Caspase-8
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CASP8 |
| UNP ID | Q14790 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
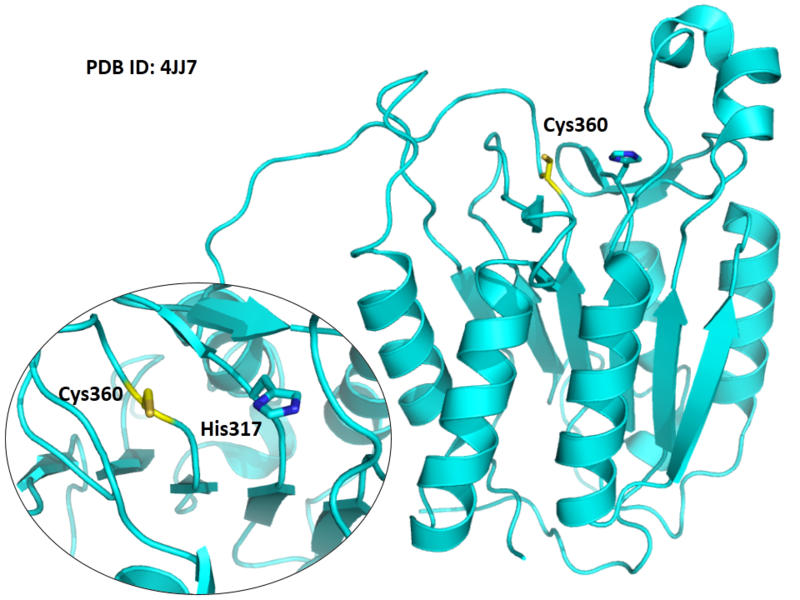
| Cys Site | Cys360 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C14A family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family) are a family of cysteine proteases that have important intracellular roles in inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of caspases ensures that the cellular components are degraded in a controlled manner, carrying out cell death with minimal effect on surrounding tissues. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits.
Caspase-8 activates downstream caspases which are unable to carry out autocatalytic processing and activation. Caspase-8 is designated as an initiator caspase and is believed to sit at the apex of the Fas- or TNF-mediated apoptotic cascade. This protein is involved in the programmed cell death induced by Fas and various apoptotic stimuli. The N-terminal FADD-like death effector domain of this protein suggests that it may interact with Fas-interacting protein FADD. This protein was detected in the insoluble fraction of the affected brain region from Huntington disease patients but not in those from normal controls, which implicated the role in neurodegenerative diseases.
Cys Function & Property
The catalytic triad in caspase-8 comprises Cys360, His317 and the backbone carbonyl oxygen atom of Arg258, which points towards the Nϵ atom of His317.
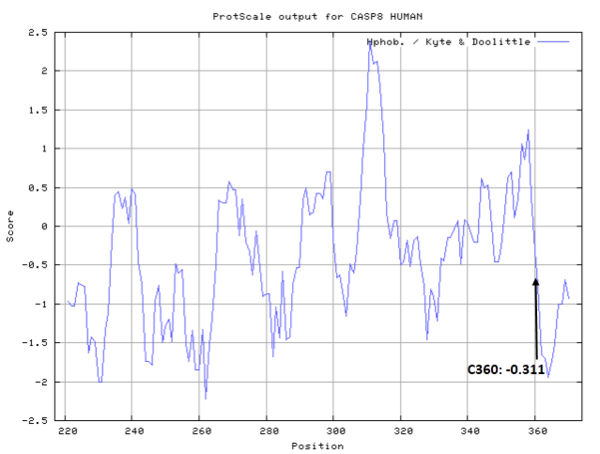
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys360: 7.975 A^2
Protein Sequence
MDFSRNLYDI GEQLDSEDLA SLKFLSLDYI PQRKQEPIKD ALMLFQRLQE
KRMLEESNLS FLKELLFRIN RLDLLITYLN TRKEEMEREL QTPGRAQISA
YRVMLYQISE EVSRSELRSF KFLLQEEISK CKLDDDMNLL DIFIEMEKRV
ILGEGKLDIL KRVCAQINKS LLKIINDYEE FSKERSSSLE GSPDEFSNGE
ELCGVMTISD SPREQDSESQ TLDKVYQMKS KPRGYCLIIN NHNFAKAREK
VPKLHSIRDR NGTHLDAGAL TTTFEELHFE IKPHDDCTVE QIYEILKIYQ
LMDHSNMDCF ICCILSHGDK GIIYGTDGQE APIYELTSQF TGLKCPSLAG
KPKVFFIQAC QGDNYQKGIP VETDSEEQPY LEMDLSSPQT RYIPDEADFL
LGMATVNNCV SYRNPAEGTW YIQSLCQSLR ERCPRGDDIL TILTEVNYEV
SNKDDKKNMG KQMPQPTFTL RKKLVFPSD
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Platinum drug resistance
- p53 signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Necroptosis
- Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Alzheimer disease
- Huntington disease
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Legionellosis
- Chagas disease
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Influenza A
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Viral myocarditis
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography
Reference
- Watt W, Koeplinger K A, Mildner A M, et al. The atomic-resolution structure of human caspase-8, a key activator of apoptosis[J]. Structure, 1999, 7(9): 1135-1143. 10508785
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Protease
- Peptidase C14A family
- Platinum drug resistance
- P53 signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Apoptosis - multiple species
- Necroptosis
- Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- NOD-like receptor signaling pathway
- RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- IL-17 signaling pathway
- TNF signaling pathway
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Alzheimer disease
- Huntington disease
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Legionellosis
- Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis)
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Measles
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Influenza A
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Viral carcinogenesis
- Viral myocarditis