Difference between revisions of "Caspase-3"
(→Reference) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
| − | Caspases (cysteine-aspartic acid protease (Caspase) family) are a family of cysteine proteases that have important intracellular roles in inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of Caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of Caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits. <br/> | + | Caspases (cysteine-aspartic acid protease (Caspase) family) are a family of cysteine proteases that have important intracellular roles in inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of Caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of Caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits. <br/> <br/> |
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| − | The catalytic triad in Caspase-3 comprises Cys163, His121 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen atom of Arg64, which points towards the Nϵ atom of His121.<br/> | + | The catalytic triad in Caspase-3 comprises Cys163, His121 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen atom of Arg64, which points towards the Nϵ atom of His121.<br/><br/> |
* Hydrophobic property: | * Hydrophobic property: | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| − | # Y Wei, T Fox, S P Chambers et al. '''The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity.''' Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10873833 10873833]<br/> | + | # Y Wei, T Fox, S P Chambers et al. '''The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity[J].''' Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10873833 10873833]<br/> |
# Erlanson D A, Lam J W, Wiesmann C, et al. '''In situ assembly of enzyme inhibitors using extended tethering[J].''' Nature biotechnology, 2003, 21(3): 308. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12563278 12563278]<br/> | # Erlanson D A, Lam J W, Wiesmann C, et al. '''In situ assembly of enzyme inhibitors using extended tethering[J].''' Nature biotechnology, 2003, 21(3): 308. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12563278 12563278]<br/> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:15, 4 January 2020
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CASP3 |
| UNP ID | P42574 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys163 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C14A family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic acid protease (Caspase) family) are a family of cysteine proteases that have important intracellular roles in inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of Caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of Caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits.
Cys Function & Property
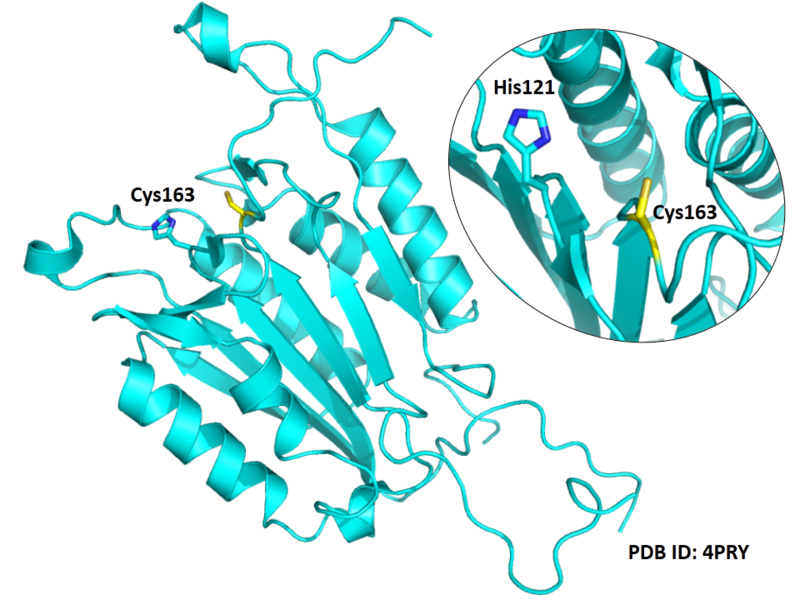
The catalytic triad in Caspase-3 comprises Cys163, His121 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen atom of Arg64, which points towards the Nϵ atom of His121.
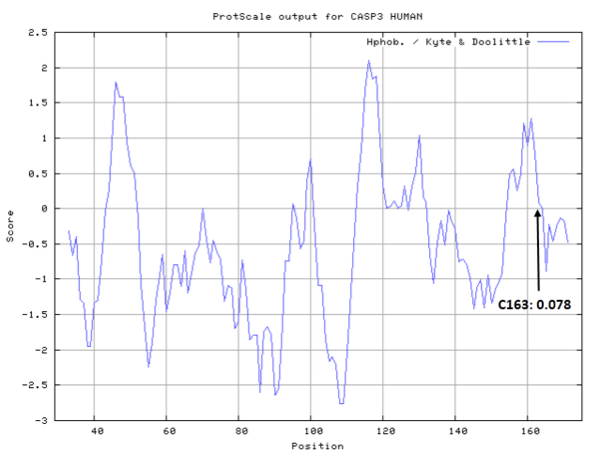
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys163: 7.11 A^2
Protein Sequence
MENTENSVDS KSIKNLEPKI IHGSESMDSG ISLDNSYKMD YPEMGLCIII
NNKNFHKSTG MTSRSGTDVD AANLRETFRN LKYEVRNKND LTREEIVELM
RDVSKEDHSK RSSFVCVLLS HGEEGIIFGT NGPVDLKKIT NFFRGDRCRS
LTGKPKLFII QACRGTELDC GIETDSGVDD DMACHKIPVE ADFLYAYSTA
PGYYSWRNSK DGSWFIQSLC AMLKQYADKL EFMHILTRVN RKVATEFESF
SFDATFHAKK QIPCIVSMLT KELYFYH
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Platinum drug resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- p53 signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Serotonergic synapse
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications
- Alzheimer disease
- Parkinson disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Pertussis
- Legionellosis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Amoebiasis
- Tuberculosis
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Influenza A
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- MicroRNAs in cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Small cell lung cancer
- Viral myocarditis
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Y Wei, T Fox, S P Chambers et al. The structures of caspases-1, -3, -7 and -8 reveal the basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity[J]. Chem Biol, 2000, 7(6): 423-432. 10873833
- Erlanson D A, Lam J W, Wiesmann C, et al. In situ assembly of enzyme inhibitors using extended tethering[J]. Nature biotechnology, 2003, 21(3): 308. 12563278
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Protease
- Peptidase C14A family
- Platinum drug resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- P53 signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Serotonergic synapse
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications
- Alzheimer disease
- Parkinson disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Pertussis
- Legionellosis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Amoebiasis
- Tuberculosis
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Influenza A
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- MicroRNAs in cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Small cell lung cancer
- Viral myocarditis