Caspase-1
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CASP-1 |
| UNP ID | P29466 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
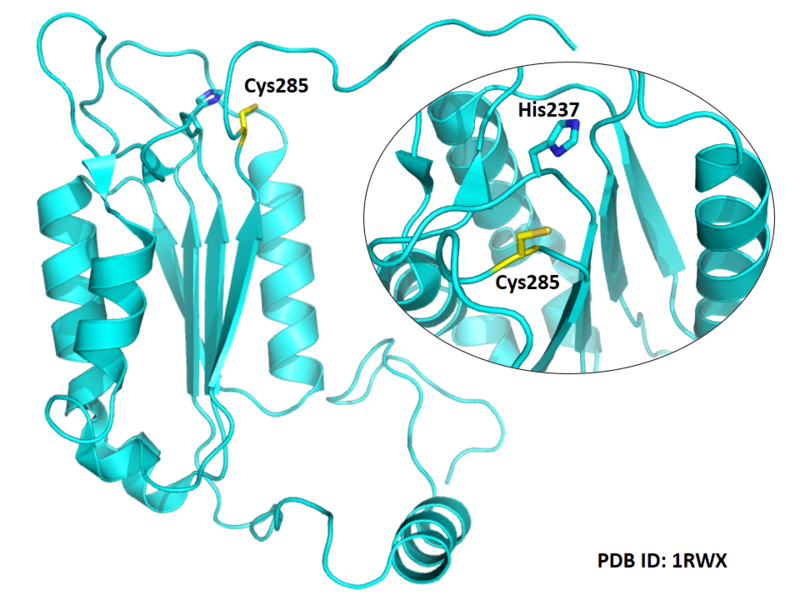
| Cys Site | Cys285 |
| Family/Domain |
Caspase recruitment domain, Peptidase C14A family] |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Caspase-1 (also known as interleukin 1β-converting enzyme or ICE) is expressed as a procaspase-1 zymogen that is processed into a catalytically competent form through autoproteolysis induced by protein oligomerization in vitro, but may require caspase-5 for efficient activation in vivo. It cleaves IL-1β between an Asp and an Ala, releasing the mature cytokine which is involved in a variety of inflammatory processes. Caspase-1 is important for defense against pathogens. It could cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). It also can promote apoptosis. (From Uniprot, PMID: 16511067)
Cys Function & Property
Cys285 is one of the active sites of CASP-1.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys285: 11.718 A^2
Protein Sequence
MADKVLKEKR KLFIRSMGEG TINGLLDELL QTRVLNKEEM EKVKRENATV
MDKTRALIDS VIPKGAQACQ ICITYICEED SYLAGTLGLS ADQTSGNYLN
MQDSQGVLSS FPAPQAVQDN PAMPTSSGSE GNVKLCSLEE AQRIWKQKSA
EIYPIMDKSS RTRLALIICN EEFDSIPRRT GAEVDITGMT MLLQNLGYSV
DVKKNLTASD MTTELEAFAH RPEHKTSDST FLVFMSHGIR EGICGKKHSE
QVPDILQLNA IFNMLNTKNC PSLKDKPKVI IIQACRGDSP GVVWFKDSVG
VSGNLSLPTT EEFEDDAIKK AHIEKDFIAF CSSTPDNVSW RHPTMGSVFI
GRLIEHMQEY ACSCDVEEIF RKVRFSFEQP DGRAQMPTTE RVTLTRCFYL
FPGH
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
1ICE, 3NS7, 1BMQ, 1RWK, 1RWM, 1RWN,
1RWO, 1RWP, 1RWV, 1RWW, 1RWX, 2H4W,
2H4Y, 2H51, 2H54, 2HBQ, 2HBR, 2HBY,
2HBZ
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Necroptosis
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Salmonella infection
- Pertussis
- Legionellosis
- Yersinia infection
- Influenza A
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Lee J, Bogyo M. Synthesis and evaluation of aza-peptidyl inhibitors of the lysosomal asparaginyl endopeptidase, legumain[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2012, 22(3): 1340-1343. 22243962
- Dall E, Brandstetter H. Mechanistic and structural studies on legumain explain its zymogenicity, distinct activation pathways, and regulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(27): 10940-10945. 23776206