Difference between revisions of "Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N"
(→Reference) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| __TOC__ | | __TOC__ | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|Ubc13, UbcH13, UBE2N|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P61088 P61088]|Homo sapiens| | + | {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|Ubc13, UbcH13, UBE2N|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P61088 P61088]|Homo sapiens|Cys87|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00179 Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family]|[[:Category:Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N|Ligand list]]|Ubiquitinase/Deubiquitinase,<br/>Post-translational Modification}} |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
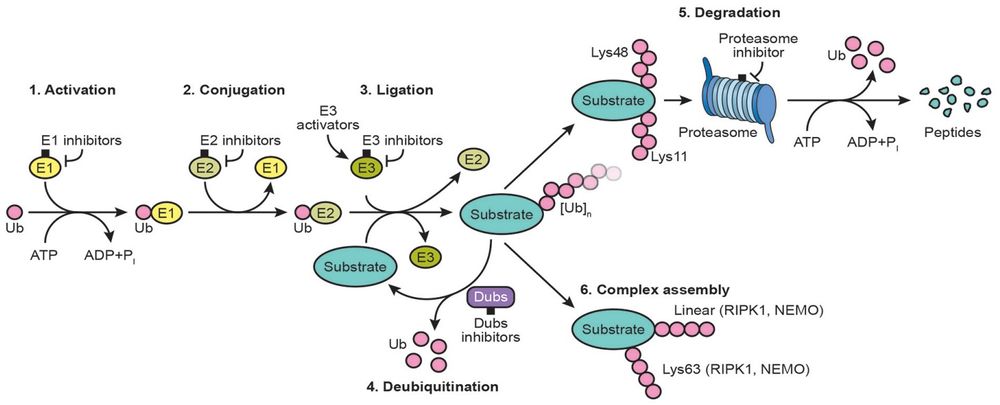
The UBE2V1-UBE2N and UBE2V2-UBE2N heterodimers catalyze the synthesis of non-canonical 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. This type of polyubiquitination does not lead to protein degradation by the proteasome. Mediates transcriptional activation of target genes. Plays a role in the control of progress through the cell cycle and differentiation. Plays a role in the error-free DNA repair pathway and contributes to the survival of cells after DNA damage. Acts together with the E3 ligases, HLTF and SHPRH, in the 'Lys-63'-linked poly-ubiquitination of PCNA upon genotoxic stress, which is required for DNA repair. Appears to act together with E3 ligase RNF5 in the 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of JKAMP thereby regulating JKAMP function by decreasing its association with components of the proteasome and ERAD. Promotes TRIM5 capsid-specific restriction activity and the UBE2V1-UBE2N heterodimer acts in concert with TRIM5 to generate 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains which activate the MAP3K7/TAK1 complex which in turn results in the induction and expression of NF-kappa-B and MAPK-responsive inflammatory genes. (From Uniprot)<br/> | The UBE2V1-UBE2N and UBE2V2-UBE2N heterodimers catalyze the synthesis of non-canonical 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. This type of polyubiquitination does not lead to protein degradation by the proteasome. Mediates transcriptional activation of target genes. Plays a role in the control of progress through the cell cycle and differentiation. Plays a role in the error-free DNA repair pathway and contributes to the survival of cells after DNA damage. Acts together with the E3 ligases, HLTF and SHPRH, in the 'Lys-63'-linked poly-ubiquitination of PCNA upon genotoxic stress, which is required for DNA repair. Appears to act together with E3 ligase RNF5 in the 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of JKAMP thereby regulating JKAMP function by decreasing its association with components of the proteasome and ERAD. Promotes TRIM5 capsid-specific restriction activity and the UBE2V1-UBE2N heterodimer acts in concert with TRIM5 to generate 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains which activate the MAP3K7/TAK1 complex which in turn results in the induction and expression of NF-kappa-B and MAPK-responsive inflammatory genes. (From Uniprot)<br/> | ||
| − | S-ubiquitinyl-[E1 | + | S-ubiquitinyl-[E1]-L-cysteine + [E2]-L-cysteine = [E1]-L-cysteine + S-ubiquitinyl-[E2]-L-cysteine. <br/> |
| + | [[File:571-function-UB.jpg|center|1000px]] | ||
| + | <div align="center">PMID: 27002218</div> | ||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
