Difference between revisions of "Calpain-2"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|CAPN2|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P17655 P17655]|Homo sapiens|Cys105|[http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00648...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 20:08, 28 July 2019
Lua error: data must be either of type string or number.
Summary
Protein Function
Calpain-2 catalytic subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN2 gene. The calpains, calcium-activated neutral proteases, are nonlysosomal, intracellular cysteine proteases. The mammalian calpains include ubiquitous, stomach-specific, and muscle-specific proteins. The ubiquitous enzymes consist of heterodimers with distinct large, catalytic subunits associated with a common small, regulatory subunit. This gene encodes the large subunit of the ubiquitous enzyme, calpain 2. Multiple heterogeneous transcriptional start sites in the 5' UTR have been reported. (From Wikipedia)
Calcium-regulated non-lysosomal thiol-protease which catalyze limited proteolysis of substrates involved in cytoskeletal remodeling and signal transduction. Proteolytically cleaves MYOC at 'Arg-226'. (From Uniprot)
Calpains are active participants in fundamental mammalian cellular processes such as cell migration and associated-cytoskeletal remodeling, apoptosis and cell cycle progression. Abnormal calpain activation is also linked to Alzheimer's disease (AD). In AD, calpain relays the toxic effect of extracellular amyloid peptides on neurons to intracellular tau aggregation and neuronal cell death. (PMID: 15491615)
Cys Function & Property
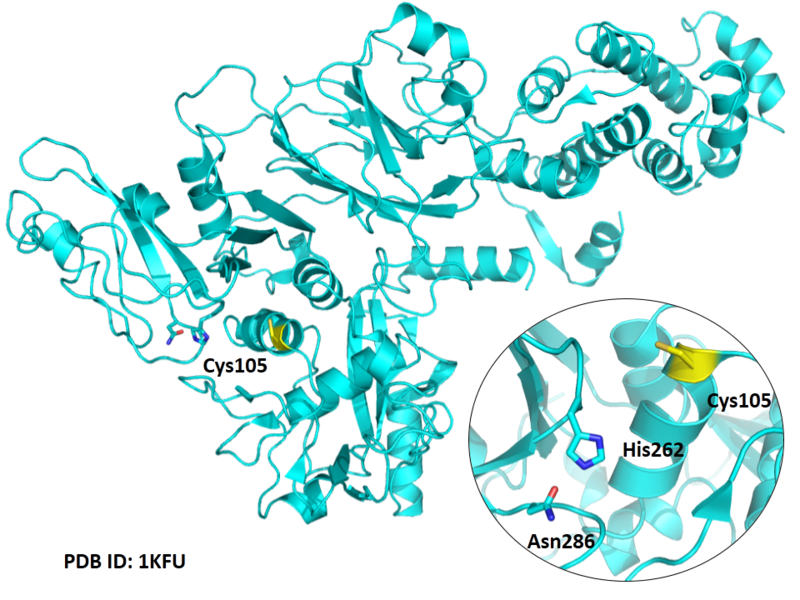
Cys105 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin H, which is very close to His262 and Asn286 in space. These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.
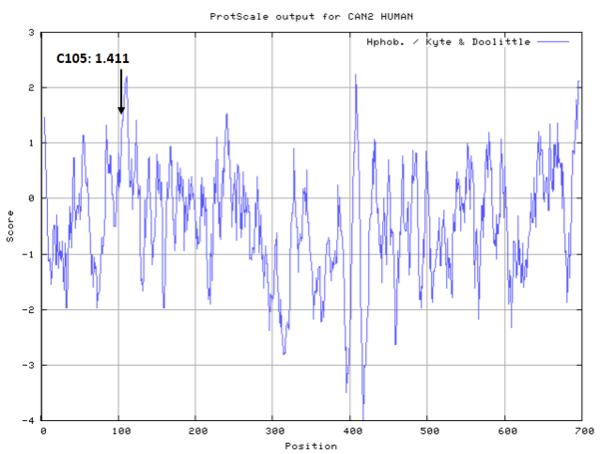
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys105: 43.83 A^2
Protein Sequence
MAGIAAKLAK DREAAEGLGS HDRAIKYLNQ DYEALRNECL EAGTLFQDPS
FPAIPSALGF KELGPYSSKT RGIEWKRPTE ICADPQFIIG GATRTDICQG
ALGDCWLLAA IASLTLNEEI LARVVPLNQS FQENYAGIFH FQFWQYGEWV
EVVVDDRLPT KDGELLFVHS AEGSEFWSAL LEKAYAKING CYEALSGGAT
TEGFEDFTGG IAEWYELKKP PPNLFKIIQK ALQKGSLLGC SIDITSAADS
EAITFQKLVK GHAYSVTGAE EVESNGSLQK LIRIRNPWGE VEWTGRWNDN
CPSWNTIDPE ERERLTRRHE DGEFWMSFSD FLRHYSRLEI CNLTPDTLTS
DTYKKWKLTK MDGNWRRGST AGGCRNYPNT FWMNPQYLIK LEEEDEDEED
GESGCTFLVG LIQKHRRRQR KMGEDMHTIG FGIYEVPEEL SGQTNIHLSK
NFFLTNRARE RSDTFINLRE VLNRFKLPPG EYILVPSTFE PNKDGDFCIR
VFSEKKADYQ AVDDEIEANL EEFDISEDDI DDGFRRLFAQ LAGEDAEISA
FELQTILRRV LAKRQDIKSD GFSIETCKIM VDMLDSDGSG KLGLKEFYIL
WTKIQKYQKI YREIDVDRSG TMNSYEMRKA LEEAGFKMPC QLHQVIVARF
ADDQLIIDFD NFVRCLVRLE TLFKIFKQLD PENTGTIELD LISWLCFSVL
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum
- Apoptosis
- Necroptosis
- Cellular senescence
- Focal adhesion
- Alzheimer disease
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Moldoveanu T, Campbell R L, Cuerrier D, et al. Crystal structures of calpain–E64 and–leupeptin inhibitor complexes reveal mobile loops gating the active site[J]. Journal of molecular biology, 2004, 343(5): 1313-1326. 15491615