Difference between revisions of "Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|5-LO, ALOX5|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09917 P09917]|Homo sapiens|Cys417|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF...") |
(→Reference) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
| − | Lipoxygenases are a family of iron-containing enzymes that catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4-pentadiene structure. It catalyses the following reaction: | + | Lipoxygenases are a family of iron-containing enzymes that catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4-pentadiene structure. It catalyses the following reaction: <br/> |
| − | '''fatty acid + O2 = fatty acid hydroperoxide''' | + | '''fatty acid + O2 = fatty acid hydroperoxide'''<br/> |
| − | These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases isozymes are involved in the metabolism of eicosanoids (such as prostaglandins, | + | These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases isozymes are involved in the metabolism of eicosanoids (such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes and nonclassic eicosanoids). (From Wikipedia)<br/> |
| − | 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of | + | 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes (LTs) which are mediators involved in the development of atherosclerosis, inflammatory diseases and cancer. 5-LO metabolizes arachidonic acid to leukotriene A4 in a two step reaction by incorporation of molecular oxygen. (PMID: 22137889)<br/> |
| − | |||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 57: | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| − | # Hörnig M, | + | # Hörnig M, Markoutsa S, Häfner A K, et al. '''Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by U73122 is due to covalent binding to cysteine 416[J].''' Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2012, 1821(2): 279-286. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=22137889 22137889]<br/> |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic enzyme]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Lipoxygenase family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Arachidonic acid metabolism]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic pathways]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Serotonergic synapse]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Ovarian steroidogenesis]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Toxoplasmosis]] |
Latest revision as of 21:37, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | 5-LO, ALOX5 |
| UNP ID | P09917 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys417 |
| Family/Domain | Lipoxygenase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Lipoxygenases are a family of iron-containing enzymes that catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4-pentadiene structure. It catalyses the following reaction:
fatty acid + O2 = fatty acid hydroperoxide
These enzymes are most common in plants where they may be involved in a number of diverse aspects of plant physiology including growth and development, pest resistance, and senescence or responses to wounding. In mammals a number of lipoxygenases isozymes are involved in the metabolism of eicosanoids (such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes and nonclassic eicosanoids). (From Wikipedia)
5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes (LTs) which are mediators involved in the development of atherosclerosis, inflammatory diseases and cancer. 5-LO metabolizes arachidonic acid to leukotriene A4 in a two step reaction by incorporation of molecular oxygen. (PMID: 22137889)
Cys Function & Property
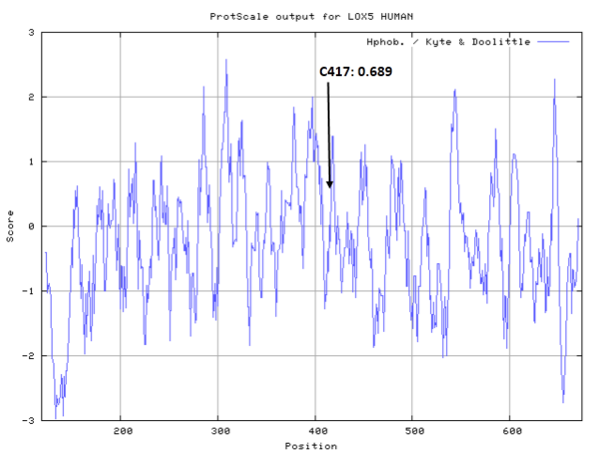
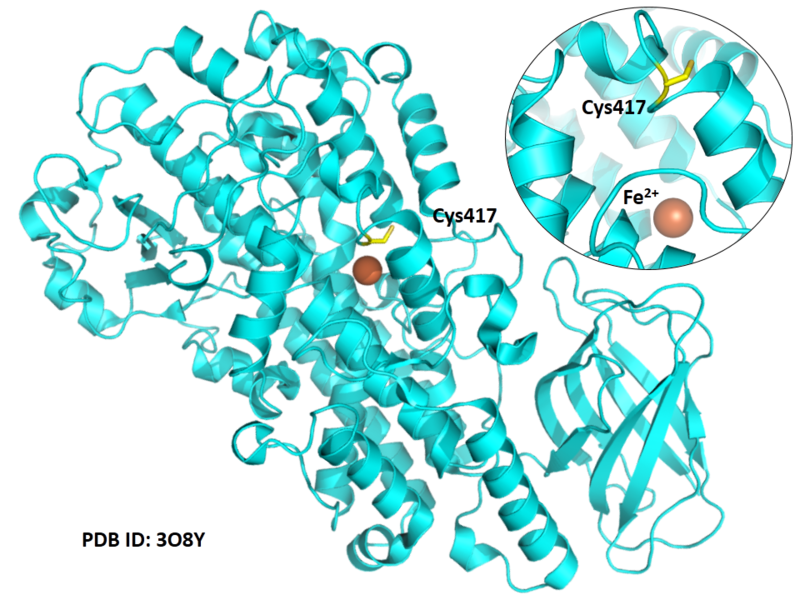
Cys417 is close to the active site and the Fe cation in space.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys417: 26.389 A^2
Protein Sequence
MPSYTVTVAT GSQWFAGTDD YIYLSLVGSA GCSEKHLLDK PFYNDFERGA
VDSYDVTVDE ELGEIQLVRI EKRKYWLNDD WYLKYITLKT PHGDYIEFPC
YRWITGDVEV VLRDGRAKLA RDDQIHILKQ HRRKELETRQ KQYRWMEWNP
GFPLSIDAKC HKDLPRDIQF DSEKGVDFVL NYSKAMENLF INRFMHMFQS
SWNDFADFEK IFVKISNTIS ERVMNHWQED LMFGYQFLNG CNPVLIRRCT
ELPEKLPVTT EMVECSLERQ LSLEQEVQQG NIFIVDFELL DGIDANKTDP
CTLQFLAAPI CLLYKNLANK IVPIAIQLNQ IPGDENPIFL PSDAKYDWLL
AKIWVRSSDF HVHQTITHLL RTHLVSEVFG IAMYRQLPAV HPIFKLLVAH
VRFTIAINTK AREQLICECG LFDKANATGG GGHVQMVQRA MKDLTYASLC
FPEAIKARGM ESKEDIPYYF YRDDGLLVWE AIRTFTAEVV DIYYEGDQVV
EEDPELQDFV NDVYVYGMRG RKSSGFPKSV KSREQLSEYL TVVIFTASAQ
HAAVNFGQYD WCSWIPNAPP TMRAPPPTAK GVVTIEQIVD TLPDRGRSCW
HLGAVWALSQ FQENELFLGM YPEEHFIEKP VKEAMARFRK NLEAIVSVIA
ERNKKKQLPY YYLSPDRIPN SVAI
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Arachidonic acid metabolism
- Metabolic pathways
- Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway
- Serotonergic synapse
- Ovarian steroidogenesis
- Toxoplasmosis
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, MALDI-MS
Reference
- Hörnig M, Markoutsa S, Häfner A K, et al. Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by U73122 is due to covalent binding to cysteine 416[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2012, 1821(2): 279-286. 22137889