Difference between revisions of "Solute carrier family 22 member 5"
(→Cys Function & Property) |
(→Reference) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| __TOC__ | | __TOC__ | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|OCTN2, CT1, Ust2r|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O70594 O70594]|Rattus norvegicus|Cys50, Cys81,<br/>Cys113, Cys136|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00083 Sugar (and other) transporter],<br/>Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily,<br/> Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family|[[:Category:Solute carrier family 22 member 5|Ligand list]]}} | + | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|OCTN2, CT1, Ust2r|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O70594 O70594]|Rattus norvegicus|Cys50, Cys81,<br/>Cys113, Cys136|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00083 Sugar (and other) transporter],<br/>Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily,<br/> Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family|[[:Category:Solute carrier family 22 member 5|Ligand list]]|Transporter}} |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
| − | This protein is a sodium-ion dependent, high affinity carnitine transporter, which involved in the active cellular uptake of carnitine. It could transport one sodium ion with one molecule of carnitine, and also transports organic cations such as tetraethylammonium (TEA) without the involvement of sodium | + | This protein is a sodium-ion dependent, high affinity carnitine transporter, which involved in the active cellular uptake of carnitine. It could transport one sodium ion with one molecule of carnitine, and also transports organic cations such as tetraethylammonium (TEA) without the involvement of sodium. (From Uniprot) |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Related Pathway== | ==Related Pathway== | ||
| − | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway? | + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko05231 Choline metabolism in cancer]<br/> |
| − | |||
==Experimental Evidence== | ==Experimental Evidence== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 51: | ||
# Pochini L, Peta V, Indiveri C. '''Inhibition of the OCTN2 carnitine transporter by HgCl2 and methylmercury in the proteoliposome experimental model: insights in the mechanism of toxicity[J].''' Toxicology mechanisms and methods, 2013, 23(2): 68-76. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=22900493 22900493]<br/> | # Pochini L, Peta V, Indiveri C. '''Inhibition of the OCTN2 carnitine transporter by HgCl2 and methylmercury in the proteoliposome experimental model: insights in the mechanism of toxicity[J].''' Toxicology mechanisms and methods, 2013, 23(2): 68-76. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=22900493 22900493]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category:Rattus norvegicus | + | [[Category:Rattus norvegicus]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Transporter]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily]] |
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Sugar (and other) transporter]] |
| + | [[Category:Choline metabolism in cancer]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:15, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | OCTN2, CT1, Ust2r |
| UNP ID | O70594 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
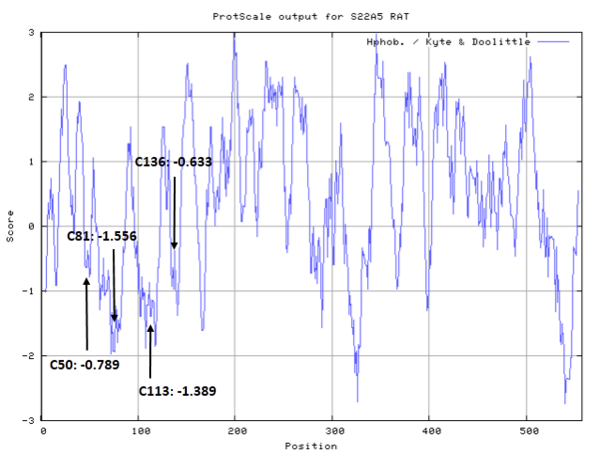
| Cys Site |
Cys50, Cys81, Cys113, Cys136 |
| Family/Domain |
Sugar (and other) transporter, Major facilitator (TC 2.A.1) superfamily, Organic cation transporter (TC 2.A.1.19) family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transporter |
Summary
Protein Function
This protein is a sodium-ion dependent, high affinity carnitine transporter, which involved in the active cellular uptake of carnitine. It could transport one sodium ion with one molecule of carnitine, and also transports organic cations such as tetraethylammonium (TEA) without the involvement of sodium. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
These cysteines are located on the extracellular domain, as shown below.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MRDYDEVTAF LGEWGPFQRL IFFLLSASII PNGFNGMSIV FLAGTPEHRC
LVPHTVNLSS AWRNHSIPLE TKDGRQVPQS CRRYRLATIA NFSALGLEPG
RDVDLEQLEQ ENCLDGWEYN KDVFLSTIVT EWDLVCKDDW KAPLTTSLFF
VGVLMGSFIS GQLSDRFGRK NVLFLTMGMQ TGFSFLQLFS VNFEMFTVLF
VLVGMGQISN YVAAFVLGTE ILSKSIRIIF ATLGVCIFYA FGFMVLPLFA
YFIRDWRMLL LALTVPGVLC GALWWFIPES PRWLISQGRV KEAEVIIRKA
AKFNGIVAPS TIFDPSELQD LNSKKPQSHH IYDLVRTRNI RIITIMSIIL
WLTISVGYFG LSLDTPNLHG DIYVNCFLLA AVEVPAYVLA WLLLQHLPRR
YSISAALFLG GSVLLFIQLV PSELFYLSTA LVMVGKFGIT SAYSMVYVYT
AELYPTVVRN MGVGVSSTAS RLGSILSPYF VYLGAYDRFL PYILMGSLTI
LTAILTLFFP ESFGAPLPDT IDQMLRVKGI KQWQIQSQTR TQKDGGESPT
VLKSTAF
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Homologous Analysis of Sequence
Reference
- Pochini L, Scalise M, Indiveri C. Inactivation by omeprazole of the carnitine transporter (OCTN2) reconstituted in liposomes[J]. Chemico-biological interactions, 2009, 179(2-3): 394-401. 19041296
- Pochini L, Peta V, Indiveri C. Inhibition of the OCTN2 carnitine transporter by HgCl2 and methylmercury in the proteoliposome experimental model: insights in the mechanism of toxicity[J]. Toxicology mechanisms and methods, 2013, 23(2): 68-76. 22900493