Difference between revisions of "Regulator of G-protein signaling 4"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|RGP4, RGS4|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P49798 P49798]|Homo sapiens|Cys71, Cys132, Cys148, Cys183|[http://p...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 02:38, 31 July 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | RGP4, RGS4 |
| UNP ID | P49798 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys71, Cys132, Cys148, Cys183 |
| Family/Domain | Regulator of G protein signaling domain |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | ATPase/GTPase |
Summary
Protein Function
Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Activity on G(z)-alpha is inhibited by phosphorylation of the G-protein. Activity on G(z)-alpha and G(i)-alpha-1 is inhibited by palmitoylation of the G-protein. (From Uniprot)
Regulator of G protein signaling 4 also known as RGP4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS4 gene. RGP4 regulates G protein signaling. Regulator of G protein signalling (RGS) family members are regulatory molecules that act as GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) for G alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. RGS proteins are able to deactivate G protein subunits of the Gi alpha, Go alpha and Gq alpha subtypes. They drive G proteins into their inactive GDP-bound forms. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 belongs to this family. All RGS proteins share a conserved 120-amino acid sequence termed the RGS domain which conveys GAP activity.#Regulator of G protein signaling 4 protein is 37% identical to RGS1 and 97% identical to rat Rgs4. This protein negatively regulates signaling upstream or at the level of the heterotrimeric G protein and is localized in the cytoplasm. (From Wiki)
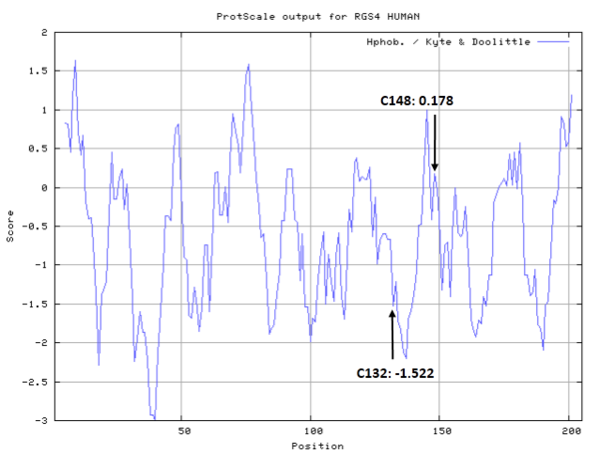
Cys Function & Property
To be added.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MCKGLAGLPA SCLRSAKDMK HRLGFLLQKS DSCEHNSSHN KKDKVVICQR
VSQEEVKKWA ESLENLISHE CGLAAFKAFL KSEYSEENID FWISCEEYKK
IKSPSKLSPK AKKIYNEFIS VQATKEVNLD SCTREETSRN MLEPTITCFD
EAQKKIFNLM EKDSYRRFLK SRFYLDLVNP SSCGAEKQKG AKSSADCASL
VPQCA
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
- Unknown
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, Surface Plasmon Resonance-based Binding Assay, MS, Western Blot
Reference
- Monroy C A, Doorn J A, Roman D L. Modification and functional inhibition of regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal[J]. Chemical research in toxicology, 2013, 26(12): 1832-1839. 24229325
- Kimple A J, Willard F S, Giguère P M, et al. The RGS protein inhibitor CCG-4986 is a covalent modifier of the RGS4 Gα-interaction face[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 2007, 1774(9): 1213-1220. 17660054
- Roof R A, Roman D L, Clements S T, et al. A covalent peptide inhibitor of RGS4 identified in a focused one-bead, one compound library screen[J]. BMC pharmacology, 2009, 9(1): 9. 19463173
- Roman D L, Ota S, Neubig R R. Polyplexed flow cytometry protein interaction assay: a novel high-throughput screening paradigm for RGS protein inhibitors[J]. Journal of biomolecular screening, 2009, 14(6): 610-619. 19531661
- Storaska A J, Mei J P, Wu M, et al. Reversible inhibitors of regulators of G-protein signaling identified in a high-throughput cell-based calcium signaling assay[J]. Cellular signalling, 2013, 25(12): 2848-2855. 24041654
- Blazer L L, Roman D L, Chung A, et al. Reversible, allosteric small-molecule inhibitors of regulator of G protein signaling proteins[J]. Molecular pharmacology, 2010, 78(3): 524-533. 20571077