Peroxiredoxin-2
Lua error: data must be either of type string or number.
Summary
Protein Function
Involved in redox regulation of the cell. Reduces peroxides with reducing equivalents provided through the thioredoxin system. It is not able to receive electrons from glutaredoxin. May play an important role in eliminating peroxides generated during metabolism. Might participate in the signaling cascades of growth factors and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by regulating the intracellular concentrations of H2O2. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
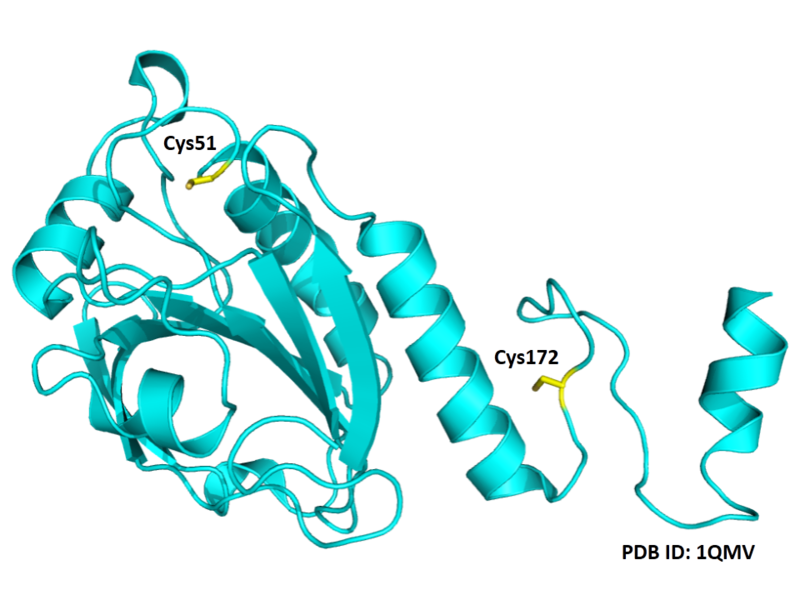
Cys51 is the active site of Peroxiredoxin-2. This redox-active residue is conserved in AhpC/TSA family. It considered as a peroxidatic cysteine (C(P)), which makes the nucleophilic attack on the peroxide substrate. The peroxide oxidizes the C(P)-SH to cysteine sulfenic acid (C(P)-SOH), which then reacts with another cysteine residue, the resolving cysteine (C(R)), to form a disulfide bridge. The disulfide is subsequently reduced by an appropriate electron donor to complete the catalytic cycle. In this typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxin, C(R) is provided by the other dimeric subunit to form an intersubunit disulfide. The disulfide is subsequently reduced by thioredoxin.
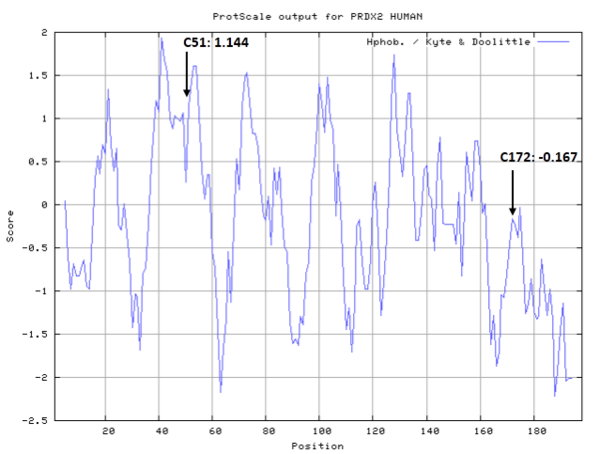
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys51: Unknown
- Cys172: 32.083 A^2
Protein Sequence
MASGNARIGK PAPDFKATAV VDGAFKEVKL SDYKGKYVVL FFYPLDFTFV
CPTEIIAFSN RAEDFRKLGC EVLGVSVDSQ FTHLAWINTP RKEGGLGPLN
IPLLADVTRR LSEDYGVLKT DEGIAYRGLF IIDGKGVLRQ ITVNDLPVGR
SVDEALRLVQ AFQYTDEHGE VCPAGWKPGS DTIKPNVDDS KEYFSKHN
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Homologous Analysis of Sequence, Enzymatic Assay
Reference
- Nguyen J B, Pool C D, Wong C Y B, et al. Peroxiredoxin-1 from the human hookworm Ancylostoma ceylanicum forms a stable oxidized decamer and is covalently inhibited by conoidin A[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2013, 20(8): 991-1001. 23891152