Thioredoxin
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | Trx, TRDX, TXN |
| UNP ID | P10599 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys32, Cys35 |
| Family/Domain | Thioredoxin family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Redox protein |
Summary
Protein Function
Thioredoxin is a class of small redox proteins known to be present in all organisms. It plays a role in many important biological processes, including redox signaling. In humans, thioredoxins are encoded by TXN and TXN2 genes. Loss-of-function mutation of either of the two human thioredoxin genes is lethal at the four-cell stage of the developing embryo. Although not entirely understood, thioredoxin plays a central role in humans and is increasingly linked to medicine through their response to reactive oxygen species (ROS). (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
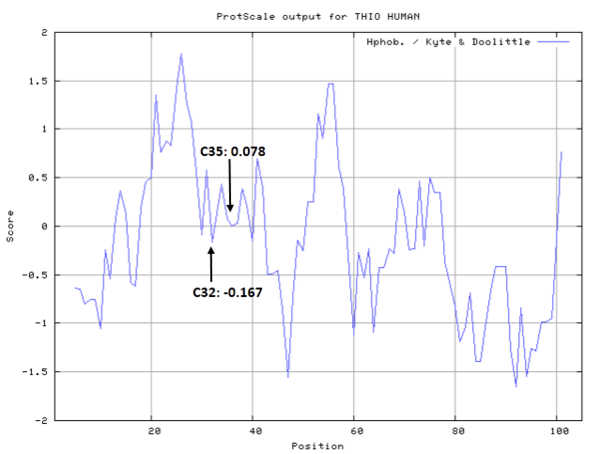
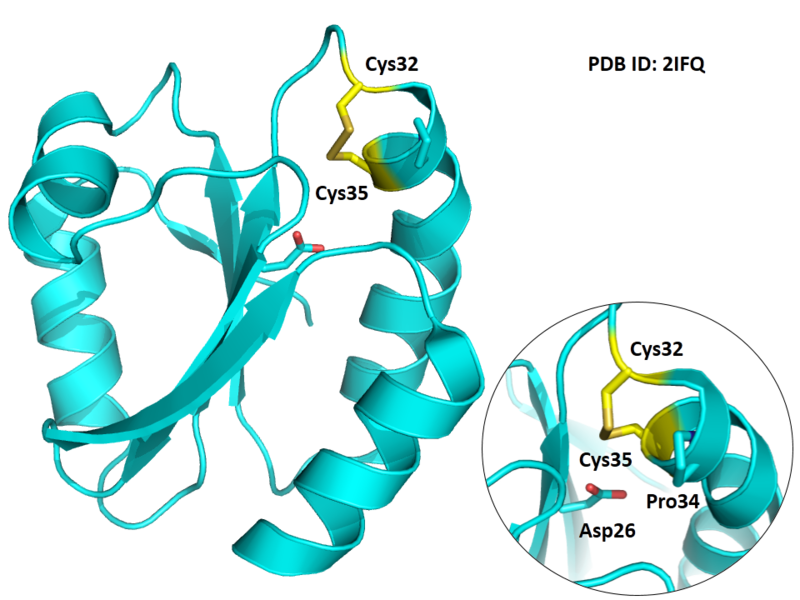
Cys32 and Cys35 are quite close to the active site of Trx, which could form disulfide bond or free state under differrent situtation.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys32: 7.575 A^2
- Cys35: 4.701 A^2
Protein Sequence
MVKQIESKTA FQEALDAAGD KLVVVDFSAT WCGPCKMIKP FFHSLSEKYS
NVIFLEVDVD DCQDVASECE VKCMPTFQFF KKGQKVGEFS GANKEKLEAT
INELV
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- MS/MS spectra, Tryptic Digest, Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Bradshaw T D, Matthews C S, Cookson J, et al. Elucidation of thioredoxin as a molecular target for antitumor quinols[J]. Cancer research, 2005, 65(9): 3911-3919. 23441730
15867391 - Ji W, Yang M, Praggastis A, et al. Carbamoylating activity associated with the activation of the antitumor agent laromustine inhibits angiogenesis by inducing ASK1-dependent endothelial cell death[J]. PloS one, 2014, 9(7): e103224. 23441730
25068797