Polypeptide deformylase
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | PDF1A |
| UNP ID | Q9HBH1 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys172 |
| Family/Domain | Polypeptide deformylase family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Removal of the formyl moiety on methionine of nascent proteins by the metalloprotease peptide deformylase (PDF) is a necessary activity for prokaryotic cell viability. This activity was not believed to be important in eukaryotic cells until recently, because nuclear encoded proteins are not N-formylated. However, in eukaryotes, mitochondrial protein synthesis may involve the formylation and deformylation of proteins, as evidenced by the presence of the enzymatic machinery to perform these activities in mammals and plants, among other eukaryotes. A human peptide deformylase (HsPDF) was recently shown to be present in mitochondria.
The physiologic role of PDF in mammalian cells is unclear. The mitochondrial localization of HsPDF, and the N-terminal Met-formylation of mammalian mitochondrial translation products for translation initiation point at the 13 proteins encoded by the mitochondrial genome as putative substrates of HsPDF.
Cys Function & Property
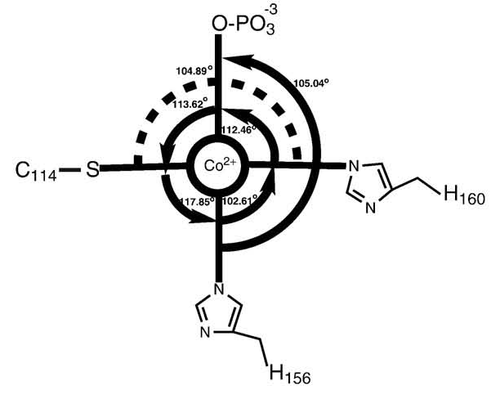
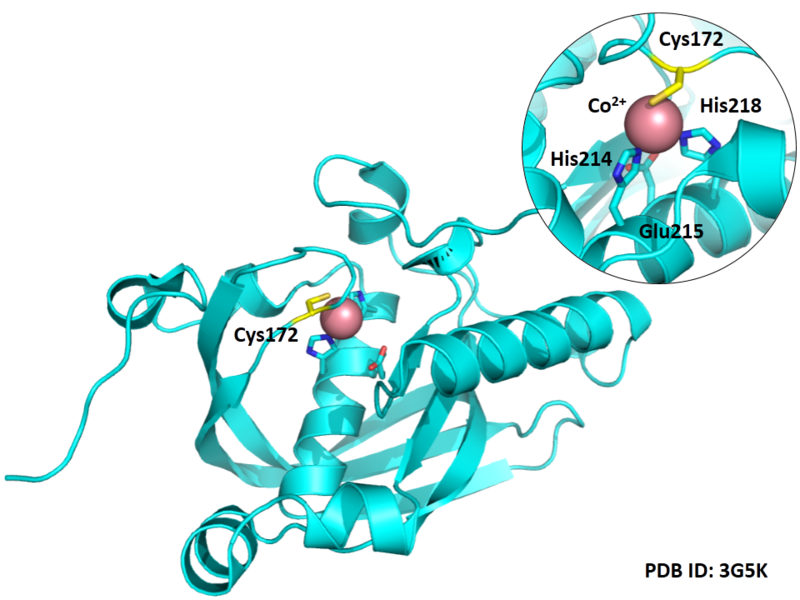
Cys172 is used to bind with metal ion (Co2+), as shown below.
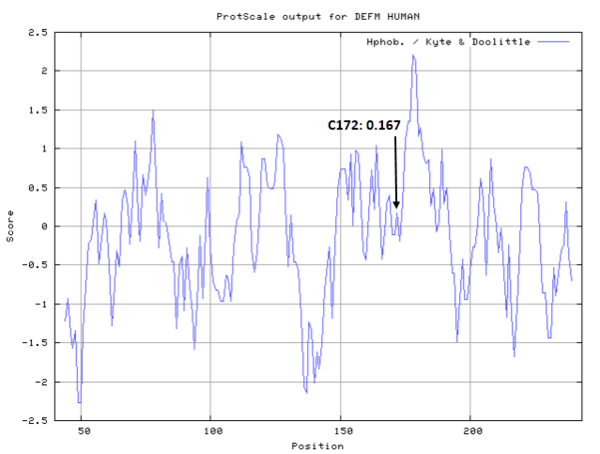
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys172: 8.759 A^2
Protein Sequence
MARLWGALSL WPLWAAVPWG GAAAVGVRAC SSTAAPDGVE GPALRRSYWR
HLRRLVLGPP EPPFSHVCQV GDPVLRGVAA PVERAQLGGP ELQRLTQRLV
QVMRRRRCVG LSAPQLGVPR QVLALELPEA LCRECPPRQR ALRQMEPFPL
RVFVNPSLRV LDSRLVTFPE GCESVAGFLA CVPRFQAVQI SGLDPNGEQV
VWQASGWAAR IIQHEMDHLQ GCLFIDKMDS RTFTNVYWMK VND
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Unknown
Experimental Evidence
- Crystallography, Homologous Analysis of Sequence
Reference
- Escobar-Alvarez S, Goldgur Y, Yang G, et al. Structure and activity of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a novel cancer target[J]. Journal of molecular biology, 2009, 387(5): 1211-1228. 19236878