Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | MALT1, Paracaspase |
| UNP ID | Q9UDY8 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys464 |
| Family/Domain |
Caspase domain, Peptidase C14B family] |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
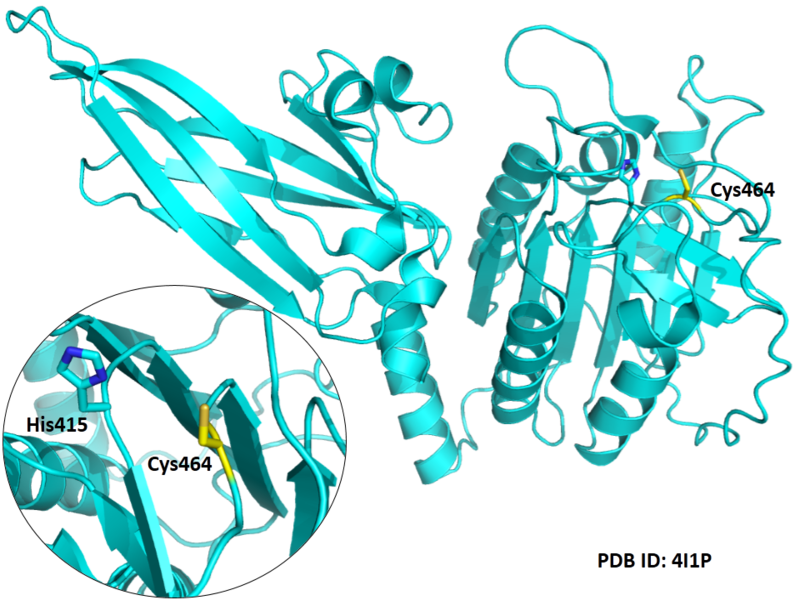
MALT1 paracaspase is part of the CARMA1-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM)-complex that connects proximal antigen receptor signaling to the IkB kinase complex to induce the canonical NF-kB pathway. The central paracaspase domain of MALT1 forms an active site with a catalytic dyad of cysteine 464 and histidine 415 that is structurally highly homologous to classical caspases. In contrast to most caspases, MALT1 does not require an autoproteolytic cleavage reaction for activation and displays a high preference for arginine in the position 1 (P1). Therefore, cleavage activity resembles metacaspases that are exclusively found in protozoa, fungi, and plants, and thus MALT1 confers a unique proteolytic activity in mammals.
MALT1 binds to TRAF6, inducing TRAF6 oligomerization and activation of its ligase activity. It has ubiquitin ligase activity. MALT1-dependent BCL10 cleavage plays an important role in T-cell antigen receptor-induced integrin adhesion. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
Cys464 is one of the active sites of MALT1.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
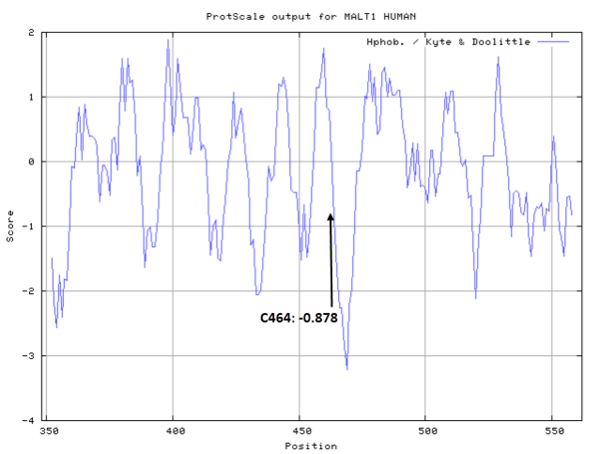
- Cys464: 11.124 A^2
Protein Sequence
MSLLGDPLQA LPPSAAPTGP LLAPPAGATL NRLREPLLRR LSELLDQAPE
GRGWRRLAEL AGSRGRLRLS CLDLEQCSLK VLEPEGSPSL CLLKLMGEKG
CTVTELSDFL QAMEHTEVLQ LLSPPGIKIT VNPESKAVLA GQFVKLCCRA
TGHPFVQYQW FKMNKEIPNG NTSELIFNAV HVKDAGFYVC RVNNNFTFEF
SQWSQLDVCD IPESFQRSVD GVSESKLQIC VEPTSQKLMP GSTLVLQCVA
VGSPIPHYQW FKNELPLTHE TKKLYMVPYV DLEHQGTYWC HVYNDRDSQD
SKKVEIIIGR TDEAVECTED ELNNLGHPDN KEQTTDQPLA KDKVALLIGN
MNYREHPKLK APLVDVYELT NLLRQLDFKV VSLLDLTEYE MRNAVDEFLL
LLDKGVYGLL YYAGHGYENF GNSFMVPVDA PNPYRSENCL CVQNILKLMQ
EKETGLNVFL LDMCRKRNDY DDTIPILDAL KVTANIVFGY ATCQGAEAFE
IQHSGLANGI FMKFLKDRLL EDKKITVLLD EVAEDMGKCH LTKGKQALEI
RSSLSEKRAL TDPIQGTEYS AESLVRNLQW AKAHELPESM CLKFDCGVQI
QLGFAAEFSN VMIIYTSIVY KPPEIIMCDA YVTDFPLDLD IDPKDANKGT
PEETGSYLVS KDLPKHCLYT RLSSLQKLKE HLVFTVCLSY QYSGLEDTVE
DKQEVNVGKP LIAKLDMHRG LGRKTCFQTC LMSNGPYQSS AATSGGAGHY
HSLQDPFHGV YHSHPGNPSN VTPADSCHCS RTPDAFISSF AHHASCHFSR
SNVPVETTDE IPFSFSDRLR ISEK
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- NF-kappa B signaling pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- Tuberculosis
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Jong W Y, Jeffrey P D, Ha J Y, et al. Crystal structure of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation 1 (MALT1) paracaspase region[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2011, 108(52): 21004-21009. 22158899
- Eitelhuber A C, Vosyka O, Nagel D, et al. Activity-based probes for detection of active MALT1 paracaspase in immune cells and lymphomas[J]. Chemistry & biology, 2015, 22(1): 129-138. 25556945