Difference between revisions of "Caspase-7"
(→Reference) |
(→Related Pathway) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==Related Pathway== | ==Related Pathway== | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04210 Apoptosis]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04210 Apoptosis]<br/> | ||
| − | |||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04668 TNF signaling pathway]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04668 TNF signaling pathway]<br/> | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04932 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko04932 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)]<br/> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 47: | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko05134 Legionellosis]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko05134 Legionellosis]<br/> | ||
*[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko05200 Pathways in cancer]<br/> | *[https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?ko05200 Pathways in cancer]<br/> | ||
| − | |||
==Experimental Evidence== | ==Experimental Evidence== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
# Agniswamy J, Fang B, Weber I T. '''Conformational similarity in the activation of caspase-3 and-7 revealed by the unliganded and inhibited structures of caspase-7[J].''' Apoptosis, 2009, 14(10): 1135-1144. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19655253 19655253]<br/> | # Agniswamy J, Fang B, Weber I T. '''Conformational similarity in the activation of caspase-3 and-7 revealed by the unliganded and inhibited structures of caspase-7[J].''' Apoptosis, 2009, 14(10): 1135-1144. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19655253 19655253]<br/> | ||
| − | # Wei Y, Fox T, Chambers S P et al. '''The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity.''' Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10873833 10873833]<br/> | + | # Wei Y, Fox T, Chambers S P et al. '''The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity[J].''' Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10873833 10873833]<br/> |
[[Category:Targets]] | [[Category:Targets]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:10, 4 January 2020
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CASP7 |
| UNP ID | P55210 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys186 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C14A family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic acid protease (Caspase) family) are a family of cysteine proteases that have important intracellular roles in inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of Caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of Caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits.
Caspase-7 is a member of the Caspase family of proteins, and has been shown to be an executioner protein of apoptosis. Sequential activation of Caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes that undergo proteolytic processing by upstream Caspases (Caspase-8, -9) at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme in the form of a heterotetramer. The precursor of this Caspase is cleaved by Caspase 3, Caspase 10, and Caspase 9. It is activated upon cell death stimuli and induces apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in four transcript variants, encoding three distinct isoforms. (From Wikipedia)
Involved in the activation cascade of Caspases responsible for apoptosis execution. Cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). Proteolytically cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) at a '216-Asp-|-Gly-217' bond. Overexpression promotes programmed cell death. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
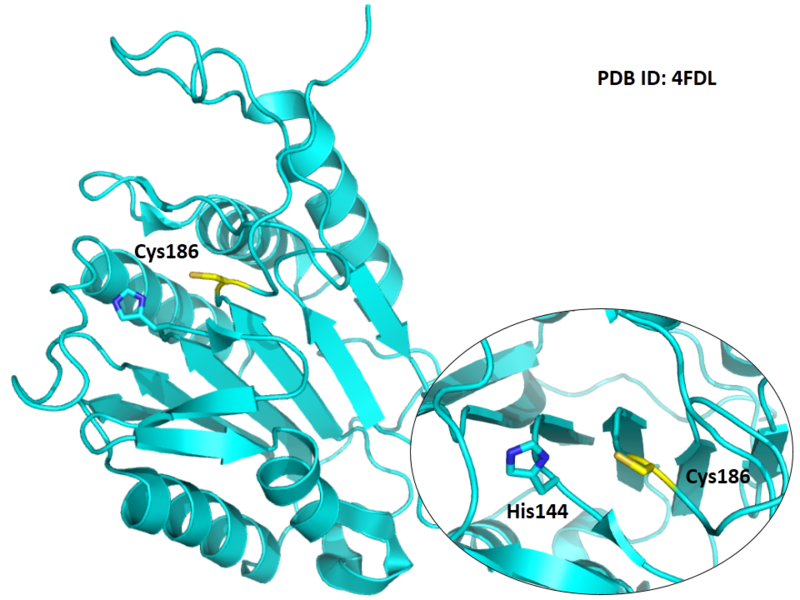
The catalytic triad in Caspase-7 comprises Cys186, His144 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen atom of Arg87, which points towards the Nϵ atom of His144.
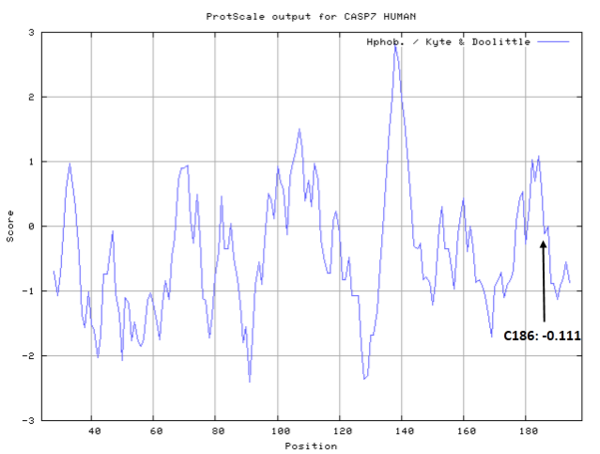
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys186: 14.133 A^2
Protein Sequence
MADDQGCIEE QGVEDSANED SVDAKPDRSS FVPSLFSKKK KNVTMRSIKT
TRDRVPTYQY NMNFEKLGKC IIINNKNFDK VTGMGVRNGT DKDAEALFKC
FRSLGFDVIV YNDCSCAKMQ DLLKKASEED HTNAACFACI LLSHGEENVI
YGKDGVTPIK DLTAHFRGDR CKTLLEKPKL FFIQACRGTE LDDGIQADSG
PINDTDANPR YKIPVEADFL FAYSTVPGYY SWRSPGRGSW FVQALCSILE
EHGKDLEIMQ ILTRVNDRVA RHFESQSDDP HFHEKKQIPC VVSMLTKELY
FSQ
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Apoptosis
- TNF signaling pathway
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Alzheimer disease
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Pertussis
- Legionellosis
- Pathways in cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Agniswamy J, Fang B, Weber I T. Conformational similarity in the activation of caspase-3 and-7 revealed by the unliganded and inhibited structures of caspase-7[J]. Apoptosis, 2009, 14(10): 1135-1144. 19655253
- Wei Y, Fox T, Chambers S P et al. The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity[J]. Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. 10873833