Difference between revisions of "Fatty-acid amide hydrolase 1"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|FAAH, FAAH1|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P97612 P97612]|Rattus norvegicus|Cys269|[http://pfam.xfam.org/fami...") |
(→Related Pathway) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| − | Cys269 is close to the active sites of FAAH.</ | + | Cys269 is close to the active sites of FAAH in space.<br/> |
* Hydrophobic property: | * Hydrophobic property: | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Related Pathway== | ==Related Pathway== | ||
| − | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway? | + | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04723 Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling] <br/> |
| − | |||
==Experimental Evidence== | ==Experimental Evidence== | ||
Latest revision as of 05:10, 2 December 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | FAAH, FAAH1 |
| UNP ID | P97612 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
| Cys Site | Cys269 |
| Family/Domain | Amidase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Fatty acid amide hydrolase or FAAH (EC 3.5.1.99, oleamide hydrolase, anandamide amidohydrolase) is a member of the serine hydrolase family of enzymes. FAAH is an integral membrane hydrolase with a single N-terminal transmembrane domain. In vitro, FAAH has esterase and amidase activity. In vivo, FAAH is the principal catabolic enzyme for a class of bioactive lipids called the fatty acid amides (FAAs). (From Wikipedia)
Degrades bioactive fatty acid amides like oleamide, the endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide and myristic amide to their corresponding acids, thereby serving to terminate the signaling functions of these molecules. Hydrolyzes polyunsaturated substrate anandamide preferentially as compared to monounsaturated substrates. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
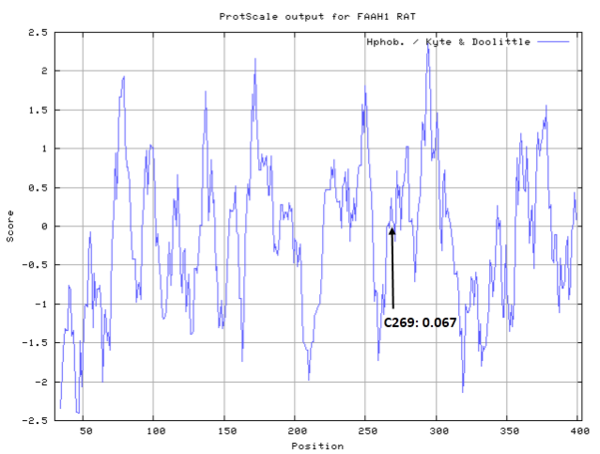
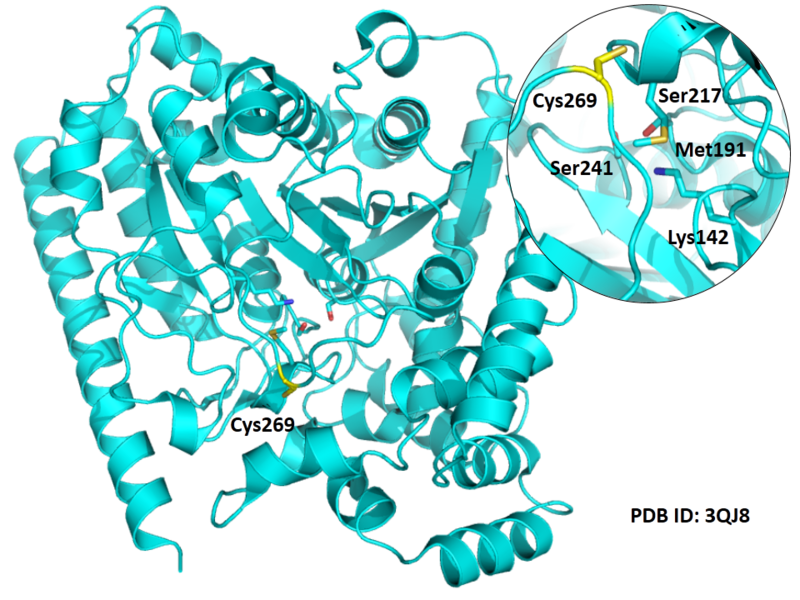
Cys269 is close to the active sites of FAAH in space.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys269: 13.878 A^2
Protein Sequence
MVLSEVWTTL SGVSGVCLAC SLLSAAVVLR WTGRQKARGA ATRARQKQRA
SLETMDKAVQ RFRLQNPDLD SEALLTLPLL QLVQKLQSGE LSPEAVFFTY
LGKAWEVNKG TNCVTSYLTD CETQLSQAPR QGLLYGVPVS LKECFSYKGH
DSTLGLSLNE GMPSESDCVV VQVLKLQGAV PFVHTNVPQS MLSFDCSNPL
FGQTMNPWKS SKSPGGSSGG EGALIGSGGS PLGLGTDIGG SIRFPSAFCG
ICGLKPTGNR LSKSGLKGCV YGQTAVQLSL GPMARDVESL ALCLKALLCE
HLFTLDPTVP PLPFREEVYR SSRPLRVGYY ETDNYTMPSP AMRRALIETK
QRLEAAGHTL IPFLPNNIPY ALEVLSAGGL FSDGGRSFLQ NFKGDFVDPC
LGDLILILRL PSWFKRLLSL LLKPLFPRLA AFLNSMRPRS AEKLWKLQHE
IEMYRQSVIA QWKAMNLDVL LTPMLGPALD LNTPGRATGA ISYTVLYNCL
DFPAGVVPVT TVTAEDDAQM ELYKGYFGDI WDIILKKAMK NSVGLPVAVQ
CVALPWQEEL CLRFMREVEQ LMTPQKQPS
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed mutation, Homologous Analysis Of Sequence, Molecular Docking
Reference
- Otrubova K, Cravatt B F, Boger D L. Design, synthesis, and characterization of α-ketoheterocycles that additionally target the cytosolic port Cys269 of fatty acid amide hydrolase[J]. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2014, 57(3): 1079-1089. 24456116
- Otrubova K, Brown M, McCormick M S, et al. Rational design of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors that act by covalently bonding to two active site residues[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(16): 6289-6299. 23581831