Difference between revisions of "Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 (Rattus norvegicus)"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|HBB|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P02091 P02091]|Rattus norvegicus|Cys126|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF000...") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Beta globin (also referred to as HBB, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta, or preferably haemoglobin subunit beta) is a globin protein, which along with alpha globin (HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, the HbA. It is 146 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. <br/> | Beta globin (also referred to as HBB, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta, or preferably haemoglobin subunit beta) is a globin protein, which along with alpha globin (HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, the HbA. It is 146 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. <br/> | ||
HBB is encoded by the HBB gene on human chromosome 11. Mutations in the gene produce several variants of the proteins which are implicated with genetic disorders such as sickle-cell disease and beta thalassemia, as well as beneficial traits such as genetic resistance to malaria. (From Wikipedia) <br/> | HBB is encoded by the HBB gene on human chromosome 11. Mutations in the gene produce several variants of the proteins which are implicated with genetic disorders such as sickle-cell disease and beta thalassemia, as well as beneficial traits such as genetic resistance to malaria. (From Wikipedia) <br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
The covalent modification on Cys126 could inhibit the fomration of dimer with HBA1. <br/> | The covalent modification on Cys126 could inhibit the fomration of dimer with HBA1. <br/> | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 28 April 2020
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | HBB |
| UNP ID | P02091 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
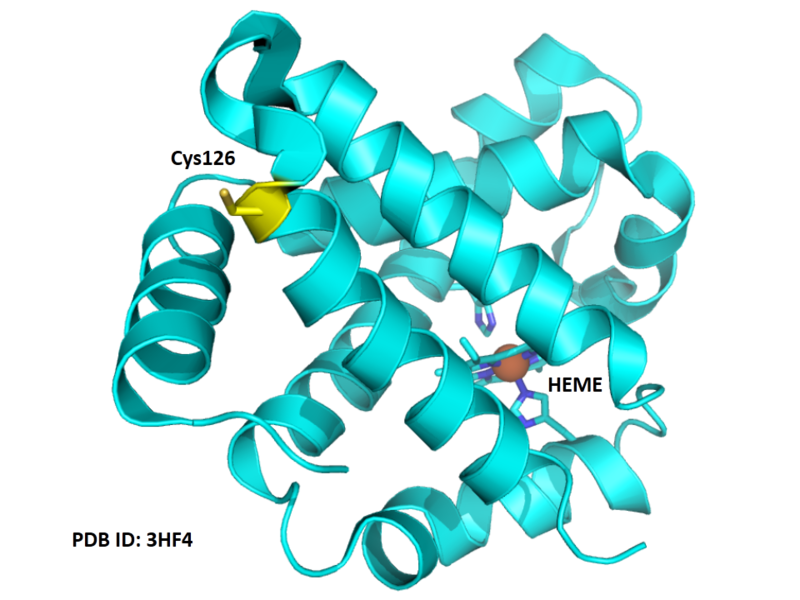
| Cys Site | Cys126 |
| Family/Domain | Globin family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transporter |
Summary
Protein Function
Beta globin (also referred to as HBB, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta, or preferably haemoglobin subunit beta) is a globin protein, which along with alpha globin (HBA), makes up the most common form of haemoglobin in adult humans, the HbA. It is 146 amino acids long and has a molecular weight of 15,867 Da. Normal adult human HbA is a heterotetramer consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains.
HBB is encoded by the HBB gene on human chromosome 11. Mutations in the gene produce several variants of the proteins which are implicated with genetic disorders such as sickle-cell disease and beta thalassemia, as well as beneficial traits such as genetic resistance to malaria. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
The covalent modification on Cys126 could inhibit the fomration of dimer with HBA1.
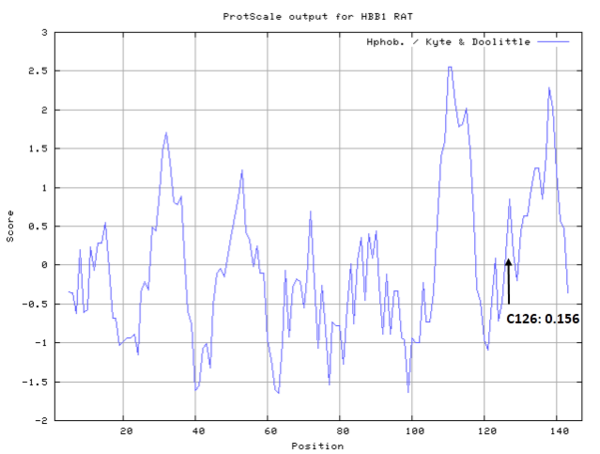
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys126: 88.89 A^2
Protein Sequence
MVHLTPEEKS AVTALWGKVN VDEVGGEALG RLLVVYPWTQ RFFESFGDLS
TPDAVMGNPK VKAHGKKVLG AFSDGLAHLD NLKGTFATLS ELHCDKLHVD
PENFRLLGNV LVCVLAHHFG KEFTPPVQAA YQKVVAGVAN ALAHKYH
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- FTIR spectra, Electrospray Mass Spectra
Reference
- Erve J C L, Jensen O N, Valentine H S, et al. Disulfiram generates a stable N, N-diethylcarbamoyl adduct on Cys-125 of rat hemoglobin β-chains in vivo[J]. Chemical research in toxicology, 2000, 13(4): 237-244. 10775322
- Zimmerman L J, Valentine H S, Amarnath K, et al. Identification of a S-Hexahydro-1 H-azepine-1-carbonyl Adduct Produced by Molinate on Rat Hemoglobin β2 and β3 Chains in Vivo[J]. Chemical research in toxicology, 2002, 15(2): 209-217. 11849047