Cofilin-1
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Cofilin-1, p18 |
| UNP ID | P23528 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
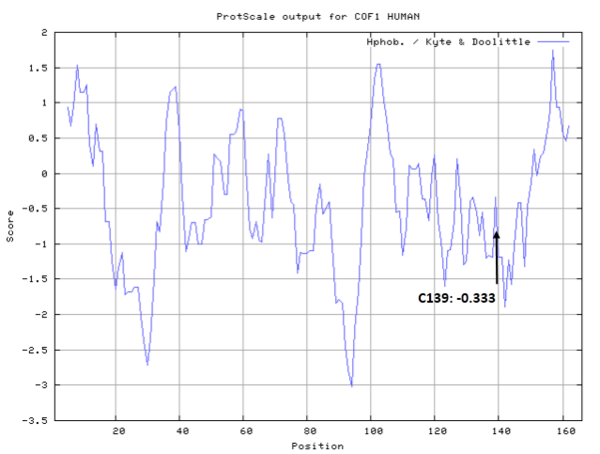
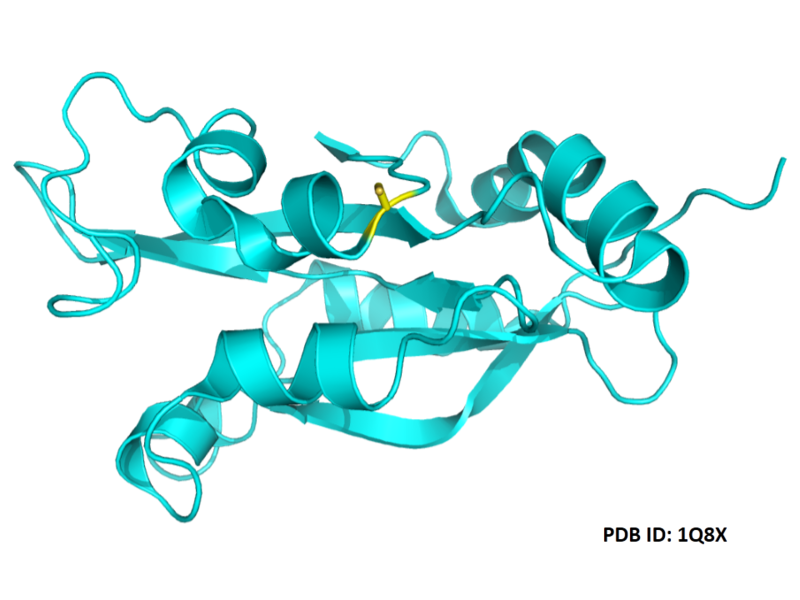
| Cys Site | Cys139 |
| Family/Domain |
Cofilin/tropomyosin-type actin-binding protein, Actin-binding proteins ADF family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Structural protein |
Summary
Protein Function
Cofilin is a widely distributed intracellular actin-modulating protein that binds and depolymerizes filamentous F-actin and inhibits the polymerization of monomeric G-actin in a pH-dependent manner. It is involved in the translocation of actin-cofilin complex from cytoplasm to nucleus.
One group reports that reelin signaling leads to serine3-phosphorylation of cofilin-1, and this interaction may play a role in the reelin-related regulation of neuronal migration.
Cys Function & Property
Both Cys234 and Cys179 are located within the first catalytic cysteine domain (FCCH) of E1, a subdomain conserved in human E1 that spans from residues 175–265 and forms one wall of a broad deep groove unique to eukaryotic E1. The rat Cys234 location is identical to that reported for human E1 in vitro whereas the modified Cys179 on rat E1 represents an additional modification.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys139: 36.275 A^2
Protein Sequence
MASGVAVSDG VIKVFNDMKV RKSSTPEEVK KRKKAVLFCL SEDKKNIILE
EGKEILVGDV GQTVDDPYAT FVKMLPDKDC RYALYDATYE TKESKKEDLV
FIFWAPESAP LKSKMIYASS KDAIKKKLTG IKHELQANCY EEVKDRCTLA
EKLGGSAVIS LEGKPL
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Axon guidance
- Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis
- Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
- Pertussis
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
Experimental Evidence
- Mass Spectrometry, Tryptic Digest
Reference
- Gabrielsen M, Schuldt M, Munro J, et al. Cucurbitacin covalent bonding to cysteine thiols: the filamentous-actin severing protein Cofilin1 as an exemplary target[J]. Cell Communication and Signaling, 2013, 11(1): 58. 23945128