Difference between revisions of "Laforin"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|Glucan phosphatase, LAFPTPase, EPM2A|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O95278 O95278]|Homo sapiens|Cys266|[http:...") |
(→Reference) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| __TOC__ | | __TOC__ | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run| | + | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|LAFPTPase, EPM2A|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O95278 O95278]|Homo sapiens|Cys266|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00782 Dual specificity phosphatase, catalytic domain],<br/>Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family|[[:Category:Laforin|Ligand list]]|Phosphatase,<br/>Post-translational Modification}} |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
# Ueda K, Usui T, Nakayama H, et al. '''4‐Isoavenaciolide covalently binds and inhibits VHR, a dual‐specificity phosphatase[J].''' FEBS letters, 2002, 525(1-3): 48-52. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12163160 12163160]<br/> | # Ueda K, Usui T, Nakayama H, et al. '''4‐Isoavenaciolide covalently binds and inhibits VHR, a dual‐specificity phosphatase[J].''' FEBS letters, 2002, 525(1-3): 48-52. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12163160 12163160]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Phosphatase]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Post-translational Modification]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family]] |
Latest revision as of 23:04, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | LAFPTPase, EPM2A |
| UNP ID | O95278 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys266 |
| Family/Domain |
Dual specificity phosphatase, catalytic domain, Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type |
Phosphatase, Post-translational Modification |
Summary
Protein Function
Plays an important role in preventing glycogen hyperphosphorylation and the formation of insoluble aggregates, via its activity as glycogen phosphatase, and by promoting the ubiquitination of proteins involved in glycogen metabolism via its interaction with the E3 ubiquitin ligase NHLRC1/malin. Shows strong phosphatase activity towards complex carbohydrates in vitro, avoiding glycogen hyperphosphorylation which is associated with reduced branching and formation of insoluble aggregates. Dephosphorylates phosphotyrosine and synthetic substrates, such as para-nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP), and has low activity with phosphoserine and phosphothreonine substrates (in vitro). Has been shown to dephosphorylate MAPT. Forms a complex with NHLRC1/malin and HSP70, which suppresses the cellular toxicity of misfolded proteins by promoting their degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). Acts as a scaffold protein to facilitate PPP1R3C/PTG ubiquitination by NHLRC1/malin. Also promotes proteasome-independent protein degradation through the macroautophagy pathway. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
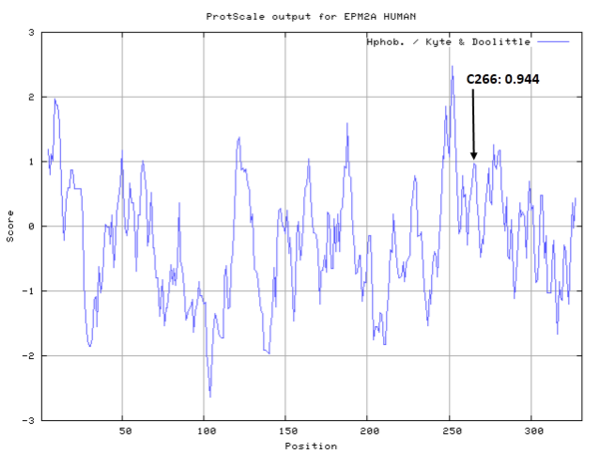
Cys266 is the active site of Laforin, act as the phosphocysteine intermediate.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys266: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MRFRFGVVVP PAVAGARPEL LVVGSRPELG RWEPRGAVRL RPAGTAAGDG
ALALQEPGLW LGEVELAAEE AAQDGAEPGR VDTFWYKFLK REPGGELSWE
GNGPHHDRCC TYNENNLVDG VYCLPIGHWI EATGHTNEMK HTTDFYFNIA
GHQAMHYSRI LPNIWLGSCP RQVEHVTIKL KHELGITAVM NFQTEWDIVQ
NSSGCNRYPE PMTPDTMIKL YREEGLAYIW MPTPDMSTEG RVQMLPQAVC
LLHALLEKGH IVYVHCNAGV GRSTAAVCGW LQYVMGWNLR KVQYFLMAKR
PAVYIDEEAL ARAQEDFFQK FGKVRSSVCS L
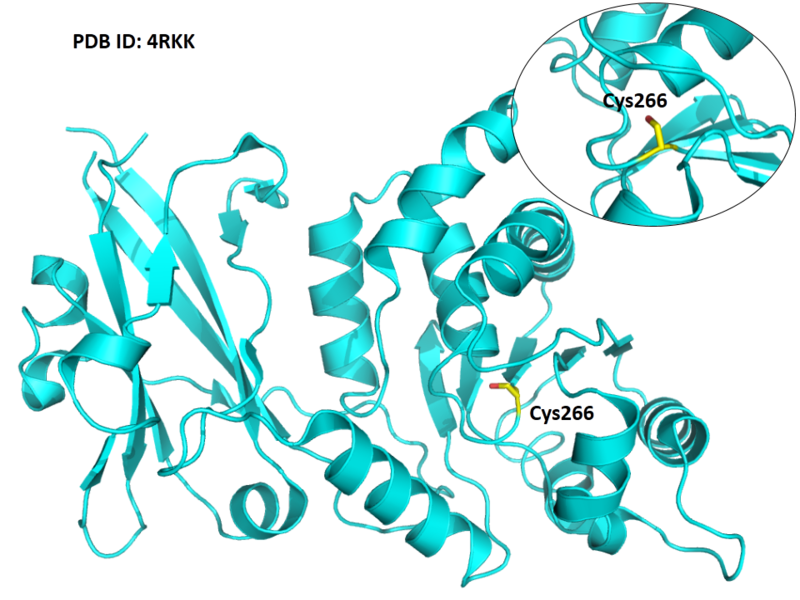
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Unknown
Experimental Evidence
- LC-MS/MS, Achromobacter Protease I Digest
Reference
- Ueda K, Usui T, Nakayama H, et al. 4‐Isoavenaciolide covalently binds and inhibits VHR, a dual‐specificity phosphatase[J]. FEBS letters, 2002, 525(1-3): 48-52. 12163160