Difference between revisions of "Thymidylate synthase"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|TSase, TYMS|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04818 P04818]|Homo sapiens|Cys195|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF...") |
(→Protein Function) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
Thymidylate synthetase (EC 2.1.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). dTMP is one of the three nucleotides (dTMP, dTTP, and dTDP) that form thymine. Thymine is a nucleic acid in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUTP arise. Both cause DNA damage.The following reaction catalyzed by thymidylate synthetase:<br/> | Thymidylate synthetase (EC 2.1.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). dTMP is one of the three nucleotides (dTMP, dTTP, and dTDP) that form thymine. Thymine is a nucleic acid in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUTP arise. Both cause DNA damage.The following reaction catalyzed by thymidylate synthetase:<br/> | ||
| − | 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + dUMP ↔ dihydrofolate + dTMP<br/> | + | <div align="center">5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate + dUMP ↔ dihydrofolate + dTMP</div><br/> |
This provides the sole de novo pathway for production of dTMP and is the only enzyme in folate metabolism in which the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is oxidised during one-carbon transfer. The enzyme is essential for regulating the balanced supply of the four DNA precursors in normal DNA replication: defects in the enzyme activity affecting the regulation process cause various biological and genetic abnormalities, such as thymineless death. Thymidylate synthase is an enzyme of about 30 to 35 Kd in most species except in protozoan and plants where it exists as a bifunctional enzyme that includes a dihydrofolate reductase domain. A cysteine residue is involved in the catalytic mechanism (it covalently binds the 5,6-dihydro-dUMP intermediate). The sequence around the active site of this enzyme is conserved from phages to vertebrates. (From Wikipedia)<br/> | This provides the sole de novo pathway for production of dTMP and is the only enzyme in folate metabolism in which the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is oxidised during one-carbon transfer. The enzyme is essential for regulating the balanced supply of the four DNA precursors in normal DNA replication: defects in the enzyme activity affecting the regulation process cause various biological and genetic abnormalities, such as thymineless death. Thymidylate synthase is an enzyme of about 30 to 35 Kd in most species except in protozoan and plants where it exists as a bifunctional enzyme that includes a dihydrofolate reductase domain. A cysteine residue is involved in the catalytic mechanism (it covalently binds the 5,6-dihydro-dUMP intermediate). The sequence around the active site of this enzyme is conserved from phages to vertebrates. (From Wikipedia)<br/> | ||
Revision as of 03:02, 29 July 2019
Lua error: data must be either of type string or number.
Summary
Protein Function
Thymidylate synthetase (EC 2.1.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). dTMP is one of the three nucleotides (dTMP, dTTP, and dTDP) that form thymine. Thymine is a nucleic acid in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUTP arise. Both cause DNA damage.The following reaction catalyzed by thymidylate synthetase:
This provides the sole de novo pathway for production of dTMP and is the only enzyme in folate metabolism in which the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is oxidised during one-carbon transfer. The enzyme is essential for regulating the balanced supply of the four DNA precursors in normal DNA replication: defects in the enzyme activity affecting the regulation process cause various biological and genetic abnormalities, such as thymineless death. Thymidylate synthase is an enzyme of about 30 to 35 Kd in most species except in protozoan and plants where it exists as a bifunctional enzyme that includes a dihydrofolate reductase domain. A cysteine residue is involved in the catalytic mechanism (it covalently binds the 5,6-dihydro-dUMP intermediate). The sequence around the active site of this enzyme is conserved from phages to vertebrates. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
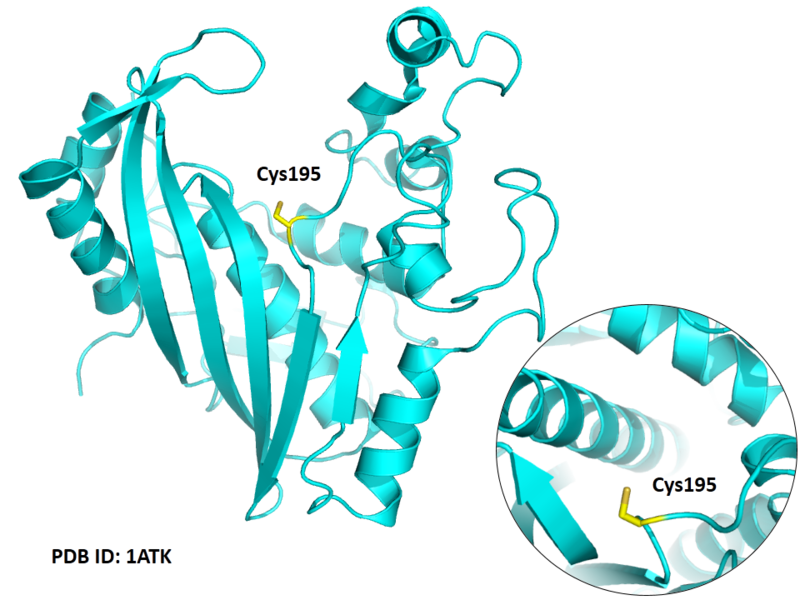
Cys195 is the active site of Thymidylate synthase, act as nucleophile.
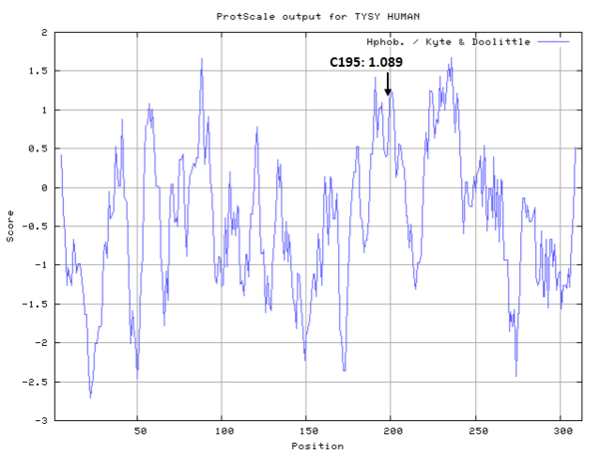
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys195: 25.299 A^2
Protein Sequence
MPVAGSELPR RPLPPAAQER DAEPRPPHGE LQYLGQIQHI LRCGVRKDDR
TGTGTLSVFG MQARYSLRDE FPLLTTKRVF WKGVLEELLW FIKGSTNAKE
LSSKGVKIWD ANGSRDFLDS LGFSTREEGD LGPVYGFQWR HFGAEYRDME
SDYSGQGVDQ LQRVIDTIKT NPDDRRIIMC AWNPRDLPLM ALPPCHALCQ
FYVVNSELSC QLYQRSGDMG LGVPFNIASY ALLTYMIAHI TGLKPGDFIH
TLGDAHIYLN HIEPLKIQLQ REPRPFPKLR ILRKVEKIDD FKAEDFQIEG
YNPHPTIKME MAV
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- MALDI-MS, Tryptic Digest
Reference
- Nonoo R H, Armstrong A, Mann D J. Kinetic Template‐Guided Tethering of Fragments[J]. ChemMedChem, 2012, 7(12): 2082-2086. 23033251