole cells[J].''' Analytical biochemistry, 2004, 335(2): 218-227. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15556560 15556560]<br/> | + | # Falgueyret J P, Black W C, Cromlish W, et al. '''An activity-based probe for the determination of cysteine cathepsin protease activities in whole cells[J].''' Analytical biochemistry, 2004, 335(2): 218-227. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15556560 15556560]<br/> |
# Shenoy R T, Sivaraman J. '''Structural basis for reversible and irreversible inhibition of human cathepsin L by their respective dipeptidyl glyoxal and diazomethylketone inhibitors[J].''' Journal of structural biology, 2011, 173(1): 14-19. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=20850545 20850545]<br/> | # Shenoy R T, Sivaraman J. '''Structural basis for reversible and irreversible inhibition of human cathepsin L by their respective dipeptidyl glyoxal and diazomethylketone inhibitors[J].''' Journal of structural biology, 2011, 173(1): 14-19. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=20850545 20850545]<br/> | ||
# Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. '''Systematic investigation of halogen bonding in protein–ligand interactions[J].''' Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(1): 314-318. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21184410 21184410]<br/> | # Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. '''Systematic investigation of halogen bonding in protein–ligand interactions[J].''' Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(1): 314-318. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21184410 21184410]<br/> | ||
| − | Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. '''Halogen bonding at the active sites of human cathepsin L and MEK1 kinase: efficient interactions in different environments[J].''' ChemMedChem, 2011, 6(11): 2048-2054. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21898833 21898833]<br/> | + | # Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. '''Halogen bonding at the active sites of human cathepsin L and MEK1 kinase: efficient interactions in different environments[J].''' ChemMedChem, 2011, 6(11): 2048-2054. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21898833 21898833]<br/> |
# Bethel P A, Gerhardt S, Jones E V, et al. '''Design of selective cathepsin inhibitors[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(16): 4622-4625. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19616430 19616430]<br/> | # Bethel P A, Gerhardt S, Jones E V, et al. '''Design of selective cathepsin inhibitors[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(16): 4622-4625. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19616430 19616430]<br/> | ||
# Asaad N, Bethel P A, Coulson M D, et al. '''Dipeptidyl nitrile inhibitors of Cathepsin L[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(15): 4280-4283. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19515558 19515558]<br/> | # Asaad N, Bethel P A, Coulson M D, et al. '''Dipeptidyl nitrile inhibitors of Cathepsin L[J].''' Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(15): 4280-4283. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19515558 19515558]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Protease]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Peptidase C1 family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Autophagy - animal]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Lysosome]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Phagosome]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Apoptosis]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Antigen processing and presentation]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Proteoglycans in cancer]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Rheumatoid arthritis]] |
Latest revision as of 21:52, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CTSL, CTSL1 |
