Potassium-transporting ATPase alpha chain 1 (Rattus norvegicus)
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | ATP4A |
| UNP ID | P09626 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
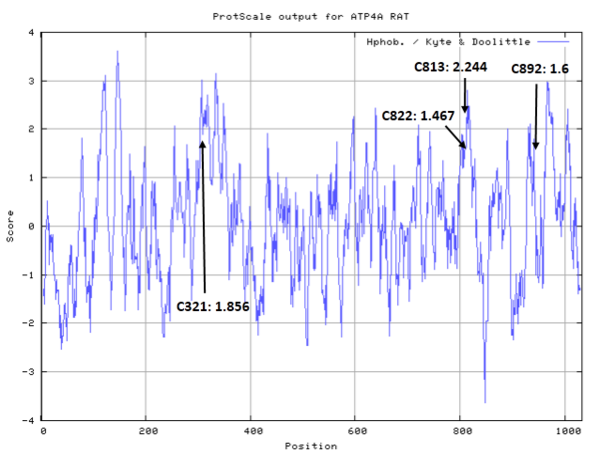
| Cys Site | Cys321, Cys813, Cys822, Cys892 |
| Family/Domain |
Cation transporting ATPase, C-terminus, Cation transport ATPase (P-type) family, Type IIC subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Ion channel |
Summary
Protein Function
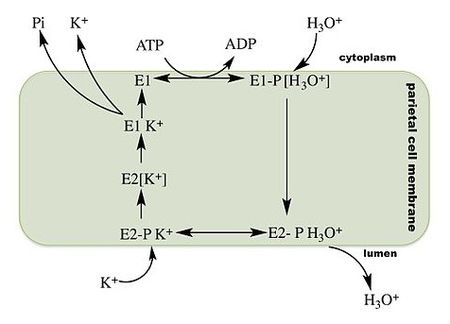
The gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase or H+/K+ ATPase is the proton pump of the stomach. It exchanges potassium from the intestinal lumen with cytoplasmic hydronium and is the enzyme primarily responsible for the acidification of the stomach contents and the activation of the digestive enzyme pepsin.
H+/K+ ATPase is a P2-type ATPase, a member of the eukaryotic class of P-type ATPases. Like the Ca2+ and the Na+/K+ ATPases, the H+/K+ ATPase functions as an α, β protomer. Unlike other eukaryotic ATPases, the H+/K+ ATPase is electroneutral, transporting one proton into the stomach lumen per potassium retrieved from the gastric lumen. As an ion pump the H+/K+ ATPase is able to transport ions against a concentration gradient using energy derived from the hydrolysis of ATP. Like all P-type ATPases, a phosphate group is transferred from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to the H+/K+ ATPase during the transport cycle. This phosphate transfer powers a conformational change in the enzyme that helps drive ion transport. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MGKENYELYS VELGTGPGGD MAAKMSKKKA GGGGGKKKEK LENMKKEMEM
NDHQLSVSEL EQKYQTSATK GLKASLAAEL LLRDGPNALR PPRGTPEYVK
FARQLAGGLQ CLMWVAAAIC LIAFAIQASE GDLTTDDNLY LALALIAVVV
VTGCFGYYQE FKSTNIIASF KNLVPQQATV IRDGDKFQIN ADQLVVGDLV
EMKGGDRVPA DIRILSAQGC KVDNSSLTGE SEPQTRSPEC THESPLETRN
IAFFSTMCLE GTAQGLVVST GDRTIIGRIA SLASGVENEK TPIAIEIEHF
VDIIAGLAIL FGATFFVVAM CCIGYTFLRAM VFFMAIVVAY VPEGLLATVT
VCLSLTAKRL ASKNCVVKNL EAVETLGSTS VICSDKTGTL TQNRMTVSHL
WFDNHIHTAD TTEDQSGQTF DQSSETWRAL CRVLTLCNRA AFKSGQDAVP
VPKRIVIGDA SETALLKFSE LTLGNAMGYR DRFPKVCEIP FNSTNKFQLS
IHTLEDPRDP RHLLVMKGAP ERVLERCSSI LIKGQELPLD EQWREAFQTA
YLSLGGLGER VLGFCQLYLN EKDYPPGYTF DVEAMNFPSS GLCFAGLVSM
IDPPRATVPD AVLKCRTAGI RVIMVTGDHP ITAKAIAASV GIISEGSETV
EDIAARLRMP VDQVNKKDAR ACVINGMQLK DMDPSELVEA LRTHPEMVFA
RTSPQQKLVI VESCQRLGAI VAVTGDGVND SPALKKADIG VAMGIAGSDA
AKNAADMILL DDNFASIVTG VEQGRLIFDN LKKSIAYTLT KNIPELTPYL
IYITVSVPLP LGCITILFIE LCTDIFPSVS LAYEKAESDI MHLRPRNPRR
DRLVNEPLAA YSYFQIGAIQ SFAGFADYFT AMAQEGWFPL LCVGLRPQWE
DHHLQDLQDS YGQEWTFGQR LYQQYTCYTV FFISIEMCQI ADVLIRKTRR
LSAFQQGFFR NRILVIAIVF QVCIGCFLCY CPGMPNIFNF MPIRFQWWLV
PMPFGLLIFV YDEIRKLGVR CCPGSWWDQE LYY
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Tryptic Digest, Isotope Labeling, Tricine-SDS-PAGE, Protein Electrophoresis
Reference
- Sachs G, Shin J M, Besancon M, et al. The continuing development of gastric acid pump inhibitors[J]. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 1993, 7: 4-12. 8387826
- Fujisaki H, Shibata H, Oketani K, et al. Effects of the proton pump inhibitor, E3810, on gastric secretion and gastric and duodenal ulcers or erosions in rats[J]. Drug Investigation, 1991, 3(5): 328-332. DOI: 10.1007/BF03259747.