Estrogen receptor
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | ESR1 |
| UNP ID | P11473 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
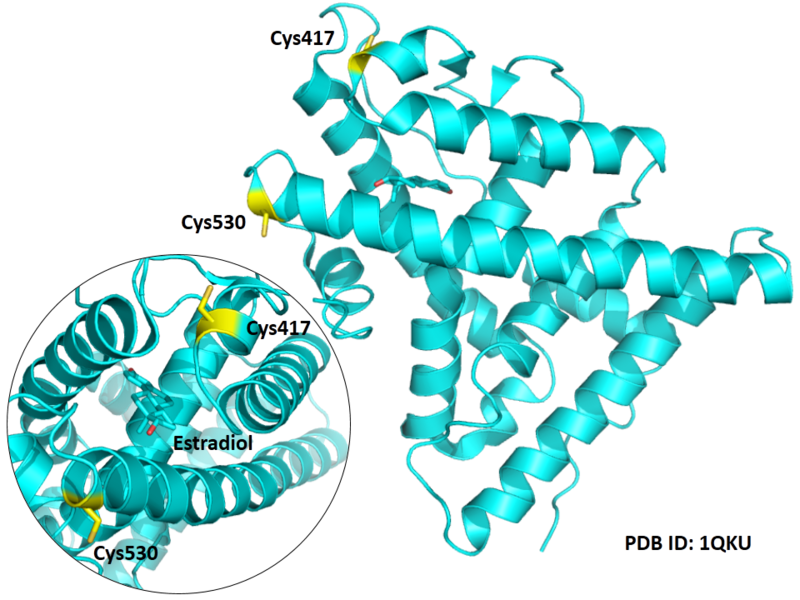
| Cys Site | Cys417, Cys530 |
| Family/Domain |
Ligand-binding domain of nuclear hormone receptor, Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR3 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transcription Related, Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full-length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
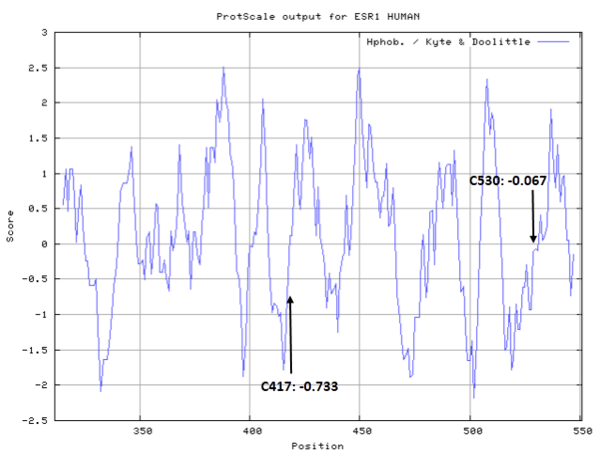
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys417: 55.382 A^2
- Cys530: 73.207 A^2
Protein Sequence
MTMTLHTKAS GMALLHQIQG NELEPLNRPQ LKIPLERPLG EVYLDSSKPA
VYNYPEGAAY EFNAAAAANA QVYGQTGLPY GPGSEAAAFG SNGLGGFPPL
NSVSPSPLML LHPPPQLSPF LQPHGQQVPY YLENEPSGYT VREAGPPAFY
RPNSDNRRQG GRERLASTND KGSMAMESAK ETRYCAVCND YASGYHYGVW
SCEGCKAFFK RSIQGHNDYM CPATNQCTID KNRRKSCQAC RLRKCYEVGM
MKGGIRKDRR GGRMLKHKRQ RDDGEGRGEV GSAGDMRAAN LWPSPLMIKR
SKKNSLALSL TADQMVSALL DAEPPILYSE YDPTRPFSEA SMMGLLTNLA
DRELVHMINW AKRVPGFVDL TLHDQVHLLE CAWLEILMIG LVWRSMEHPG
KLLFAPNLLL DRNQGKCVEG MVEIFDMLLA TSSRFRMMNL QGEEFVCLKS
IILLNSGVYT FLSSTLKSLE EKDHIHRVLD KITDTLIHLM AKAGLTLQQQ
HQRLAQLLLI LSHIRHMSNK GMEHLYSMKC KNVVPLYDLL LEMLDAHRLH
APTSRGGASV EETDQSHLAT AGSTSSHSLQ KYYITGEAEG FPATV
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Endocrine resistance
- Estrogen signaling pathway
- Prolactin signaling pathway
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption
- Pathways in cancer
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Breast cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Aliau S, El Garrouj D, Yasri A, et al. 17α-(Haloacetamidoalkyl) estradiols alkylate the human estrogen receptor at cysteine residues 417 and 530[J]. Biochemistry, 1997, 36(19): 5861-5867. 9153427
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Transcription Related
- Metabolic enzyme
- Nuclear hormone receptor family
- NR3 subfamily
- Endocrine resistance
- Estrogen signaling pathway
- Prolactin signaling pathway
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption
- Pathways in cancer
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Breast cancer