Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit (Homo sapiens)
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | PP-1A, PPP1A, PPP1CA |
| UNP ID | P62136 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys273 |
| Family/Domain |
PPP phosphatase family, PP-1 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Phosphatase |
Summary
Protein Function
Protein phosphatase that associates with over 200 regulatory proteins to form highly specific holoenzymes which dephosphorylate hundreds of biological targets.
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is essential for cell division, and participates in the regulation of glycogen metabolism, muscle contractility and protein synthesis. Involved in regulation of ionic conductances and long-term synaptic plasticity. May play an important role in dephosphorylating substrates such as the postsynaptic density-associated Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II. Component of the PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex, which plays a role in the control of chromatin structure and cell cycle progression during the transition from mitosis into interphase. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
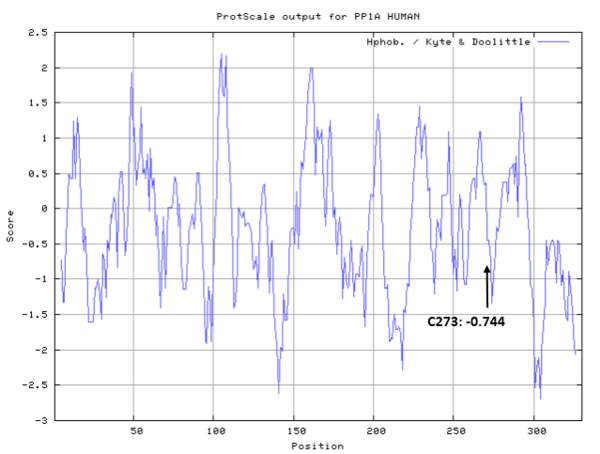
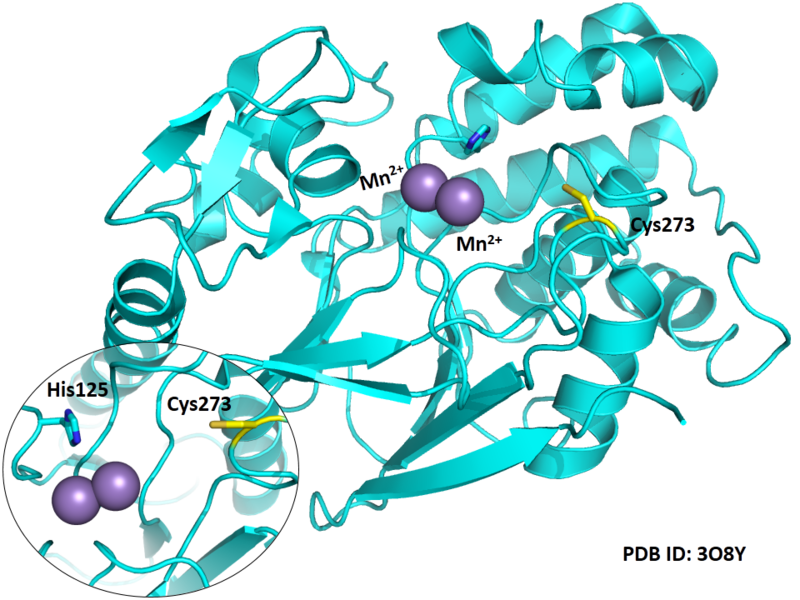
Cys273 is close to the active site and the manganese ions in space.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys273: 31.279 A^2
Protein Sequence
MSDSEKLNLD SIIGRLLEVQ GSRPGKNVQL TENEIRGLCL KSREIFLSQP
ILLELEAPLK ICGDIHGQYY DLLRLFEYGG FPPESNYLFL GDYVDRGKQS
LETICLLLAY KIKYPENFFL LRGNHECASI NRIYGFYDEC KRRYNIKLWK
TFTDCFNCLP IAAIVDEKIF CCHGGLSPDL QSMEQIRRIM RPTDVPDQGL
LCDLLWSDPD KDVQGWGEND RGVSFTFGAE VVAKFLHKHD LDLICRAHQV
VEDGYEFFAK RQLVTLFSAP NYCGEFDNAG AMMSVDETLM CSFQILKPAD
KNKGKYGQFS GLNPGGRPIT PPRNSAKAKK
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- mRNA surveillance pathway
- cGMP-PKG signaling pathway
- cAMP signaling pathway
- Oocyte meiosis
- Cellular senescence
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- Vascular smooth muscle contraction
- Hippo signaling pathway
- Focal adhesion
- Platelet activation
- Long-term potentiation
- Dopaminergic synapse
- Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels
- Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
- Insulin signaling pathway
- Oxytocin signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance
- Amphetamine addiction
- Alcoholism
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Proteoglycans in cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, Isotope Labeling
Reference
- Pereira S R, Vasconcelos V M, Antunes A. Computational study of the covalent bonding of microcystins to cysteine residues–a reaction involved in the inhibition of the PPP family of protein phosphatases[J]. The FEBS journal, 2013, 280(2): 674-680. 22177231
- MacKintosh R W, Dalby K N, Campbell D G, et al. The cyanobacterial toxin microcystin binds covalently to cysteine-273 on protein phosphatase 1[J]. Febs Letters, 1995, 371(3): 236-240. 7556599
- Hastie C J, Borthwick E B, Morrison L F, et al. Inhibition of several protein phosphatases by a non-covalently interacting microcystin and a novel cyanobacterial peptide, nostocyclin[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2005, 1726(2): 187-193. 16046071
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Phosphatase
- Lipoxygenase family
- MRNA surveillance pathway
- CGMP-PKG signaling pathway
- CAMP signaling pathway
- Oocyte meiosis
- Cellular senescence
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- Vascular smooth muscle contraction
- Hippo signaling pathway
- Focal adhesion
- Platelet activation
- Long-term potentiation
- Dopaminergic synapse
- Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels
- Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
- Insulin signaling pathway
- Oxytocin signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance
- Amphetamine addiction
- Alcoholism
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Proteoglycans in cancer