Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | AR, AKR1B1 |
| UNP ID | P15121 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
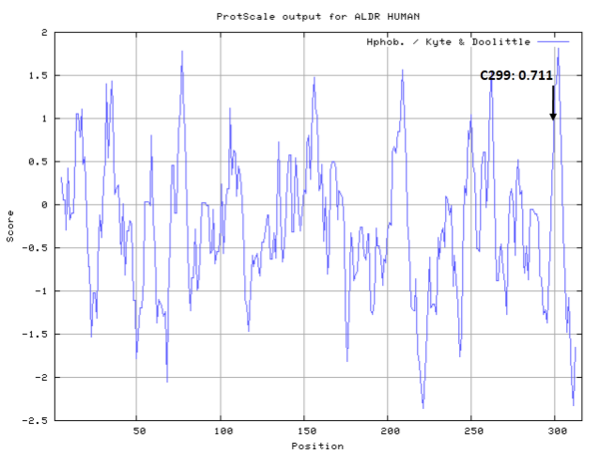
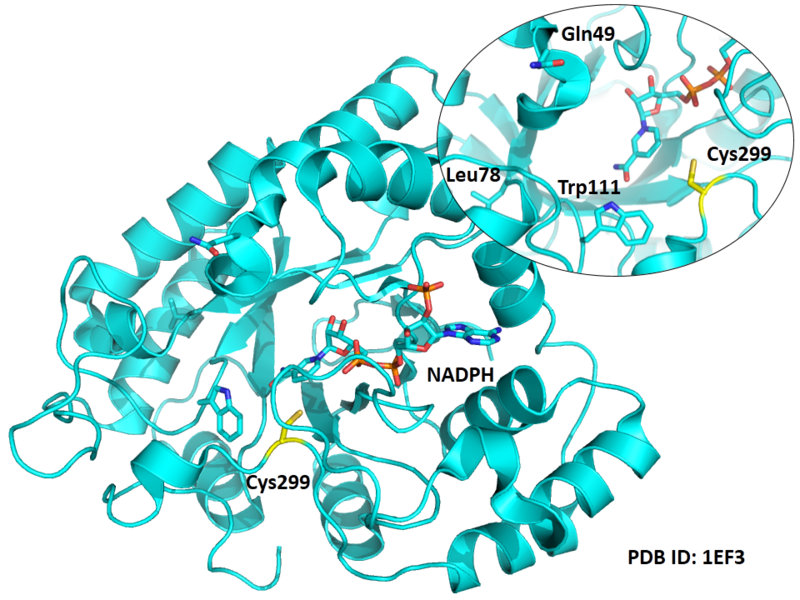
| Cys Site | Cys299 |
| Family/Domain | Aldo/keto reductase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Aldose reductase is a member of the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily (AKR1B1). It catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a broad spectrum of substrates that range from simple aromatic aldehydes and steroid carbonyls to aldo-keto sugars. The wide substrate specificity of AR suggests that the enzyme may be involved in detoxification of endogenous and xenobiotic aldehydes. (PMID: 18223294)
Cys Function & Property
Cys299 is close to the active sites of AKR1B1 in space, include Trp111, Gln49.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys299: 10.044 A^2
Protein Sequence
MASRLLLNNG AKMPILGLGT WKSPPGQVTE AVKVAIDVGY RHIDCAHVYQ
NENEVGVAIQ EKLREQVVKR EELFIVSKLW CTYHEKGLVK GACQKTLSDL
KLDYLDLYLI HWPTGFKPGK EFFPLDESGN VVPSDTNILD TWAAMEELVD
EGLVKAIGIS NFNHLQVEMI LNKPGLKYKP AVNQIECHPY LTQEKLIQYC
QSKGIVVTAY SPLGSPDRPW AKPEDPSLLE DPRIKAIAAK HNKTTAQVLI
RFPMQRNLVV IPKSVTPERI AENFKVFDFE LSSQDMTTLL SYNRNWRVCA
LLSCTSHKDY PFHEEF
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Pentose and glucuronate interconversions
- Fructose and mannose metabolism
- Galactose metabolism
- Glycerolipid metabolism
- Folate biosynthesis
- Metabolic pathways
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Kaiserova K, Tang X L, Srivastava S, et al. Role of nitric oxide in regulating aldose reductase activation in the ischemic heart[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(14): 9101-9112. 18223294