Cellular tumor antigen p53
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | P53 |
| UNP ID | P04637 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys277 |
| Family/Domain |
P53 DNA-binding domain, P53 family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transcription factor |
Summary
Protein Function
Acts as a tumor suppressor in many tumor types; induces growth arrest or apoptosis depending on the physiological circumstances and cell type. Involved in cell cycle regulation as a trans-activator that acts to negatively regulate cell division by controlling a set of genes required for this process. One of the activated genes is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Apoptosis induction seems to be mediated either by stimulation of BAX and FAS antigen expression, or by repression of Bcl-2 expression. In cooperation with mitochondrial PPIF is involved in activating oxidative stress-induced necrosis; the function is largely independent of transcription. Induces the transcription of long intergenic non-coding RNA p21 (lincRNA-p21) and lincRNA-Mkln1. LincRNA-p21 participates in TP53-dependent transcriptional repression leading to apoptosis and seems to have an effect on cell-cycle regulation. Implicated in Notch signaling cross-over. Prevents CDK7 kinase activity when associated to CAK complex in response to DNA damage, thus stopping cell cycle progression. Isoform 2 enhances the transactivation activity of isoform 1 from some but not all TP53-inducible promoters. Isoform 4 suppresses transactivation activity and impairs growth suppression mediated by isoform 1. Isoform 7 inhibits isoform 1-mediated apoptosis. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1-mediated transcriptional activation of PER2. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
The DNA-binding domain of human p53 contains 10 cysteine residues. These cysteine thiol groups appear to be critical for binding of p53 to DNA. (PMID: 20208557)
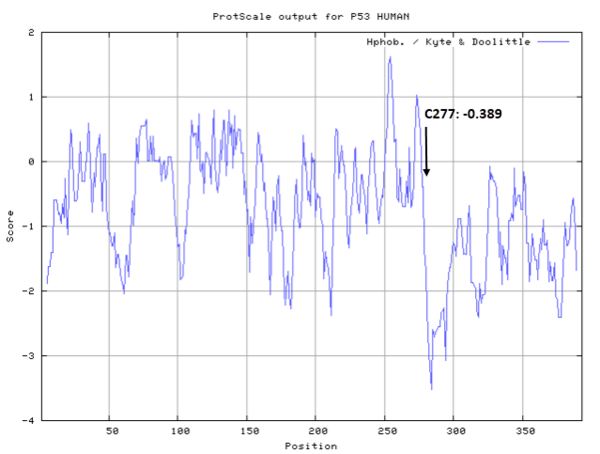
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys277: 22.376 A^2
Protein Sequence
MEEPQSDPSV EPPLSQETFS DLWKLLPENN VLSPLPSQAM DDLMLSPDDI
EQWFTEDPGP DEAPRMPEAA PPVAPAPAAP TPAAPAPAPS WPLSSSVPSQ
KTYQGSYGFR LGFLHSGTAK SVTCTYSPAL NKMFCQLAKT CPVQLWVDST
PPPGTRVRAM AIYKQSQHMT EVVRRCPHHE RCSDSDGLAP PQHLIRVEGN
LRVEYLDDRN TFRHSVVVPY EPPEVGSDCT TIHYNYMCNS SCMGGMNRRP
ILTIITLEDS SGNLLGRNSF EVRVCACPGR DRRTEEENLR KKGEPHHELP
PGSTKRALPN NTSSSPQPKK KPLDGEYFTL QIRGRERFEM FRELNEALEL
KDAQAGKEPG GSRAHSSHLK SKKGQSTSRH KKLMFKTEGP DSD
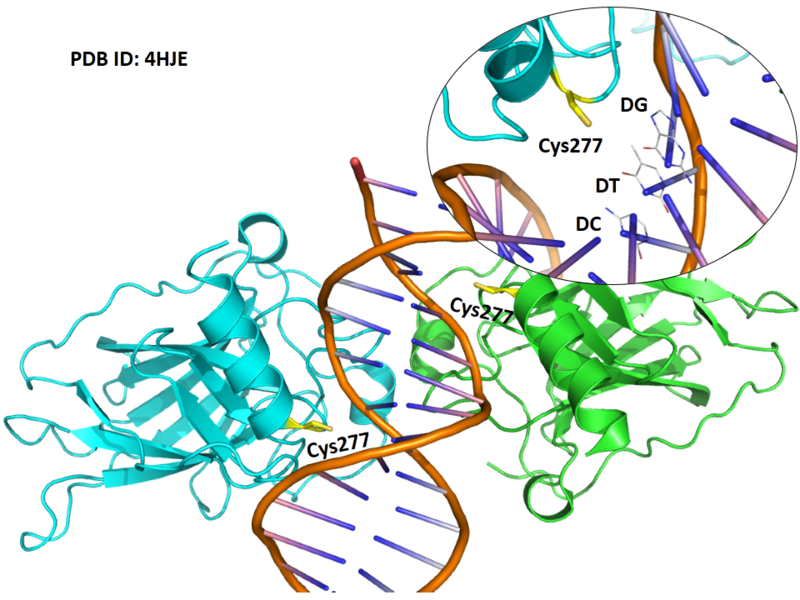
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Endocrine resistance
- Platinum drug resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- Cell cycle
- p53 signaling pathway
- Mitophagy - animal
- PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Longevity regulating pathway
- Ferroptosis
- Cellular senescence
- Wnt signaling pathway
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- MicroRNAs in cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Glioma
- Prostate cancer
- Thyroid cancer
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Bladder cancer
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Small cell lung cancer
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Breast cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Gastric cancer
- Central carbon metabolism in cancer
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
Experimental Evidence
- Western Blot, Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Kim D H, Kim E H, Na H K, et al. 15-Deoxy-Δ12, 14-prostaglandin J2 stabilizes, but functionally inactivates p53 by binding to the cysteine 277 residue[J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(17): 2560. 20208557
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Transcription factor
- P53 family
- Endocrine resistance
- Platinum drug resistance
- MAPK signaling pathway
- Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- Cell cycle
- P53 signaling pathway
- Mitophagy - animal
- PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Longevity regulating pathway
- Ferroptosis
- Cellular senescence
- Wnt signaling pathway
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Huntington disease
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- MicroRNAs in cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Glioma
- Prostate cancer
- Thyroid cancer
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Bladder cancer
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Small cell lung cancer
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Breast cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Gastric cancer
- Central carbon metabolism in cancer
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis