Monoglyceride lipase
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | MgII, MGL |
| UNP ID | Q8R431 |
| Organism | Rattus norvegicus |
| Cys Site | Cys208 |
| Family/Domain |
Serine aminopeptidase, S33, AB hydrolase superfamily, Monoacylglycerol lipase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) is a cytosolic serine hydrolase that cleaves monoacylglycerols into fatty acid and glycerol through a catalytic mechanism that involves a classical serine-aspartate-histidine triad. MGL is a member of the α/β-hydrolase family of enzymes and is distantly related to microbial lysophospholipases and haloperoxidases. Because of its abundant expression in mammals in lipid-metabolizing tissues, such as white fat and liver, MGL is thought to catalyse the final step of the lipolytic cascade that releases fatty acids from triacylglycerol stores. In the brain, however, a primary role of MGL may be to carry out the hydrolysis and inactivation of the endocannabinoid neurotransmitter, 2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol (2-AG). (PMID: 19486005)
Cys Function & Property
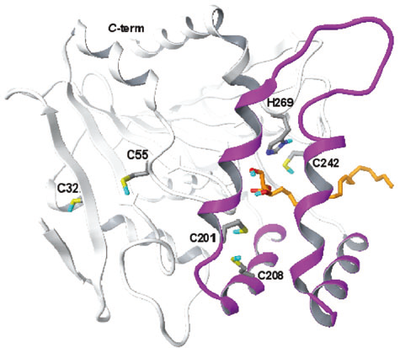
Residues Cys201 and Cys208 are located within the lid domain, wherefrom they might be able to extend their sulphydryl groups towards the substrate-binding site, while residues Cys32 and Cys55 are positioned in two structurally conserved regions: Cys32 in the second beta-strand and Cys55 in a loop before the beginning of the first alpha-helix. Cys301 is not included in the model because it occupies a region of MGL that is not present in the chloroperoxidase template. (PMID: 19486005)
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MPEASSPRRT PQNVPYQDLP HLVNADGQYL FCRYWKPSGT PKALIFVSHG
AGEHCGRYDE LAQMLKRLDM LVFAHDHVGH GQSEGERMVV SDFQVFVRDL
LQHVNTVQKD YPEVPVFLLG HSMGGAISIL AAAERPTHFS GMILISPLIL
ANPESASTLK VLAAKLLNFV LPNISLGRID SSVLSRNKSE VDLYNSDPLI
CHAGVKVCFG IQLLNAVSRV ERAMPRLTLP FLLLQGSADR LCDSKGAYLL
MESSPSQDKT LKMYEGAYHV LHKELPEVTN SVLHEINTWV SHRIAVAGAR
CLP
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed mutation, Homologous Analysis Of Sequence, Molecular Docking
Reference
- King A R, Lodola A, Carmi C, et al. A critical cysteine residue in monoacylglycerol lipase is targeted by a new class of isothiazolinone‐based enzyme inhibitors[J]. British journal of pharmacology, 2009, 157(6): 974-983. 19486005