Difference between revisions of "Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|UBE2D3|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P61077 P61077]|Homo sapiens|Cys85|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00179...") |
(→Protein Function) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
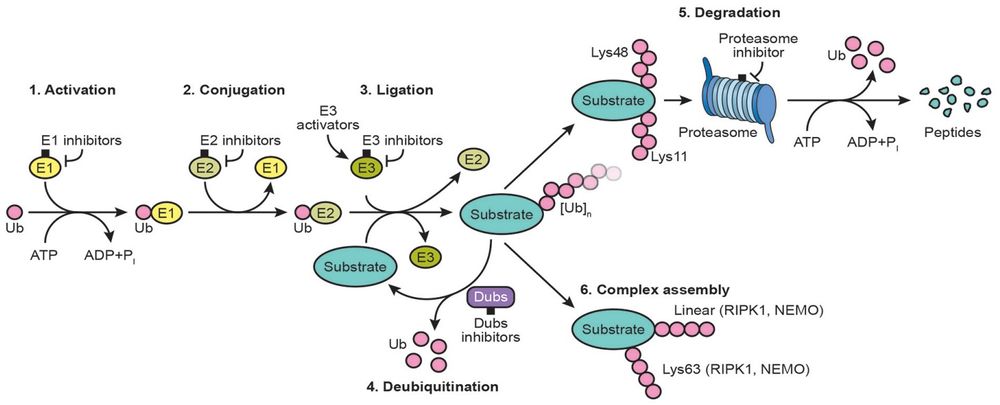
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ubiquitin-carrier enzymes, perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction that targets a protein for degradation via the proteasome. The ubiquitination process covalently attaches ubiquitin, a short protein of 76 amino acids, to a lysine residue on the target protein. Once a protein has been tagged with one ubiquitin molecule, additional rounds of ubiquitination form a polyubiquitin chain that is recognized by the proteasome's 19S regulatory particle, triggering the ATP-dependent unfolding of the target protein that allows passage into the proteasome's 20S core particle, where proteases degrade the target into short peptide fragments for recycling by the cell. <br/> | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ubiquitin-carrier enzymes, perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction that targets a protein for degradation via the proteasome. The ubiquitination process covalently attaches ubiquitin, a short protein of 76 amino acids, to a lysine residue on the target protein. Once a protein has been tagged with one ubiquitin molecule, additional rounds of ubiquitination form a polyubiquitin chain that is recognized by the proteasome's 19S regulatory particle, triggering the ATP-dependent unfolding of the target protein that allows passage into the proteasome's 20S core particle, where proteases degrade the target into short peptide fragments for recycling by the cell. <br/> | ||
| − | [[File:571-function-UB.jpg|center| | + | [[File:571-function-UB.jpg|center|1000px]] |
<div align="center">PMID: 27002218</div> | <div align="center">PMID: 27002218</div> | ||
Revision as of 02:24, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | UBE2D3 |
| UNP ID | P61077 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
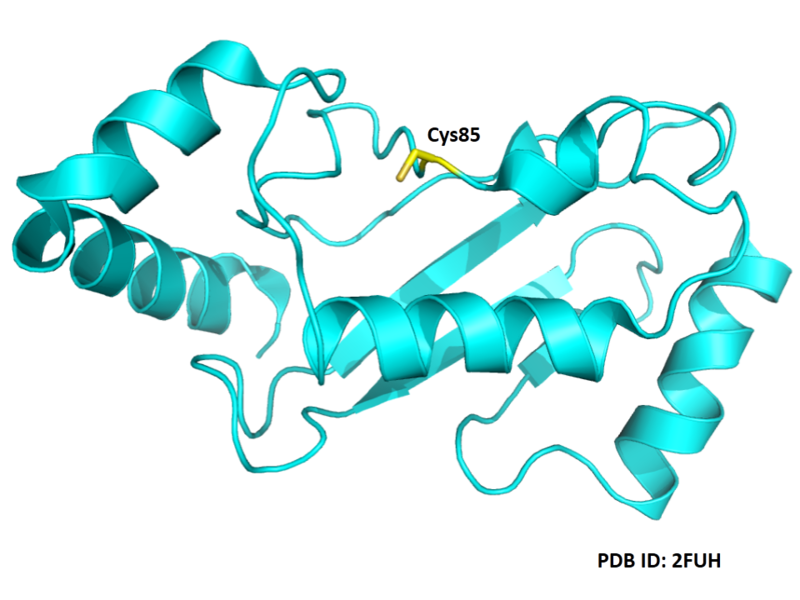
| Cys Site | Cys85 |
| Family/Domain | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Post-translational Modification, Ubiquitinase/Deubiquitinase |
Summary
Protein Function
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ubiquitin-carrier enzymes, perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction that targets a protein for degradation via the proteasome. The ubiquitination process covalently attaches ubiquitin, a short protein of 76 amino acids, to a lysine residue on the target protein. Once a protein has been tagged with one ubiquitin molecule, additional rounds of ubiquitination form a polyubiquitin chain that is recognized by the proteasome's 19S regulatory particle, triggering the ATP-dependent unfolding of the target protein that allows passage into the proteasome's 20S core particle, where proteases degrade the target into short peptide fragments for recycling by the cell.
Cys Function & Property
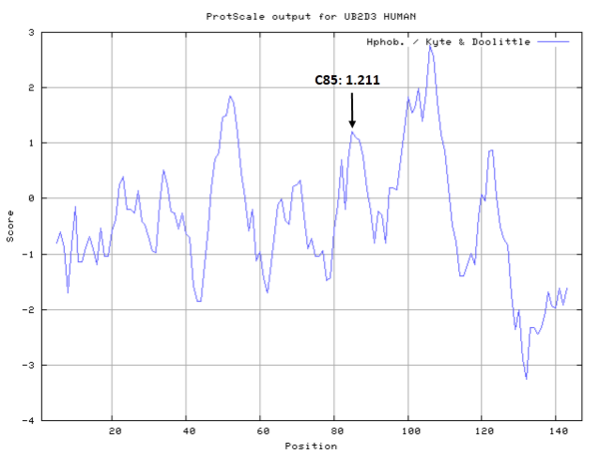
Cys85 is the active site of UBE2D3, act as a glycyl thioester intermediate.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys85: 22.494 A^2
Protein Sequence
MALKRINKEL SDLARDPPAQ CSAGPVGDDM FHWQATIMGP NDSPYQGGVF
FLTIHFPTDY PFKPPKVAFT TRIYHPNINS NGSICLDILR SQWSPALTIS
KVLLSICSLL CDPNPDDPLV PEIARIYKTD RDKYNRISRE WTQKYAM
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- LC-CID-MS/MS, Tryptic Digest
Reference
- Liu L, Hua Y, Wang D, et al. A sesquiterpene lactone from a medicinal herb inhibits proinflammatory activity of TNF-α by inhibiting ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH5[J]. Chemistry & biology, 2014, 21(10): 1341-1350. 25200604