Difference between revisions of "Potassium-transporting ATPase alpha chain 1"
(→Cys Function & Property) |
(→Experimental Evidence) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
==Experimental Evidence== | ==Experimental Evidence== | ||
| − | :Cys-directed mutation, Tricine-SDS-PAGE | + | :Cys-directed mutation, Tricine-SDS-PAGE, Microsequence analysis |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Revision as of 04:16, 29 July 2019
Lua error: data must be either of type string or number.
Summary
Protein Function
The H,K-ATPase (ATP4A), also known as Gastric H(+)/K(+) ATPase subunit alpha, the enzyme responsible for generating gastric acid by pumping hydronium ions out of the parietal cell of the stomach in exchange for potassium, belongs to the family of P2-type ATPases and has homology with other members of this family such as the Na,K-ATPases (65%) and Ca-ATPases (23%). ATP4A Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of H+ and K+ ions across the plasma membrane. (From Uniprot, PMID: 10660561)
Cys Function & Property
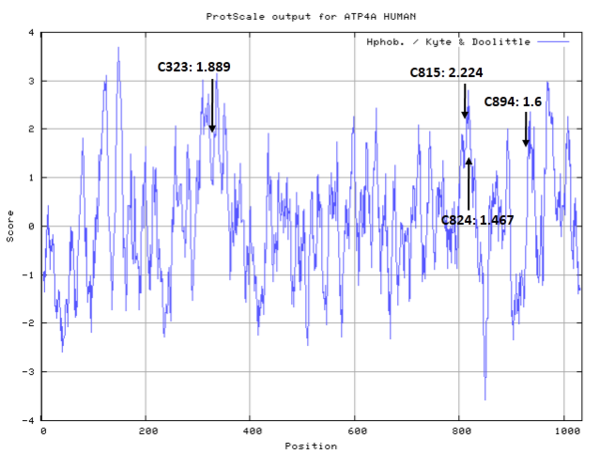
From microsequence analysis, lansoprazole labels the enzyme at three positions, cysteine 321 in the TM3/4 domain, cys 813/822 in the TM5/6 domain, and cys 892 in the TM7/8 domain. Omeprazole labels the enzyme at two positions, again cys 813/822 in the TM5/6 domain and cys 892 in the TM718 domain. (PMID: 9405786)
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MGKAENYELY SVELGPGPGG DMAAKMSKKK KAGGGGGKRK EKLENMKKEM
EINDHQLSVA ELEQKYQTSA TKGLSASLAA ELLLRDGPNA LRPPRGTPEY
VKFARQLAGG LQCLMWVAAA ICLIAFAIQA SEGDLTTDDN LYLAIALIAV
VVVTGCFGYY QEFKSTNIIA SFKNLVPQQA TVIRDGDKFQ INADQLVVGD
LVEMKGGDRV PADIRILAAQ GCKVDNSSLT GESEPQTRSP ECTHESPLET
RNIAFFSTMC LEGTVQGLVV NTGDRTIIGR IASLASGVEN EKTPIAIEIE
HFVDIIAGLA ILFGATFFIV AMCIGYTFLR AMVFFMAIVV AYVPEGLLAT
VTVCLSLTAK RLASKNCVVK NLEAVETLGS TSVICSDKTG TLTQNRMTVS
HLWFDNHIHT ADTTEDQSGQ TFDQSSETWR ALCRVLTLCN RAAFKSGQDA
VPVPKRIVIG DASETALLKF SELTLGNAMG YRDRFPKVCE IPFNSTNKFQ
LSIHTLEDPR DPRHLLVMKG APERVLERCS SILIKGQELP LDEQWREAFQ
TAYLSLGGLG ERVLGFCQLY LNEKDYPPGY AFDVEAMNFP SSGLCFAGLV
SMIDPPRATV PDAVLKCRTA GIRVIMVTGD HPITAKAIAA SVGIISEGSE
TVEDIAARLR VPVDQVNRKD ARACVINGMQ LKDMDPSELV EALRTHPEMV
FARTSPQQKL VIVESCQRLG AIVAVTGDGV NDSPALKKAD IGVAMGIAGS
DAAKNAADMI LLDDNFASIV TGVEQGRLIF DNLKKSIAYT LTKNIPELTP
YLIYITVSVP LPLGCITILF IELCTDIFPS VSLAYEKAES DIMHLRPRNP
KRDRLVNEPL AAYSYFQIGA IQSFAGFTDY FTAMAQEGWF PLLCVGLRAQ
WEDHHLQDLQ DSYGQEWTFG QRLYQQYTCY TVFFISIEVC QIADVLIRKT
RRLSAFQQGF FRNKILVIAI VFQVCIGCFL CYCPGMPNIF NFMPIRFQWW
LVPLPYGILI FVYDEIRKLG VRCCPGSWWD QELYY
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Oxidative phosphorylation
- Metabolic pathways
- Collecting duct acid secretion
- Gastric acid secretion
- Focal adhesion
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed mutation, Tricine-SDS-PAGE, Microsequence analysis
Reference
- Lambrecht N, Munson K, Vagin O, et al. Comparison of covalent with reversible inhibitor binding sites of the gastric H, K-ATPase by site-directed mutagenesis[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(6): 4041-4048. 10660561
- Shin J M, Besancon M, Bamberg K, et al. Structural aspects of the gastric H, K ATPase[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1997, 834: 65-76. 9405786