Difference between revisions of "Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A (Homo sapiens)"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|CCT-alpha, CCT-A, PCYT1A|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P49585 P49585]|Homo sapiens|Cys37|[http://pfam.xfam.o...") |
(→Reference) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:<br/> | Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:<br/> | ||
| − | CTP + choline phosphate ↔ diphosphate + CDP-choline<br/> | + | CTP + choline phosphate <font size="4">↔</font> diphosphate + CDP-choline<br/> |
It is responsible for regulating phosphatidylcholine content in membranes.<br/> | It is responsible for regulating phosphatidylcholine content in membranes.<br/> | ||
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing nucleotide groups (nucleotidyltransferases). This enzyme participates in aminophosphonate metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. (From Wikipedia)<br/> | This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing nucleotide groups (nucleotidyltransferases). This enzyme participates in aminophosphonate metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. (From Wikipedia)<br/> | ||
| − | |||
The main pathway for Phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) biosynthesis in mammalian cells is the Kennedy or CDP-choline pathway, which is regulated by the activity of CCT. CCT activity is essential for cell survival as inhibition of CCT activity leading to decreased PtdCho synthesis impairs cell proliferation, induces apoptosiss, and reduces pulmonary surfactant biosynthesis. (PMID: 18614529) | The main pathway for Phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) biosynthesis in mammalian cells is the Kennedy or CDP-choline pathway, which is regulated by the activity of CCT. CCT activity is essential for cell survival as inhibition of CCT activity leading to decreased PtdCho synthesis impairs cell proliferation, induces apoptosiss, and reduces pulmonary surfactant biosynthesis. (PMID: 18614529) | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 52: | ||
# Ryan A J, Chen B B, Vennalaganti P R, et al. '''15-Deoxy-δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 impairs phosphatidylcholine synthesis and induces nuclear accumulation of thiol-modified cytidylyltransferase[J].''' Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(36): 24628-24640. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=18614529 18614529]<br/> | # Ryan A J, Chen B B, Vennalaganti P R, et al. '''15-Deoxy-δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 impairs phosphatidylcholine synthesis and induces nuclear accumulation of thiol-modified cytidylyltransferase[J].''' Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(36): 24628-24640. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=18614529 18614529]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic enzyme]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Cytidylyltransferase family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Glycerophospholipid metabolism]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic pathways]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Choline metabolism in cancer]] |
Latest revision as of 21:59, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CCT-alpha, CCT-A, PCYT1A |
| UNP ID | P49585 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys37 |
| Family/Domain | Cytidylyltransferase-like family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
CTP + choline phosphate ↔ diphosphate + CDP-choline
It is responsible for regulating phosphatidylcholine content in membranes.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing nucleotide groups (nucleotidyltransferases). This enzyme participates in aminophosphonate metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. (From Wikipedia)
The main pathway for Phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) biosynthesis in mammalian cells is the Kennedy or CDP-choline pathway, which is regulated by the activity of CCT. CCT activity is essential for cell survival as inhibition of CCT activity leading to decreased PtdCho synthesis impairs cell proliferation, induces apoptosiss, and reduces pulmonary surfactant biosynthesis. (PMID: 18614529)
Cys Function & Property
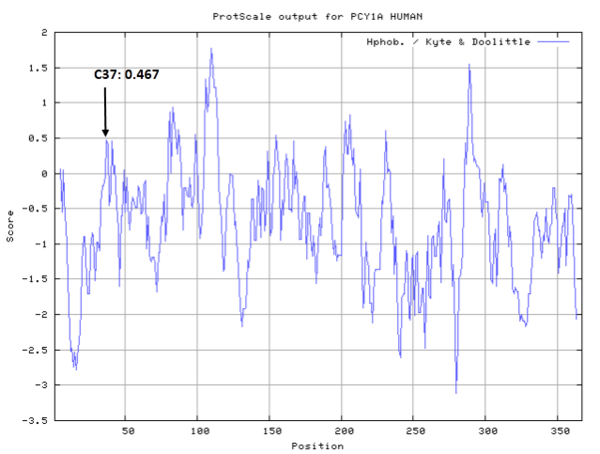
CCT-alpha exists as an inactive soluble form and a membrane-associated active form. Both soluble and membrane-bound forms are present in cells as a noncovalently associated dimer comprised of a 42-kDa monomer. A pair of Cys37 residues, located within the aminoterminal domain, are thought to be within disulfide bond distance in the soluble form of the enzyme, but after binding activatinglipids, these Cys37 residues shift slightly with increased separation in the lipid-bound dimer. (PMID: 18614529)
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys37: Unknown A^2
Protein Sequence
MDAQCSAKVN ARKRRKEAPG PNGATEEDGV PSKVQRCAVG LRQPAPFSDE
IEVDFSKPYV RVTMEEASRG TPCERPVRVY ADGIFDLFHS GHARALMQAK
NLFPNTYLIV GVCSDELTHN FKGFTVMNEN ERYDAVQHCR YVDEVVRNAP
WTLTPEFLAE HRIDFVAHDD IPYSSAGSDD VYKHIKEAGM FAPTQRTEGI
STSDIITRIV RDYDVYARRN LQRGYTAKEL NVSFINEKKY HLQERVDKVK
KKVKDVEEKS KEFVQKVEEK SIDLIQKWEE KSREFIGSFL EMFGPEGALK
HMLKEGKGRM LQAISPKQSP SSSPTRERSP SPSFRWPFSG KTSPPCSPAN
LSRHKAAAYD ISEDEED
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism
- Glycerophospholipid metabolism
- Metabolic pathways
- Choline metabolism in cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Western Blot, Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Ryan A J, Chen B B, Vennalaganti P R, et al. 15-Deoxy-δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 impairs phosphatidylcholine synthesis and induces nuclear accumulation of thiol-modified cytidylyltransferase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(36): 24628-24640. 18614529