GMP synthetase
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | GMPS |
| UNP ID | P49915 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys104 |
| Family/Domain | Glutamine amidotransferase |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Metabolic enzyme |
Summary
Protein Function
Involved in the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides which are not only essential for DNA and RNA synthesis, but also provide GTP, which is involved in a number of cellular processes important for cell division. (From Uniprot)
Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate. In the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides, IMP is the branch point metabolite at which point the pathway diverges to the synthesis of either guanine or adenine nucleotides. In the guanine nucleotide pathway, there are 2 enzymes involved in converting IMP to GMP, namely IMP dehydrogenase (IMPD1), which catalyzes the oxidation of IMP to XMP, and GMP synthetase, which catalyzes the amination of XMP to GMP.
In enzymology, a GMP synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
The four substrates of this enzyme are ATP, xanthosine 5'-phosphate, L-glutamine, and H2O, whereas its four products are AMP, diphosphate, GMP, and L-glutamate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, specifically those forming carbon-nitrogen bonds carbon-nitrogen ligases with glutamine as amido-N-donor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is xanthosine-5'-phosphate:L-glutamine amido-ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include GMP synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing), guanylate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing), guanosine monophosphate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing), xanthosine 5'-phosphate amidotransferase, and guanosine 5'-monophosphate synthetase. This enzyme participates in purine metabolism and glutamate metabolism. At least one compound, Psicofuranin is known to inhibit this enzyme. (From Wiki)
Cys Function & Property
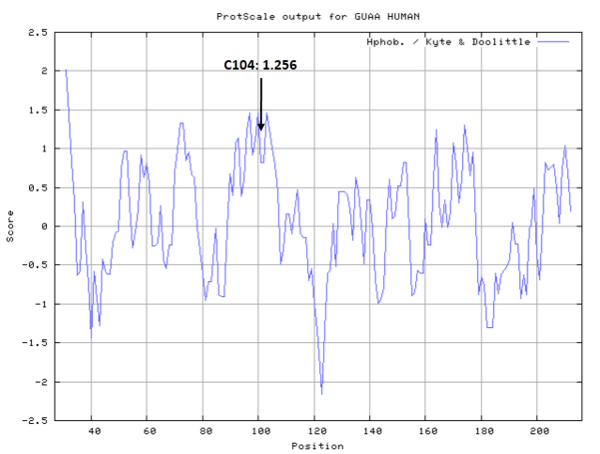
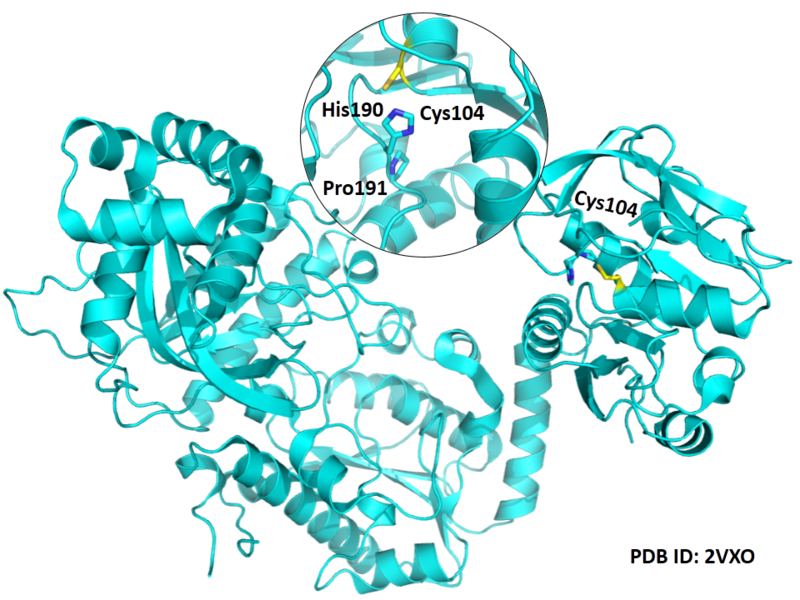
Cys104 is one of the active sites of GMPS.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys104: 7.43 A^2
Protein Sequence
MALCNGDSKL ENAGGDLKDG HHHYEGAVVI LDAGAQYGKV IDRRVRELFV
QSEIFPLETP AFAIKEQGFR AIIISGGPNS VYAEDAPWFD PAIFTIGKPV
LGICYGMQMM NKVFGGTVHK KSVREDGVFN ISVDNTCSLF RGLQKEEVVL
LTHGDSVDKV ADGFKVVARS GNIVAGIANE SKKLYGAQFH PEVGLTENGK
VILKNFLYDI AGCSGTFTVQ NRELECIREI KERVGTSKVL VLLSGGVDST
VCTALLNRAL NQEQVIAVHI DNGFMRKRES QSVEEALKKL GIQVKVINAA
HSFYNGTTTL PISDEDRTPR KRISKTLNMT TSPEEKRKII GDTFVKIANE
VIGEMNLKPE EVFLAQGTLR PDLIESASLV ASGKAELIKT HHNDTELIRK
LREEGKVIEP LKDFHKDEVR ILGRELGLPE ELVSRHPFPG PGLAIRVICA
EEPYICKDFP ETNNILKIVA DFSASVKKPH TLLQRVKACT TEEDQEKLMQ
ITSLHSLNAF LLPIKTVGVQ GDCRSYSYVC GISSKDEPDW ESLIFLARLI
PRMCHNVNRV VYIFGPPVKE PPTDVTPTFL TTGVLSTLRQ ADFEAHNILR
ESGYAGKISQ MPVILTPLHF DRDPLQKQPS CQRSVVIRTF ITSDFMTGIP
ATPGNEIPVE VVLKMVTEIK KIPGISRIMY DLTSKPPGTT EWE
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Edman degradation, HPLC-MS, Tryptic Digest
Reference
- Nakamura J, Straub K, Wu J, et al. The Glutamine Hydrolysis Function of Human GMP Synthetase Identification of an essential active site cysteine[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(40): 23450-23455. 7559506