| UNP ID | P07711 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys138 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C1 family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Important for the overall degradation of proteins in lysosomes. (From Uniprot)
Cathepsin L1 is a lysosomal cysteine protease that plays a major role in intracellular protein catabolism. Its substrates include collagen and elastin, as well as alpha-1 protease inhibitor, a major controlling element of neutrophil elastase activity. Cathepsin L1 has been implicated in several pathologic processes, including myofibril necrosis in myopathies and in myocardial ischemia, and in the renal tubular response to proteinuria. This protein, which is a member of the peptidase C1 family, is a dimer composed of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. At least two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. CTSL1 has been shown to interact with Cystatin A. (From Wikipedia)
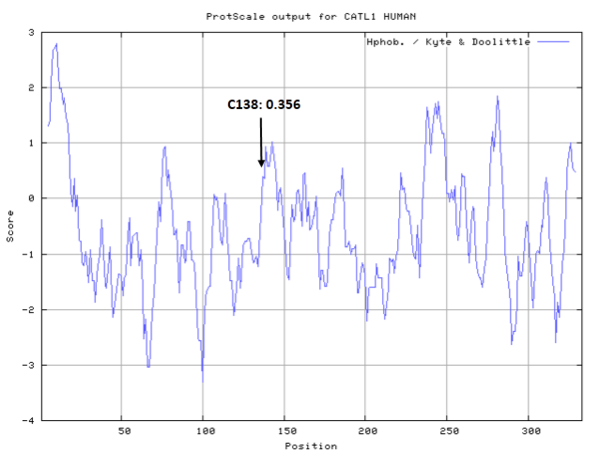
Cys Function & Property
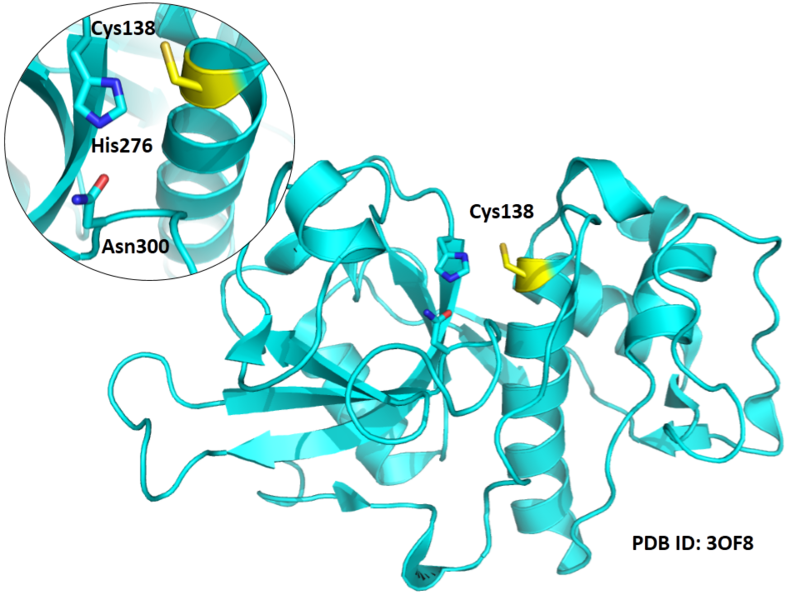
Cys138 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin B, which is very close to His276 and Asn300 in space. These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys138: 11.897 A^2
Protein Sequence
MNPTLILAAF CLGIASATLT FDHSLEAQWT KWKAMHNRLY GMNEEGWRRA
VWEKNMKMIE LHNQEYREGK HSFTMAMNAF GDMTSEEFRQ VMNGFQNRKP
RKGKVFQEPL FYEAPRSVDW REKGYVTPVK NQGQCGSCWA FSATGALEGQ
MFRKTGRLIS LSEQNLVDCS GPQGNEGCNG GLMDYAFQYV QDNGGLDSEE
SYPYEATEES CKYNPKYSVA NDTGFVDIPK QEKALMKAVA TVGPISVAID
AGHESFLFYK EGIYFEPDCS SEDMDHGVLV VGYGFESTES DNNKYWLVKN
SWGEEWGMGG YVKMAKDRRN HCGIASAASY PTV
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Autophagy - animal
- Lysosome
- Phagosome
- Apoptosis
- Antigen processing and presentation
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Homologous Analysis of Sequence, Enzymatic Assay
Reference
- Torkar A, Lenarčič B, Lah T, et al. Identification of new peptide amides as selective cathepsin L inhibitors: The first step towards selective irreversible inhibitors?[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2013, 23(10): 2968-2973. 23562595
- Respondek T, Garner R N, Herroon M K, et al. Light activation of a cysteine protease inhibitor: caging of a peptidomimetic nitrile with RuII(bpy)2[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(43): 17164-17167. 21973207
- Falgueyret J P, Black W C, Cromlish W, et al. An activity-based probe for the determination of cysteine cathepsin protease activities in whole cells[J]. Analytical biochemistry, 2004, 335(2): 218-227. 15556560
- Shenoy R T, Sivaraman J. Structural basis for reversible and irreversible inhibition of human cathepsin L by their respective dipeptidyl glyoxal and diazomethylketone inhibitors[J]. Journal of structural biology, 2011, 173(1): 14-19. 20850545
- Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. Systematic investigation of halogen bonding in protein–ligand interactions[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(1): 314-318. 21184410
- Hardegger L A, Kuhn B, Spinnler B, et al. Halogen bonding at the active sites of human cathepsin L and MEK1 kinase: efficient interactions in different environments[J]. ChemMedChem, 2011, 6(11): 2048-2054. 21898833
- Bethel P A, Gerhardt S, Jones E V, et al. Design of selective cathepsin inhibitors[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(16): 4622-4625. 19616430
- Asaad N, Bethel P A, Coulson M D, et al. Dipeptidyl nitrile inhibitors of Cathepsin L[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2009, 19(15): 4280-4283. 19515558