Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Rattus norvegicus)
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Keap1, INrf2 |
| UNP ID | P57790 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
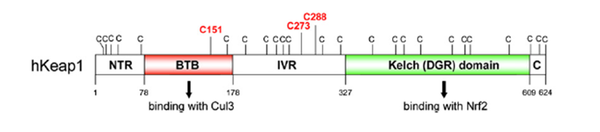
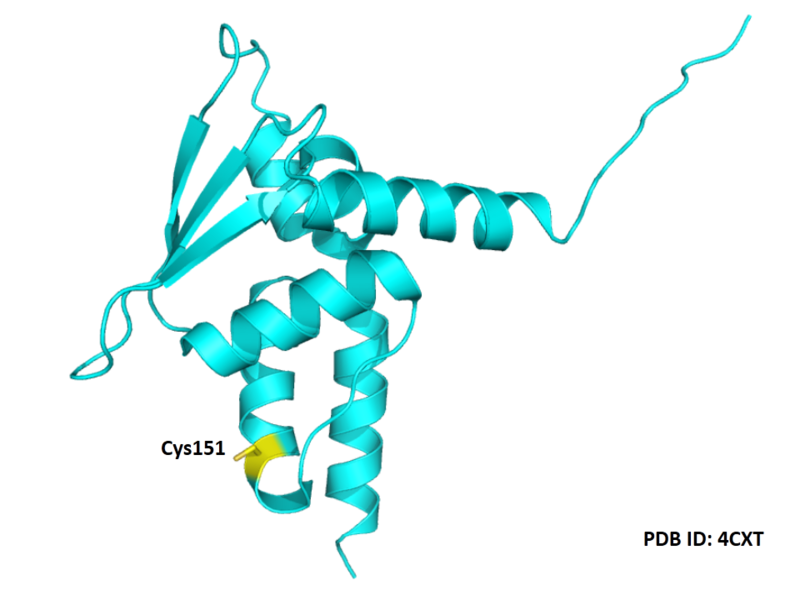
| Cys Site | Cys151 |
| Family/Domain |
BTB/POZ domain, Kelch motif |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Redox protein |
Summary
Protein Function
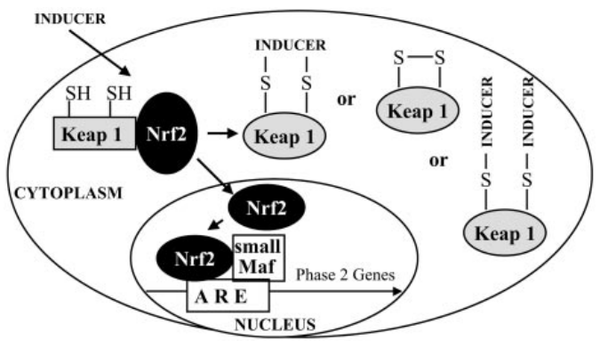
Keap1 (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1) is a multi-domain protein which plays a key role in the regulation of Nrf2, a transcription factor that mediates the expression of a large array of cytoprotective enzymes in response to electrophilic and oxidative assault. It acts in concert with members of the CRL3 class of Cullin-RING-Ligase E3 ligases to provide substrate-specific recruitment for ubiquitination, and consists of a three domain architecture composed of an N-terminal BTB (Broad complex, Tramtrack, and Bric-a-Brac) domain, an intervening region (IVR) or BACK domain, and a C-terminal Kelch repeat domain. (PMID: 24896564)
Acts as a substrate adapter protein for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex formed by CUL3 and RBX1 and targets NFE2L2/NRF2 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome, thus resulting in the suppression of its tran-scriptional activity and the repression of antioxidant response element-mediated detoxifying enzyme gene expression. Retains NFE2L2/NRF2 and may also retain BPTF in the cytosol. Targets PGAM5 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
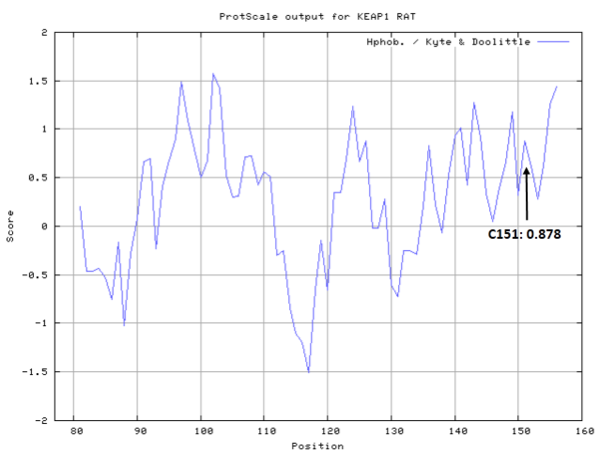
There are 25 cystien residues in Keap1, and could form multiple disulfide bonds or free thiol groups under different situations (see below).
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys151: Unknown
Protein Sequence
MQPEPKPSGA PRSSQFLPLW SKCPEGAGDA VMYASTECKA EVTPSQDGNR
TFSYTLEDHT KQAFGIMNEL RLSQQLCDVT LQVKYEDIPA AQFMAHKVVL
ASSSPVFKAM FTNGLREQGM EVVSIEGIHP KVMERLIEFA YTASISVGEK
CVLHVMNGAV MYQIDSVVRA CSDFLVQQLD PSNAIGIANF AEQIGCTELH
QRAREYIYMH FGEVAKQEEF FNLSHCQLAT LISRDDLNVR CESEVFHACI
DWVKYDCPQR RFYVQALLRA VRCHALTPRF LQTQLQKCEI LQADARCKDY
LVQIFQELTL HKPTQAVPCR APKVGRLIYT AGGYFRQSLS YLEAYNPSNG
SWLRLADLQV PRSGLAGCVV GGLLYAVGGR NNSPDGNTDS SALDCYNPMT
NQWSPCASLS VPRNRSGGGV IDGHIYAVGG SHGCIHHSSV ERYEPDRDEW
HLVAPMLTRR IGVGVAVLNR LLYAVGGFDG TNRLNSAECY YPERNEWRMI
TPMNTIRSGA GVCVLHSCIY AAGGYDGQDQ LNSVERYDVE TETWTFVASM
KHRRSALGIA VHQGRIYVLG GYDGHTFLDS VECYDPDTDT WSEVTRLTSG
RSGVGVAVTM EPCRKQIDQQ NCTC
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis
- Pathways in cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
Experimental Evidence
- Isotope Labeling, UV Spectroscopic
Reference
- Dinkova-Kostova A T, Holtzclaw W D, Cole R N, et al. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2002, 99(18): 11908-11913. 12193649
- Cleasby A, Yon J, Day P J, et al. Structure of the BTB domain of Keap1 and its interaction with the triterpenoid antagonist CDDO[J]. PloS one, 2014, 9(6): e98896. 24896564