Cathepsin K (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | CTSK |
| UNP ID | P43236 |
| Organism | Oryctolagus cuniculus |
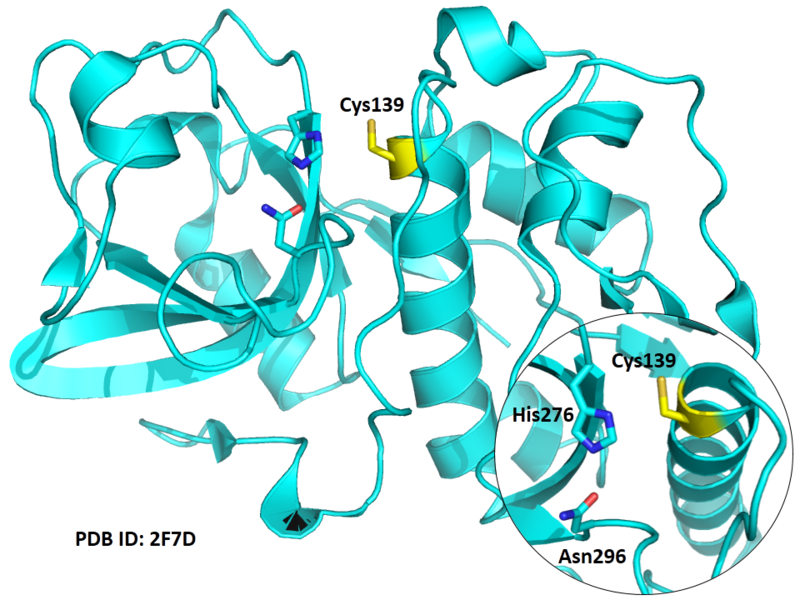
| Cys Site | Cys139 |
| Family/Domain | Peptidase C1 family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Protease |
Summary
Protein Function
Cathepsin K, a member of the peptidase C1 protein family, is expressed predominantly in osteoclasts. The enzyme's ability to catabolize elastin, collagen, and gelatin allow it to break down bone and cartilage. This catabolic activity is also partially responsible for the loss of lung elasticity and recoil in emphysema. Cathepsin K is degraded by Cathepsin S, called Controlled Cathepsin Cannibalism. Cathepsin K expression is stimulated by inflammatory cytokines that are released after tissue injury. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
Cys139 is one of the active sites of Cathepsin K, which is very close to His276 and Asn296 in space (By similiarity). These three residues formed a typical catalytic triad motif.
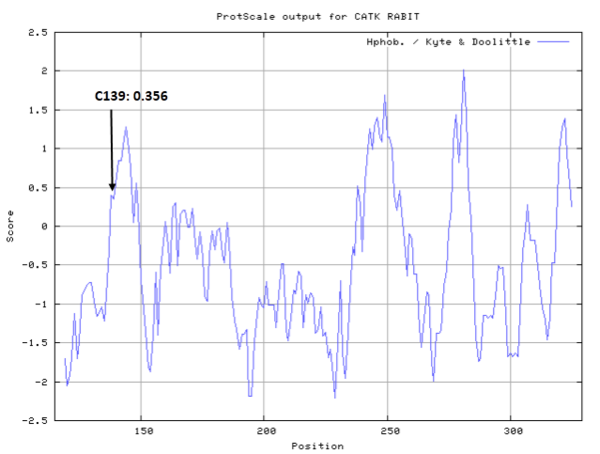
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys139: 11.628 A^2
Protein Sequence
MWGLKVLLLP VVSFALHPEE ILDTQWELWK KTYSKQYNSK VDEISRRLIW
EKNLKHISIH NLEASLGVHT YELAMNHLGD MTSEEVVQKM TGLKVPPSRS
HSNDTLYIPD WEGRTPDSID YRKKGYVTPV KNQGQCGSCW AFSSVGALEG
QLKKKTGKLL NLSPQNLVDC VSENYGCGGG YMTNAFQYVQ RNRGIDSEDA
YPYVGQDESC MYNPTGKAAK CRGYREIPEG NEKALKRAVA RVGPVSVAID
ASLTSFQFYS KGVYYDENCS SDNVNHAVLA VGYGIQKGNK HWIIKNSWGE
SWGNKGYILM ARNKNNACGI ANLASFPKM
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Lysosome
- Apoptosis
- Osteoclast differentiation
- Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Experimental Evidence
- Homologous Analysis Of Sequence, Isotope Labeling
Reference
- Falgueyret J P, Black W C, Cromlish W, et al. An activity-based probe for the determination of cysteine cathepsin protease activities in whole cells[J]. Analytical biochemistry, 2004, 335(2): 218-227. 15556560
- Barrett D G, Catalano J G, Deaton D N, et al. Potent and selective P2–P3 ketoamide inhibitors of cathepsin K with good pharmacokinetic properties via favorable P1′, P1, and/or P3 substitutions[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2004, 14(19): 4897-4902. 15341947