# Hodge C D, Edwards R A, Markin C J, et al. '''Covalent inhibition of Ubc13 affects ubiquitin signaling and reveals active site elements important for targeting[J].''' ACS chemical biology, 2015, 10(7): 1718-1728. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=25909880 25909880]<br/> | # Hodge C D, Edwards R A, Markin C J, et al. '''Covalent inhibition of Ubc13 affects ubiquitin signaling and reveals active site elements important for targeting[J].''' ACS chemical biology, 2015, 10(7): 1718-1728. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=25909880 25909880]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Ubiquitinase/Deubiquitinase]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Post-translational Modification]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family]] |
| + | [[Category:Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:02, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Ubc13, UbcH13, UBE2N |
| UNP ID | P61088 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
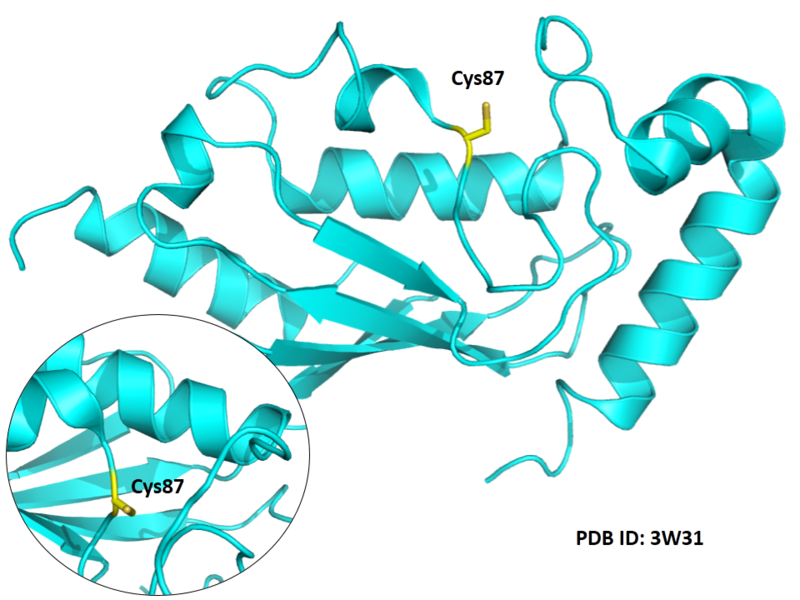
| Cys Site | Cys87 |
| Family/Domain | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type |
Ubiquitinase/Deubiquitinase, Post-translational Modification |
Summary
Protein Function
The UBE2V1-UBE2N and UBE2V2-UBE2N heterodimers catalyze the synthesis of non-canonical 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. This type of polyubiquitination does not lead to protein degradation by the proteasome. Mediates transcriptional activation of target genes. Plays a role in the control of progress through the cell cycle and differentiation. Plays a role in the error-free DNA repair pathway and contributes to the survival of cells after DNA damage. Acts together with the E3 ligases, HLTF and SHPRH, in the 'Lys-63'-linked poly-ubiquitination of PCNA upon genotoxic stress, which is required for DNA repair. Appears to act together with E3 ligase RNF5 in the 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of JKAMP thereby regulating JKAMP function by decreasing its association with components of the proteasome and ERAD. Promotes TRIM5 capsid-specific restriction activity and the UBE2V1-UBE2N heterodimer acts in concert with TRIM5 to generate 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains which activate the MAP3K7/TAK1 complex which in turn results in the induction and expression of NF-kappa-B and MAPK-responsive inflammatory genes. (From Uniprot)
S-ubiquitinyl-[E1]-L-cysteine + [E2]-L-cysteine = [E1]-L-cysteine + S-ubiquitinyl-[E2]-L-cysteine.
Cys Function & Property
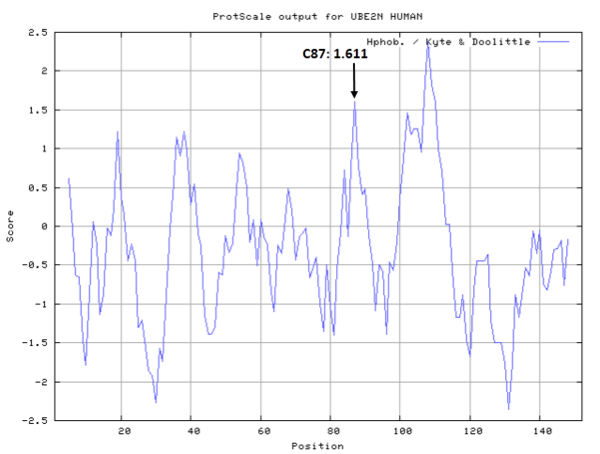
Cys87 is the active site of UBE2N, which could form a glycyl thioester intermediate during the catalysis.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys87: 27.384 A^2
Protein Sequence
MAGLPRRIIK ETQRLLAEPV PGIKAEPDES NARYFHVVIA GPQDSPFEGG
TFKLELFLPE EYPMAAPKVR FMTKIYHPNV DKLGRICLDI LKDKWSPALQ
IRTVLLSIQA LLSAPNPDDP LANDVAEQWK TNEAQAIETA RAWTRLYAMN
NI
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- MALDI-TOF/MS, Tryptic Digest, Crystallography
Reference
- Strickson S, Campbell D G, Emmerich C H, et al. The anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11-7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system[J]. Biochemical Journal, 2013, 451(3): 427-437. 23441730
- Hodge C D, Edwards R A, Markin C J, et al. Covalent inhibition of Ubc13 affects ubiquitin signaling and reveals active site elements important for targeting[J]. ACS chemical biology, 2015, 10(7): 1718-1728. 25909880