Difference between revisions of "Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 1"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|ATP2A1, SERCA1, Calcium pump 1|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O14983 O14983]|Homo sapiens|Cys674|Cation trans...") |
(→Reference) |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
# Ying J, Tong X Y, Pimentel D R, et al. '''Cysteine-674 of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase is required for the inhibition of cell migration by nitric oxide[J].''' Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 2007, 27(4): 783-790. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17234728 17234728]<br/> | # Ying J, Tong X Y, Pimentel D R, et al. '''Cysteine-674 of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase is required for the inhibition of cell migration by nitric oxide[J].''' Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 2007, 27(4): 783-790. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17234728 17234728]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Cation transport ATPase (P-type) family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:ATPase/GTPase]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Calcium signaling pathway]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:cGMP-PKG signaling pathway]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:cAMP signaling pathway]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Cardiac muscle contraction]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Thyroid hormone signaling pathway]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Pancreatic secretion]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Alzheimer disease]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)]] |
Revision as of 23:13, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | ATP2A1, SERCA1, Calcium pump 1 |
| UNP ID | O14983 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys674 |
| Family/Domain | Cation transport ATPase (P-type) family, Type IIA subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | ATPase/GTPase |
Summary
Protein Function
Key regulator of striated muscle performance by acting as the major Ca2+ ATPase responsible for the reuptake of cytosolic Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction (From Uniprot).
This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen.
SERCA Ca(2+)-ATPase is a intracellular pump located in the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticula of muscle cells. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen, and is involved in calcium sequestration associated with muscular excitation and contraction. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. (From Wikipedia)
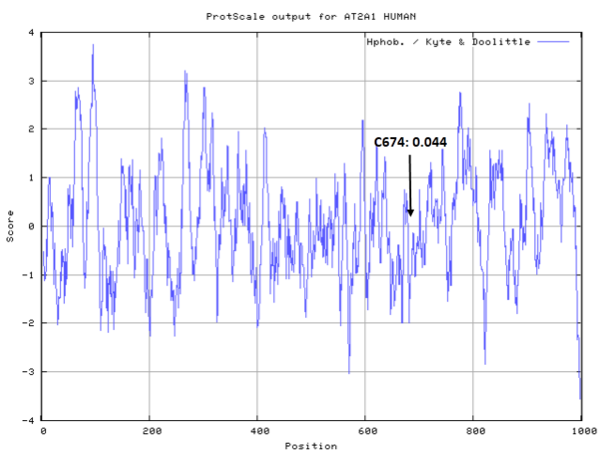
Cys Function & Property
Cys674 is very close to the ATP binding site in sequence.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys674: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MEAAHAKTTE ECLAYFGVSE TTGLTPDQVK RNLEKYGLNE LPAEEGKTLW
ELVIEQFEDL LVRILLLAAC ISFVLAWFEE GEETITAFVE PFVILLILIA
NAIVGVWQER NAENAIEALK EYEPEMGKVY RADRKSVQRI KARDIVPGDI
VEVAVGDKVP ADIRILAIKS TTLRVDQSIL TGESVSVIKH TEPVPDPRAV
NQDKKNMLFS GTNIAAGKAL GIVATTGVGT EIGKIRDQMA ATEQDKTPLQ
QKLDEFGEQL SKVISLICVA VWLINIGHFN DPVHGGSWFR GAIYYFKIAV
ALAVAAIPEG LPAVITTCLA LGTRRMAKKN AIVRSLPSVE TLGCTSVICS
DKTGTLTTNQ MSVCKMFIID KVDGDICLLN EFSITGSTYA PEGEVLKNDK
PVRPGQYDGL VELATICALC NDSSLDFNEA KGVYEKVGEA TETALTTLVE
KMNVFNTDVR SLSKVERANA CNSVIRQLMK KEFTLEFSRD RKSMSVYCSP
AKSSRAAVGN KMFVKGAPEG VIDRCNYVRV GTTRVPLTGP VKEKIMAVIK
EWGTGRDTLR CLALATRDTP PKREEMVLDD SARFLEYETD LTFVGVVGML
DPPRKEVTGS IQLCRDAGIR VIMITGDNKG TAIAICRRIG IFGENEEVAD
RAYTGREFDD LPLAEQREAC RRACCFARVE PSHKSKIVEY LQSYDEITAM
TGDGVNDAPA LKKAEIGIAM GSGTAVAKTA SEMVLADDNF STIVAAVEEG
RAIYNNMKQF IRYLISSNVG EVVCIFLTAA LGLPEALIPV QLLWVNLVTD
GLPATALGFN PPDLDIMDRP PRSPKEPLIS GWLFFRYMAI GGYVGAATVG
AAAWWFLYAE DGPHVNYSQL THFMQCTEDN THFEGIDCEV FEAPEPMTMA
LSVLVTIEMC NALNSLSENQ SLLRMPPWVN IWLLGSICLS MSLHFLILYV
DPLPMIFKLR ALDLTQWLMV LKISLPVIGL DEILKFVARN YLEDPEDERR
K
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Calcium signaling patshway
- cGMP-PKG signaling pathway
- cAMP signaling pathway
- Cardiac muscle contraction
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Pancreatic secretion
- Alzheimer disease
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, Cys Modifiaction Assay
Reference
- Lytton J, Westlin M, Hanley M R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266(26): 17067-17071. 1832668
- Duplan V, Serba C, Garcia J, et al. Synthesis of sesquiterpene-inspired derivatives designed for covalent binding and their inhibition of the NF-κB pathway[J]. Organic & biomolecular chemistry, 2014, 12(2): 370-375. 24263232
- Lancel S, Zhang J, Evangelista A, et al. Nitroxyl activates SERCA in cardiac myocytes via glutathiolation of cysteine 674[J]. Circulation research, 2009, 104(6): 720-723. 19265039
- Ying J, Tong X Y, Pimentel D R, et al. Cysteine-674 of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase is required for the inhibition of cell migration by nitric oxide[J]. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 2007, 27(4): 783-790. 17234728
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Cation transport ATPase (P-type) family
- ATPase/GTPase
- Calcium signaling pathway
- CGMP-PKG signaling pathway
- CAMP signaling pathway
- Cardiac muscle contraction
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Pancreatic secretion
- Alzheimer disease
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)