Difference between revisions of "Transcription factor AP-1"
(Created page with "{| align="left" | __TOC__ |} {{#invoke:InfoboxforTarget|run|Proto-oncogene c-Jun, AP1|[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P05412 P05412]|Homo sapiens|Cys269|[http://pfam.xfam...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 02:05, 4 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Proto-oncogene c-Jun, AP1 |
| UNP ID | P05412 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys269 |
| Family/Domain |
bZIP transcription factor Jun-like transcription factor |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transcription factor |
Summary
Protein Function
Transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. Promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. (From Uniprot)
Activator protein 1 (AP-1) is a transcription factor which is a heterodimeric protein composed of proteins belonging to the c-Fos, c-Jun, ATF and JDP families. It regulates gene expression in response to a variety of stimuli, including cytokines, growth factors, stress, and bacterial and viral infections. AP-1 in turn controls a number of cellular processes including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. AP-1 upregulates transcription of genes containing the TPA DNA response element (TRE; 5'-TGAG/CTCA-3'). AP-1 binds to this DNA sequence via a basic amino acid region, while the dimeric structure is formed by a leucine zipper. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
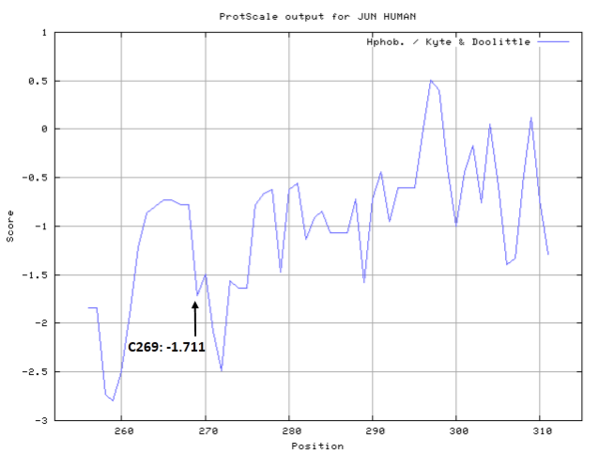
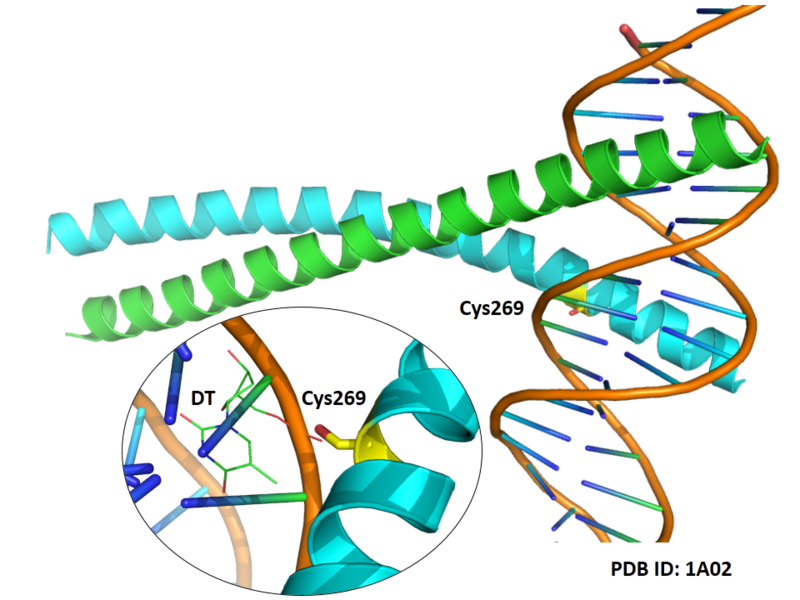
Cys269 is very close to the DNA binding site of c-Jun.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys269: 6.549 A^2
Protein Sequence
MTAKMETTFY DDALNASFLP SESGPYGYSN PKILKQSMTL NLADPVGSLK
PHLRAKNSDL LTSPDVGLLK LASPELERLI IQSSNGHITT TPTPTQFLCP
KNVTDEQEGF AEGFVRALAE LHSQNTLPSV TSAAQPVNGA GMVAPAVASV
AGGSGSGGFS ASLHSEPPVY ANLSNFNPGA LSSGGGAPSY GAAGLAFPAQ
PQQQQQPPHH LPQQMPVQHP RLQALKEEPQ TVPEMPGETP PLSPIDMESQ
ERIKAERKRM RNRIAASKCR KRKLERIARL EEKVKTLKAQ NSELASTANM
LREQVAQLKQ KVMNHVNSGC QLMLTQQLQT F
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Endocrine resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- ErbB signaling pathway
- cAMP signaling pathway
- Mitophagy - animal
- Apoptosis
- Wnt signaling pathway
- Osteoclast differentiation
- Focal adhesion
- Tight junction
- Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation
- Th17 cell differentiation
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- GnRH signaling pathway
- Estrogen signaling pathway
- Oxytocin signaling pathway
- Relaxin signaling pathway
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications
- Cocaine addiction
- Amphetamine addiction
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Salmonella infection
- Pertussis
- Yersinia infection
- Leishmaniasis
- Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis)
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Colorectal cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Breast cancer
- Choline metabolism in cancer
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
Experimental Evidence
- Mass Spectrometry, Western Blot, Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Pérez-Sala D, Cernuda-Morollón E. Molecular basis for the direct inhibition of AP-1 DNA binding by 15-deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(51): 51251-51260. 14532268
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Transcription factor
- BZIP family
- Jun subfamily
- Endocrine resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- ErbB signaling pathway
- CAMP signaling pathway
- Mitophagy - animal
- Apoptosis
- Wnt signaling pathway
- Osteoclast differentiation
- Focal adhesion
- Tight junction
- Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation
- Th17 cell differentiation
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- GnRH signaling pathway
- Estrogen signaling pathway
- Oxytocin signaling pathway
- Relaxin signaling pathway
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications
- Cocaine addiction
- Amphetamine addiction
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Salmonella infection
- Pertussis
- Yersinia infection
- Leishmaniasis
- Chagas disease
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Colorectal cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Breast cancer
- Choline metabolism in cancer
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis