Potassium-transporting ATPase alpha chain 1 (Canis familiaris)
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | ATP4A |
| UNP ID | P50996 |
| Organism | Canis familiaris |
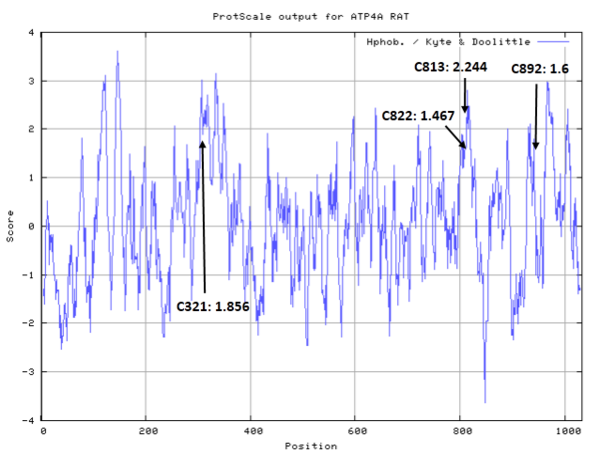
| Cys Site | Cys814, Cys823 |
| Family/Domain |
Cation transporting ATPase, C-terminus, Cation transport ATPase (P-type) family, Type IIC subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Ion channel |
Summary
Protein Function
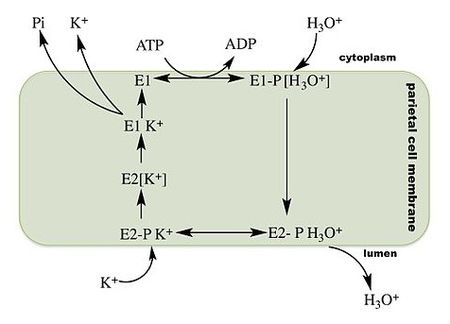
The gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase or H+/K+ ATPase is the proton pump of the stomach. It exchanges potassium from the intestinal lumen with cytoplasmic hydronium and is the enzyme primarily responsible for the acidification of the stomach contents and the activation of the digestive enzyme pepsin.
H+/K+ ATPase is a P2-type ATPase, a member of the eukaryotic class of P-type ATPases. Like the Ca2+ and the Na+/K+ ATPases, the H+/K+ ATPase functions as an α, β protomer. Unlike other eukaryotic ATPases, the H+/K+ ATPase is electroneutral, transporting one proton into the stomach lumen per potassium retrieved from the gastric lumen. As an ion pump the H+/K+ ATPase is able to transport ions against a concentration gradient using energy derived from the hydrolysis of ATP. Like all P-type ATPases, a phosphate group is transferred from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to the H+/K+ ATPase during the transport cycle. This phosphate transfer powers a conformational change in the enzyme that helps drive ion transport. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MGKAENYEMY SVELGPGPGG DMAAKMSKKK AGKGGGKKKE KLENMKKEME
INDHQLSVAE LEQKYQTSAT KGLSASLAAD LLLRDGPNAL RPPRGTPEYV
KFARQLAGGL QCLMWVAAAI CLIAFAIQAS EGDLTTDDNL YLALALIAVV
VVTGCFGYYQ EFKSTNIIAS FKNLVPQQAT VIRDGDKFQI NADQLVVGDL
VEMKGGDRVP ADIRILQAQG CKVDNSSLTG ESEPQTRSPE CTHESPLETR
NIALFSTMCL EGTAQGLVVN TGDRTIIGRI ASLASGVENE KTPIAIEIEH
FVDIIAGLAI LFGATFFVVA MCIGYTFLRA MVFFMAIVVA YVPEGLLATV
TVCLSLTAKR LASKNCVVKN LEAVETLGSK SVICSDKTGT LTQNSMTVSN
LWFDNHIHTA DTTEDQSGQK FDQSSETWRA LCRVLTLCNR AAFKSGQDAV
PVPKRIVIGD ASETALLKFS ELTLGNAMGY RERFPKVCEI PFNSTNKFQL
SIHTLEDPRD PRHVLVMKGA PERVLERCSS ILIKGQELPL DEQWREAFQT
AYLSLGGLGE RVLGFCQLYL SEKDYPPGYA FDVEAMNFPT SGLCFAGLVS
MIDPPRATVP DAVLKCRTAG IRVIMVTGDH PITAKAIAAS VGIISEGSET
VEDIAARLRV PVDQVNRKDA RACVINGMQL KDMDPSELVE ALRTHPEMVF
ARTSPQQKLV IVESCQRLGA IVAVTGDGVN DSPALKKADI GVAMGIAGSD
AAKNAADMIL LDDNFASIVT GVEQGRLIFD NLKKSIAYTL TKNIPELTPY
LIYITVSVPL PLGCITILFI ELCTDIFPSV SLAYEKAESD IMHLRPRNPK
RDRLVNEPLA AYSYFQIGAI QSFAGFTDYF TAMAQEGWFP LLCVGLRPYW
ENHHLQDLQD SYGQEWTFGQ RLYQQYTCYT VFFISIEMCQ IADVLIRKTR
RLSAFQQGFF RNRILVIAIV FQVCIGCFLC YCPGMPNIFN FMPIRYQWWL
VPMPFGLLIF VYDEIRKLGV RCCPGSWWDQ ELYY
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Isotope Labeling, DTNB Method
Reference
- Nagaya H, Satoh H, Kubo K, et al. Possible mechanism for the inhibition of gastric (H++ K+)-adenosine triphosphatase by the proton pump inhibitor AG-1749[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1989, 248(2): 799-805. 2537417