Difference between revisions of "Actin, alpha skeletal muscle (Homo sapiens)"
(→Structural Information) |
(→Cys Function & Property) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
Actin, alpha skeletal muscle expressed in skeletal muscle is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. <br/> | Actin, alpha skeletal muscle expressed in skeletal muscle is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. <br/> | ||
| + | |||
Skeletal alpha actin expression is induced by stimuli and conditions known to cause muscle formation. Such conditions result in fusion of committed cells (satellite cells) into myotubes, to form muscle fibers. Skeletal actin itself, when expressed, causes expression of several other "myogenic genes", which are essential to muscle formation. One key transcription factor that activates skeletal actin gene expression is Serum Response Factor ("SRF"), a protein that binds to specific sites on the promoter DNA of the actin gene. SRF may bring a number of other proteins to the promoter of skeletal actin, such as andogen receptor, and thereby contribute to induction of skeletal actin gene expression by androgenic (often termed "anabolic") steroids. (From Wikipedia) <br/> | Skeletal alpha actin expression is induced by stimuli and conditions known to cause muscle formation. Such conditions result in fusion of committed cells (satellite cells) into myotubes, to form muscle fibers. Skeletal actin itself, when expressed, causes expression of several other "myogenic genes", which are essential to muscle formation. One key transcription factor that activates skeletal actin gene expression is Serum Response Factor ("SRF"), a protein that binds to specific sites on the promoter DNA of the actin gene. SRF may bring a number of other proteins to the promoter of skeletal actin, such as andogen receptor, and thereby contribute to induction of skeletal actin gene expression by androgenic (often termed "anabolic") steroids. (From Wikipedia) <br/> | ||
| + | |||
Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. (From Uniprot)<br/> | Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. (From Uniprot)<br/> | ||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
Cys259 is close to the ATP binding site of ACTA1.<br/> | Cys259 is close to the ATP binding site of ACTA1.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
Cys374, the most reactive and surface-exposed thiol group in 5 cysteine reisudes in rat Actin, is located at the C-terminal, and the covalent modification maybe influence the interaction with other protein.<br/> | Cys374, the most reactive and surface-exposed thiol group in 5 cysteine reisudes in rat Actin, is located at the C-terminal, and the covalent modification maybe influence the interaction with other protein.<br/> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 54: | ||
# Dalle-Donne I, Carini M, Vistoli G, et al. '''Actin Cys374 as a nucleophilic target of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes[J].''' Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2007, 42(5): 583-598. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17291982 17291982]<br/> | # Dalle-Donne I, Carini M, Vistoli G, et al. '''Actin Cys374 as a nucleophilic target of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes[J].''' Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2007, 42(5): 583-598. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17291982 17291982]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Structural protein]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Actin family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Cardiac muscle contraction]] |
Latest revision as of 05:04, 22 January 2020
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | ACTA1 |
| UNP ID | P68133 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys259, Cys376 |
| Family/Domain | Actin family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Structural protein |
Summary
Protein Function
Actin, alpha skeletal muscle expressed in skeletal muscle is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus.
Skeletal alpha actin expression is induced by stimuli and conditions known to cause muscle formation. Such conditions result in fusion of committed cells (satellite cells) into myotubes, to form muscle fibers. Skeletal actin itself, when expressed, causes expression of several other "myogenic genes", which are essential to muscle formation. One key transcription factor that activates skeletal actin gene expression is Serum Response Factor ("SRF"), a protein that binds to specific sites on the promoter DNA of the actin gene. SRF may bring a number of other proteins to the promoter of skeletal actin, such as andogen receptor, and thereby contribute to induction of skeletal actin gene expression by androgenic (often termed "anabolic") steroids. (From Wikipedia)
Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
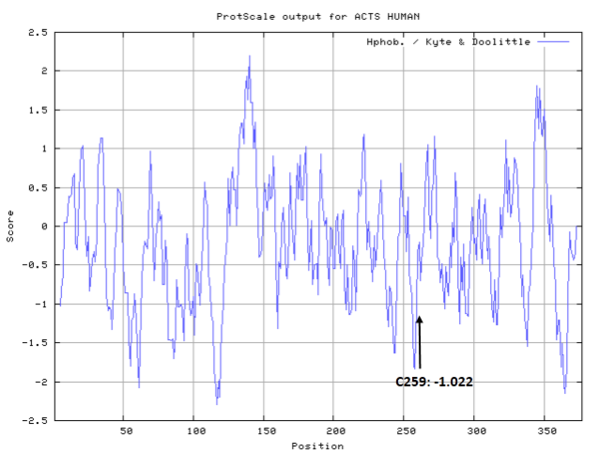
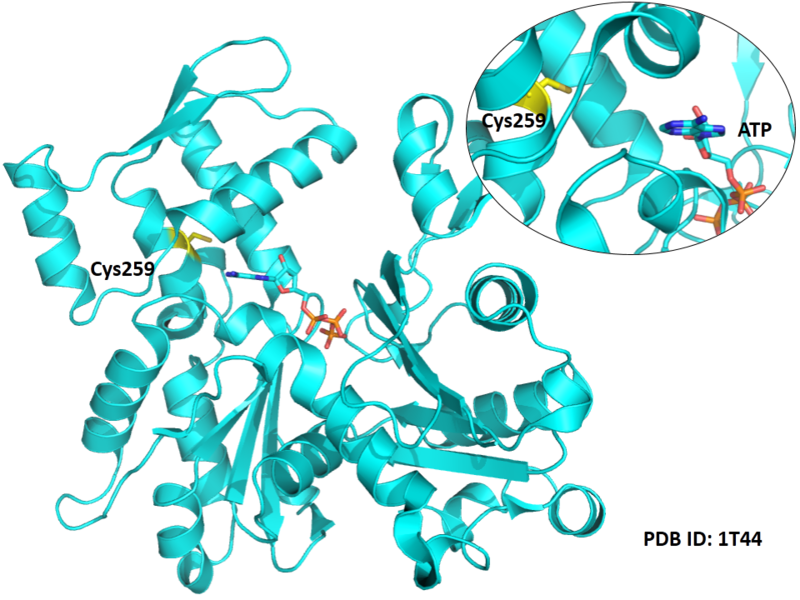
Cys259 is close to the ATP binding site of ACTA1.
Cys374, the most reactive and surface-exposed thiol group in 5 cysteine reisudes in rat Actin, is located at the C-terminal, and the covalent modification maybe influence the interaction with other protein.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys259: Unknown
- Cys376: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG
QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWHH TFYNELRVAP
EEHPTLLTEA PLNPKANREK MTQIMFETFN VPAMYVAIQA VLSLYASGRT
TGIVLDSGDG VTHNVPIYEG YALPHAIMRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY
SFVTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFENEMA TAASSSSLEK SYELPDGQVI
TIGNERFRCP ETLFQPSFIG MESAGIHETT YNSIMKCDID IRKDLYANNV
MSGGTTMYPG IADRMQKEIT ALAPSTMKIK IIAPPERKYS VWIGGSILAS
LSTFQQMWIT KQEYDEAGPS IVHRKCF
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Mass Spectrometry, Pepsin Digest
Reference
- Sörensen P M, Iacob R E, Fritzsche M, et al. The natural product cucurbitacin E inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments[J]. ACS chemical biology, 2012, 7(9): 1502-1508. 22724897
- Dalle-Donne I, Carini M, Vistoli G, et al. Actin Cys374 as a nucleophilic target of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2007, 42(5): 583-598. 17291982