Difference between revisions of "Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Mus musculus)"
(→Summary) |
(→Reference) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
# Miura T, Shinkai Y, Hirose R, et al. '''Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a quinone reductase in the suppression of 1, 2-naphthoquinone protein adduct formation[J].''' Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2011, 51(11): 2082-2089. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21963991 21963991]<br/> | # Miura T, Shinkai Y, Hirose R, et al. '''Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a quinone reductase in the suppression of 1, 2-naphthoquinone protein adduct formation[J].''' Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2011, 51(11): 2082-2089. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21963991 21963991]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Mus musculus]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic enzyme]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metabolic pathways]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Carbon metabolism]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Biosynthesis of amino acids]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:HIF-1 signaling pathway]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Alzheimer disease]] |
Latest revision as of 22:53, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Gapdh |
| UNP ID | P16858 |
| Organism | Mus musculus |
| Cys Site | Cys154 |
| Family/Domain | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Under normal cellular conditions, cytoplasmic GAPDH exists primarily as a tetramer. This form is composed of four identical 37-kDa subunits containing a single catalytic thiol group each and critical to the enzyme's catalytic function. Nuclear GAPDH has increased isoelectric point (pI) of pH 8.3–8.7. Of note, the cysteine residue Cys152 in human GAPDH's (Cys154 in mouse) active site is required for the induction of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Notably, post-translational modifications of cytoplasmic GAPDH contribute to its functions outside of glycolysis. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
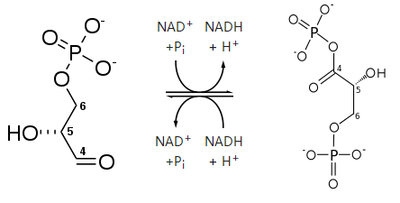
Cys154 is the active site and very close to one of the Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate binding sites of GAPDH, residues 149-151.
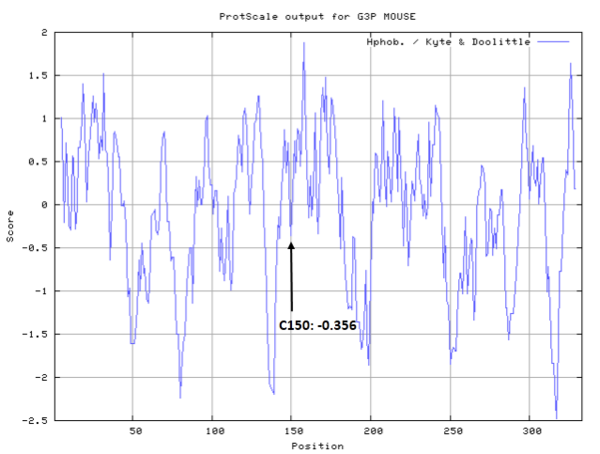
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys154: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MVKVGVNGFG RIGRLVTRAA ICSGKVEIVA INDPFIDLNY MVYMFQYDST
HGKFNGTVKA ENGKLVINGK PITIFQERDP TNIKWGEAGA EYVVESTGVF
TTMEKAGAHL KGGAKRVIIS APSADAPMFV MGVNHEKYDN SLKIVSNASC
TTNCLAPLAK VIHDNFGIVE GLMTTVHAIT ATQKTVDGPS GKLWRDGRGA
AQNIIPASTG AAKAVGKVIP ELNGKLTGMA FRVPTPNVSV VDLTCRLEKP
AKYDDIKKVV KQASEGPLKG ILGYTEDQVV SCDFNSNSHS STFDAGAGIA
LNDNFVKLIS WYDNEYGYSN RVVDLMAYMA SKE
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis
- Metabolic pathways
- Carbon metabolism
- Biosynthesis of amino acids
- HIF-1 signaling pathway
- Alzheimer disease
Experimental Evidence
- UPLC-MS, Two-dimensional SDS–PAGE
Reference
- Miura T, Shinkai Y, Hirose R, et al. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as a quinone reductase in the suppression of 1, 2-naphthoquinone protein adduct formation[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2011, 51(11): 2082-2089. 21963991