Peroxiredoxin-4
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | PRDX4 |
| UNP ID | Q13162 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
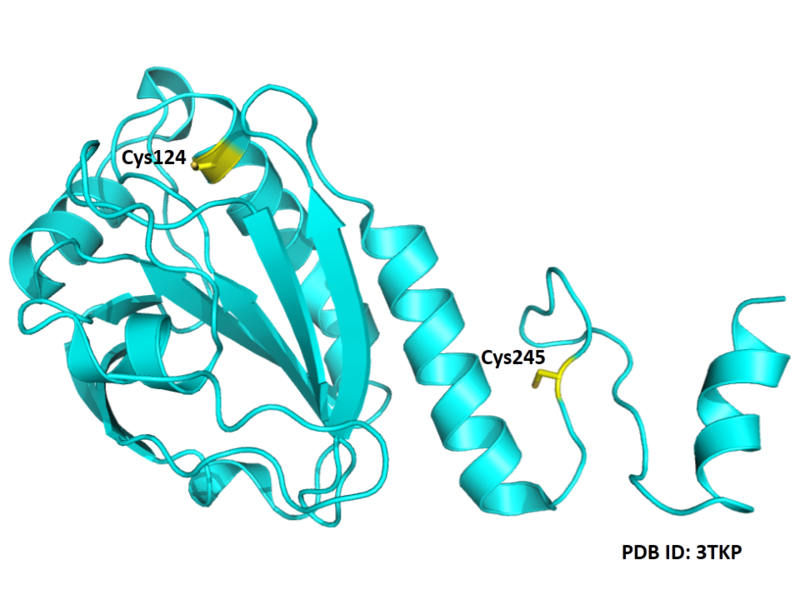
| Cys Site | Cys124, Cys245 |
| Family/Domain |
AhpC/TSA family, Peroxiredoxin family, AhpC/Prx1 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Redox protein |
Summary
Protein Function
Peroxiredoxin-4 belongs to the peroxiredoxin family. The protein is localized to the cytoplasm. Peroxidases of the peroxiredoxin family reduce hydrogen peroxide and alkyl hydroperoxides to water and alcohol with the use of reducing equivalents derived from thiol-containing donor molecules. This protein has been found to play a regulatory role in the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. (From Wikipedia)
Peroxiredoxins provide antioxidant protection and act as signaling molecules and chaperones. Peroxiredoxins are widely conserved across eukaryotes. The active site of the "typical" class of peroxiredoxins is formed at the intersubunit interface of homodimers, which can assemble into rings of ten or twelve subunits. A catalytic peroxidatic cysteine residue reduces peroxide and other ROS, resulting in hyperoxidation to sulfenic (-SOH), sulfinic (-SO2H), or sulfonic acid (-SO3H) forms of the cysteine. The sulfenic acid form reacts with a second so-called resolving catalytic cysteine residue across the dimer interface to form an intermolecular disulfide bond. Oxidation to sulfinic acid can be repaired by sulfiredoxin, while the sulfonic acid form is considered irreversible. (PMID: 23891152)
Cys Function & Property
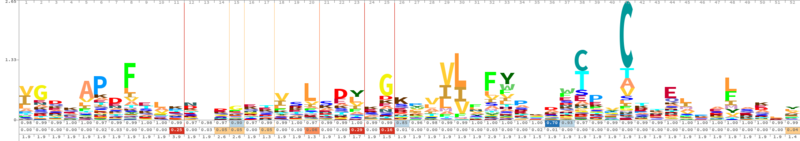
Cys124 is the active site of Peroxiredoxin-4. This redox-active residue is conserved in AhpC/TSA family. It considered as a peroxidatic cysteine (C(P)), which makes the nucleophilic attack on the peroxide substrate.
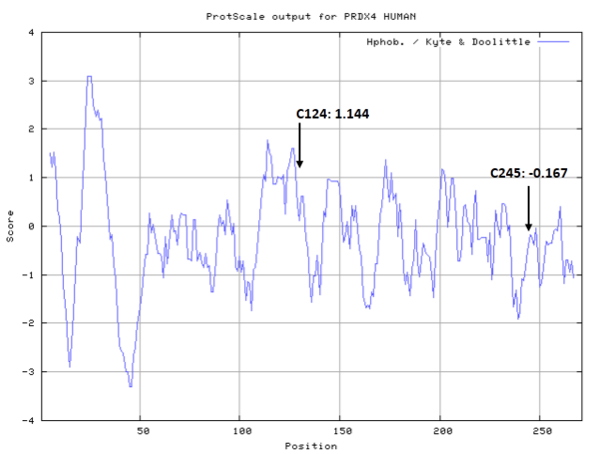
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys124: 29.867
- Cys245: 26.577
Protein Sequence
MEALPLLAAT TPDHGRHRRL LLLPLLLFLL PAGAVQGWET EERPRTREEE
CHFYAGGQVY PGEASRVSVA DHSLHLSKAK ISKPAPYWEG TAVIDGEFKE
LKLTDYRGKY LVFFFYPLDF TFVCPTEIIA FGDRLEEFRS INTEVVACSV
DSQFTHLAWI NTPRRQGGLG PIRIPLLSDL THQISKDYGV YLEDSGHTLR
GLFIIDDKGI LRQITLNDLP VGRSVDETLR LVQAFQYTDK HGEVCPAGWK
PGSETIIPDP AGKLKYFDKL N
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Homologous Analysis of Sequence, Enzymatic Assay
Reference
- Nguyen J B, Pool C D, Wong C Y B, et al. Peroxiredoxin-1 from the human hookworm Ancylostoma ceylanicum forms a stable oxidized decamer and is covalently inhibited by conoidin A[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2013, 20(8): 991-1001. 23891152