Difference between revisions of "Legumain"
(→Summary) |
(→Reference) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
# Dall E, Brandstetter H. '''Mechanistic and structural studies on legumain explain its zymogenicity, distinct activation pathways, and regulation[J].''' Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(27): 10940-10945. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=23776206 23776206]<br/> | # Dall E, Brandstetter H. '''Mechanistic and structural studies on legumain explain its zymogenicity, distinct activation pathways, and regulation[J].''' Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(27): 10940-10945. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=23776206 23776206]<br/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Targets]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Homo sapiens]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Protease]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Peptidase C13 family]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Lysosome]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Antigen processing and presentation]] |
Latest revision as of 23:05, 19 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | LGMN, PRSC1 |
| UNP ID | Q99538 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
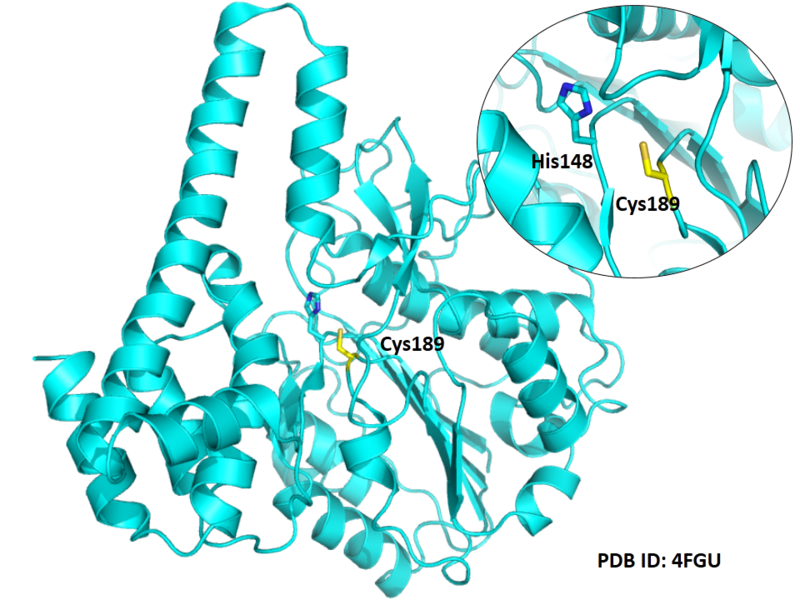
| Cys Site | Cys189 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C13 family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Legumain is a cysteine protease from the C13 family of the CD clan of proteases (MEROPS). It uses a catalytic triad of Cysteine-Histidine-Asparagine in its active site to perform covalent proteolysis of its substrate.
It catalyses the following chemical reaction: Hydrolysis of proteins and small molecule substrates at -Asn-Xaa- bonds. Both plant and animal legumains are most active in acidic environments. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
Cys189 is one of the active sites of Legumain.
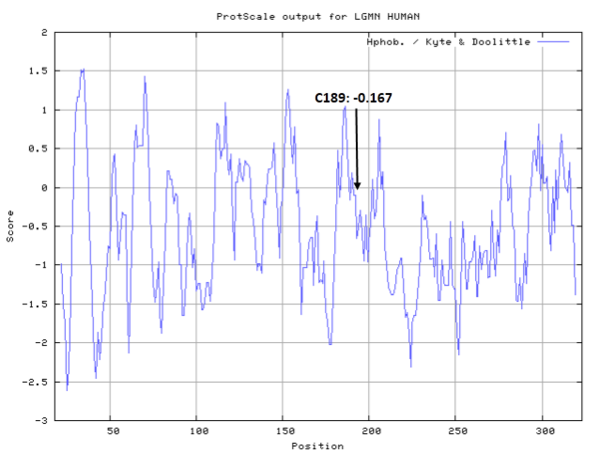
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys189: 4.399 A^2
Protein Sequence
MVWKVAVFLS VALGIGAVPI DDPEDGGKHW VVIVAGSNGW YNYRHQADAC
HAYQIIHRNG IPDEQIVVMM YDDIAYSEDN PTPGIVINRP NGTDVYQGVP
KDYTGEDVTP QNFLAVLRGD AEAVKGIGSG KVLKSGPQDH VFIYFTDHGS
TGILVFPNED LHVKDLNETI HYMYKHKMYR KMVFYIEACE SGSMMNHLPD
NINVYATTAA NPRESSYACY YDEKRSTYLG DWYSVNWMED SDVEDLTKET
LHKQYHLVKS HTNTSHVMQY GNKTISTMKV MQFQGMKRKA SSPVPLPPVT
HLDLTPSPDV PLTIMKRKLM NTNDLEESRQ LTEEIQRHLD ARHLIEKSVR
KIVSLLAASE AEVEQLLSER APLTGHSCYP EALLHFRTHC FNWHSPTYEY
ALRHLYVLVN LCEKPYPLHR IKLSMDHVCL GHY
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Lee J, Bogyo M. Synthesis and evaluation of aza-peptidyl inhibitors of the lysosomal asparaginyl endopeptidase, legumain[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2012, 22(3): 1340-1343. 22243962
- Dall E, Brandstetter H. Mechanistic and structural studies on legumain explain its zymogenicity, distinct activation pathways, and regulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(27): 10940-10945. 23776206