Difference between revisions of "Thioredoxin reductase TR1 (Rattus norvegicus)"
(→Cys Function & Property) |
(→Reference) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
# Fang J, Lu J, Holmgren A. '''Thioredoxin reductase is irreversibly modified by curcumin a novel molecular mechanism for its anticancer activity[J].''' Journal of biological chemistry, 2005, 280(26): 25284-25290. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15879598 15879598]<br/> | # Fang J, Lu J, Holmgren A. '''Thioredoxin reductase is irreversibly modified by curcumin a novel molecular mechanism for its anticancer activity[J].''' Journal of biological chemistry, 2005, 280(26): 25284-25290. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15879598 15879598]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Rattus norvegicus]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Redox protein]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Selenocompound metabolism]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Pathways in cancer]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Hepatocellular carcinoma]] |
Latest revision as of 23:16, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Txnrd1, Trxr1 |
| UNP ID | O89049 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
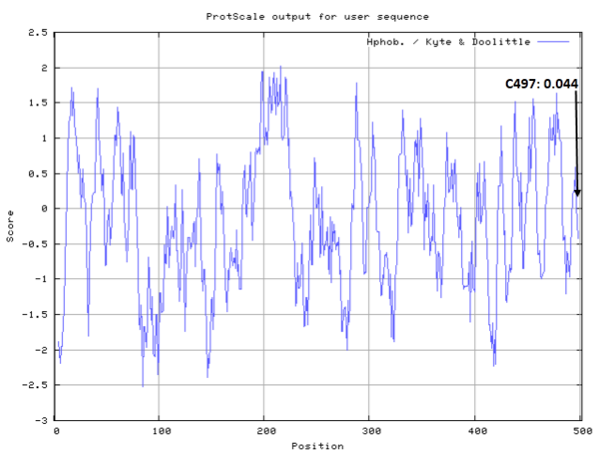
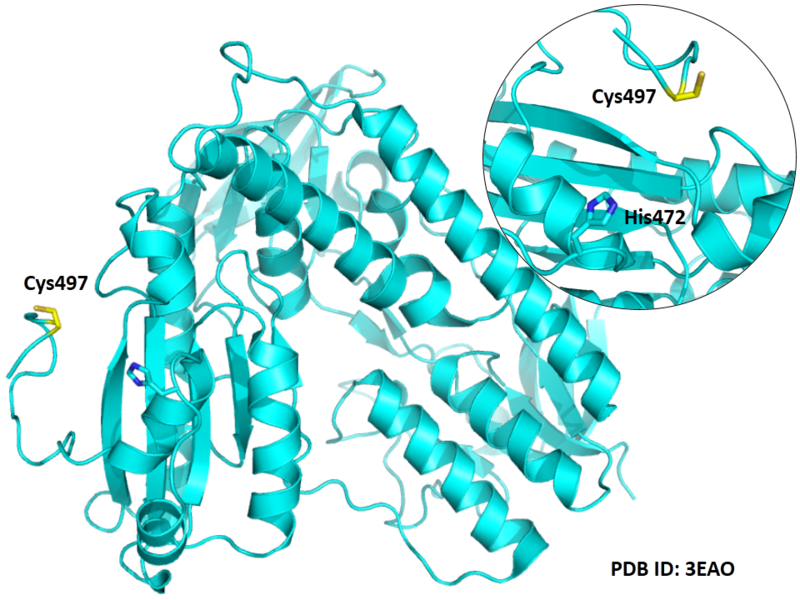
| Cys Site | Cys497 |
| Family/Domain |
Pyridine nucleotide-disulphide oxidoreductase, Class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Redox protein |
Summary
Protein Function
Thioredoxin reductases (TR, TrxR) are the only known enzymes to reduce thioredoxin (Trx). Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers. Each monomer contains a FAD prosthetic group, a NADPH binding domain, and an active site containing a redox-active disulfide bond.
Mammalian thioredoxin reductase mechanism: Mammalian TrxRs have a much higher sequence homology with glutathione reductase than E. coli. The active-site Cys residues in the FAD domain and bound NADPH domain are in close proximity removing the necessity for a 66 degree rotation for electron transfer found in E. coli. An additional feature of the mammalian mechanism is the presence of a selenocystine residue at the C-terminal end of the protein which is required for catalytic activity. The conserved residues in mammalian active site are -Cys-Val-Asn-Val-Gly-Cys-. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
Cys497 is close to the active site of His472 in space.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys497: 30.416 A^2
Protein Sequence
MNDSKDAPKS YDFDLIIIGG GSGGLAAAKE AAKFDKKVMV LDFVTPTPLG
TRWGLGGTCV NVGCIPKKLM HQAALLGQAL KDSRNYGWKL EDTVKHDWEK
MTESVQNHIG SLNWGYRVAL REKKVVYENA YGKFIGPHKI MATNNKGKEK
VYSAERFLIA TGERPRYLGI PGDKEYCISS DDLFSLPYCP GKTLVVGASY
VALECAGFLA GIGLDVTVMV RSILLRGFDQ DMANKIGEHM EEHGIKFIRQ
FVPTKIEQIE AGTPGRLKVT AKSTNSEETI EDEFNTVLLA VGRDSCTRTI
GLETVGVKIN EKTGKIPVTD EEQTNVPYIY AIGDILEGKL ELTPVAIQAG
RLLAQRLYGG STVKCDYDNV PTTVFTPLEY GCCGLSEEKA VEKFGEENIE
VYHSFFWPLE WTVPSRDNNK CYAKVICNLK DNERVVGFHV LGPNAGEVTQ
GFAAALKCGL TKQQLDSTIG IHPVCAEIFT TLSVTKRSGG DILQSGCUG
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Cys Modification Assay, Mass Spectrometry, Western Blot
Reference
- Fang J, Lu J, Holmgren A. Thioredoxin reductase is irreversibly modified by curcumin a novel molecular mechanism for its anticancer activity[J]. Journal of biological chemistry, 2005, 280(26): 25284-25290. 15879598