Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit alpha isoform
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name |
PP2A-alpha, PPP2CA, RP-C |
| UNP ID | P67775 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys269 |
| Family/Domain |
PPP phosphatase family, PP-1 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type |
Phosphatase, Post-translational Modification |
Summary
Protein Function
PP2A consists of a dimeric core enzyme composed of the structural A and catalytic C subunits, and a regulatory B subunit. When the PP2A catalytic C subunit associates with the A and B subunits several species of holoenzymes are produced with distinct functions and characteristics. The A subunit, a founding member of the HEAT repeat protein family (huntington-elongation-A subunit-TOR), is the scaffold required for the formation of the heterotrimeric complex. When the A subunit binds it alters the enzymatic activity of the catalytic subunit, even if the B subunit is absent. While C and A subunit sequences show remarkable sequence conservation throughout eukaryotes, regulatory B subunits are more heterogeneous and are believed to play key roles in controlling the localization and specific activity of different holoenzymes. (From Wikipedia)
Cys Function & Property
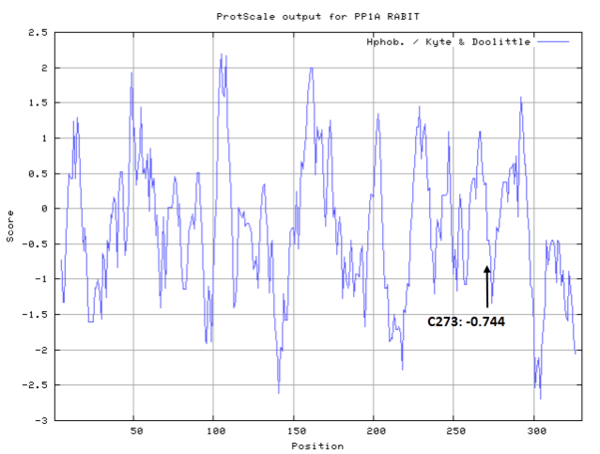
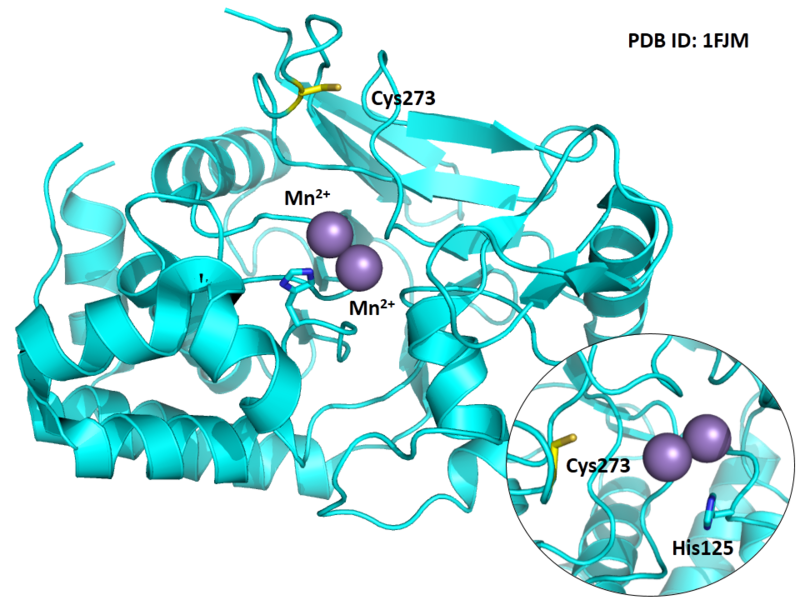
Cys273 is close to the active site and the manganese ions in space.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys273: 31.279 A^2
Protein Sequence
MDEKVFTKEL DQWIEQLNEC KQLSESQVKS LCEKAKEILT KESNVQEVRC
PVTVCGDVHG QFHDLMELFR IGGKSPDTNY LFMGDYVDRG YYSVETVTLL
VALKVRYRER ITILRGNHES RQITQVYGFY DECLRKYGNA NVWKYFTDLF
DYLPLTALVD GQIFCLHGGL SPSIDTLDHI RALDRLQEVP HEGPMCDLLW
SDPDDRGGWG ISPRGAGYTF GQDISETFNH ANGLTLVSRA HQLVMEGYNW
CHDRNVVTIF SAPNYCYRCG NQAAIMELDD TLKYSFLQFD PAPRRGEPHV
TRRTPDYFL
Structural Information
- Known structures with covalent ligands:
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- mRNA surveillance pathway
- Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- Oocyte meiosis
- Autophagy - animal
- PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
- AMPK signaling pathway
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- TGF-beta signaling pathway
- Hippo signaling pathway
- Tight junction
- Dopaminergic synapse
- Long-term depression
- Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis)
- Hepatitis C
- Human papillomavirus infection
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, Isotope Labeling
Reference
- Pereira S R, Vasconcelos V M, Antunes A. Computational study of the covalent bonding of microcystins to cysteine residues–a reaction involved in the inhibition of the PPP family of protein phosphatases[J]. The FEBS journal, 2013, 280(2): 674-680. 22177231
- MacKintosh R W, Dalby K N, Campbell D G, et al. The cyanobacterial toxin microcystin binds covalently to cysteine-273 on protein phosphatase 1[J]. Febs Letters, 1995, 371(3): 236-240. 7556599
- Hastie C J, Borthwick E B, Morrison L F, et al. Inhibition of several protein phosphatases by a non-covalently interacting microcystin and a novel cyanobacterial peptide, nostocyclin[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2005, 1726(2): 187-193. 16046071
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Phosphatase
- Post-translational Modification
- PPP phosphatase family
- PP-1 subfamily
- MRNA surveillance pathway
- Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- Oocyte meiosis
- Autophagy - animal
- PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
- AMPK signaling pathway
- Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
- TGF-beta signaling pathway
- Hippo signaling pathway
- Tight junction
- Dopaminergic synapse
- Long-term depression
- Chagas disease
- Hepatitis C
- Human papillomavirus infection