Difference between revisions of "N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1"
(→Protein Function) |
(→Protein Function) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
| − | + | Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase, as known as DDAH, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: <br/> | |
<div align="center">N-omega,N-omega'-methyl-L-arginine + H2O ↔ dimethylamine + L-citrulline</div> | <div align="center">N-omega,N-omega'-methyl-L-arginine + H2O ↔ dimethylamine + L-citrulline</div> | ||
DDAH is an enzyme found in all mammalian cells. Two isoforms exist, DDAH I and DDAH II, with some differences in tissue distribution of the two isoforms. The enzyme degrades methylarginines, specifically asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA).<br/> | DDAH is an enzyme found in all mammalian cells. Two isoforms exist, DDAH I and DDAH II, with some differences in tissue distribution of the two isoforms. The enzyme degrades methylarginines, specifically asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA).<br/> | ||
Revision as of 02:06, 15 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | DDAH1 |
| UNP ID | O94760 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
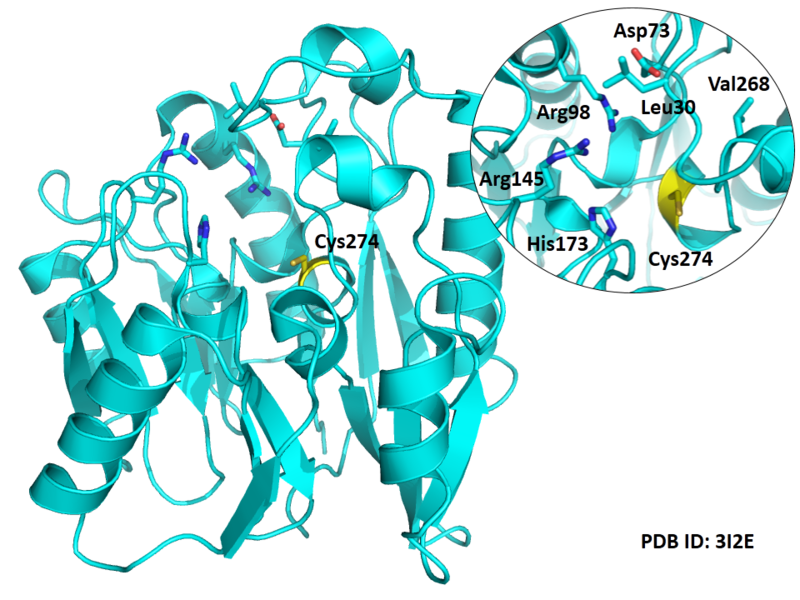
| Cys Site | Cys274 |
| Family/Domain | DDAH family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase, as known as DDAH, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
DDAH is an enzyme found in all mammalian cells. Two isoforms exist, DDAH I and DDAH II, with some differences in tissue distribution of the two isoforms. The enzyme degrades methylarginines, specifically asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA).
The methylarginines ADMA and MMA inhibit the production of nitric oxide synthase. As such, DDAH is important in removing methylarginines, generated by protein degradation, from accumulating and inhibiting the generation of nitric oxide. (From Wikipedia)
Hydrolyzes N(G),N(G)-dimethyl-L-arginine (ADMA) and N(G)-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA) which act as inhibitors of NOS. Has therefore a role in the regulation of nitric oxide generation. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
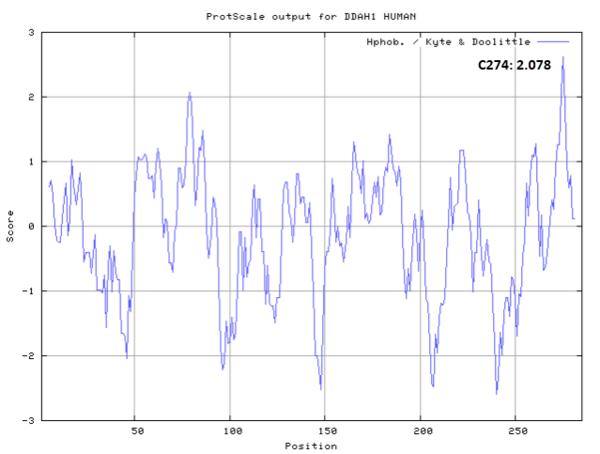
Cys274 is one of the active site of DDAH1, which act as the nucleophile group in catalyze.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys274: 7.407 A^2
Protein Sequence
MAGLGHPAAF GRATHAVVRA LPESLGQHAL RSAKGEEVDV ARAERQHQLY
VGVLGSKLGL QVVELPADES LPDCVFVEDV AVVCEETALI TRPGAPSRRK
EVDMMKEALE KLQLNIVEMK DENATLDGGD VLFTGREFFV GLSKRTNQRG
AEILADTFKD YAVSTVPVAD GLHLKSFCSM AGPNLIAIGS SESAQKALKI
MQQMSDHRYD KLTVPDDIAA NCIYLNIPNK GHVLLHRTPE EYPESAKVYE
KLKDHMLIPV SMSELEKVDG LLTCCSVLIN KKVDS
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Unknown
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Molecular Docking
Reference
- Wang Y, Monzingo A F, Hu S, et al. Developing dual and specific inhibitors of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 and nitric oxide synthase: toward a targeted polypharmacology to control nitric oxide[J]. Biochemistry, 2009, 48(36): 8624-8635. 19663506
- Lluis M, Wang Y, Monzingo A F, et al. Characterization of C‐Alkyl Amidines as Bioavailable Covalent Reversible Inhibitors of Human DDAH‐1[J]. ChemMedChem, 2011, 6(1): 81-88. 20979083
- Linsky T W, Fast W. Discovery of structurally-diverse inhibitor scaffolds by high-throughput screening of a fragment library with dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 2012, 20(18): 5550-5558. 22921743