Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | PTPN11, SHP2 |
| UNP ID | Q06124 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
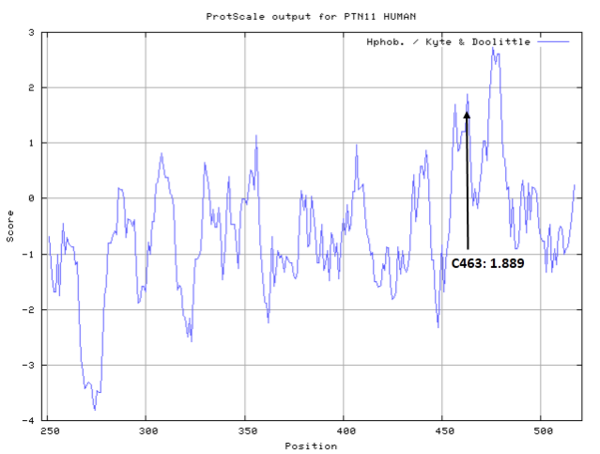
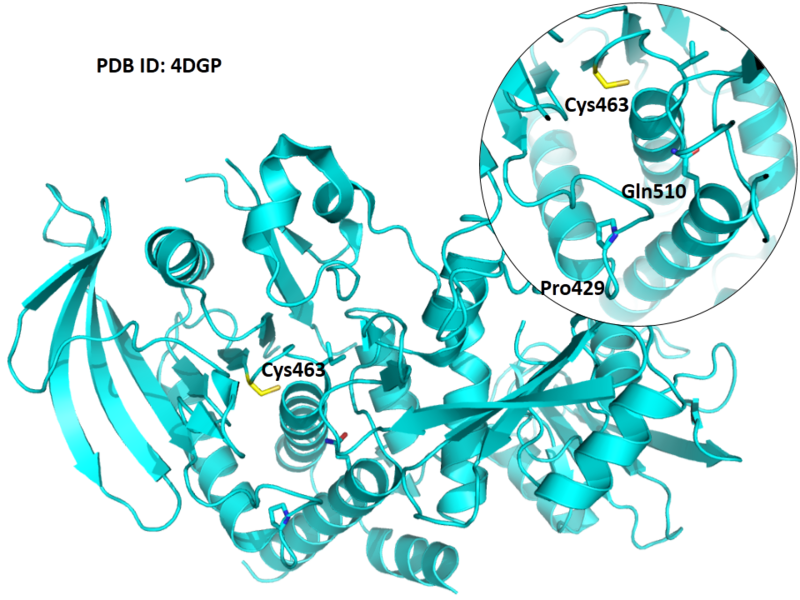
| Cys Site | Cys463 |
| Family/Domain |
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family, Non-receptor class 2 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Post-translational Modification, Phosphatase |
Summary
Protein Function
The Src homology-2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP-2), a member of the ubiquitously expressed protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family, contains a cysteine residue at its active site. SHP-2 is known to localize in the cytosol and nucleus, and plays important biological functions in response to various growth factors, hormones, and cytokines. Recent studies have shown that activation of SHP-2 increases survival of various cell types, including neural progenitor cells and neurons, through activation of ERK1/2. SHP-2 is thought to promote ERK signaling by dephosphorylating negative regulators of the Ras-ERK pathway, such as PAG/Cbp, Ras-GAP, or GAP-binding sites on receptor tyrosine kinases or Sprouty proteins. Additionally, transient activation of the ERK1/2 signaling cascade has been implicated in regulating neuronal survival after stroke. (PMID: 23382182)
Cys Function & Property
Cys463 is one the active residues of PTPN11, which act as a phosphocysteine intermediate in catalytic process.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys463: 3.3 A^2
Protein Sequence
MTSRRWFHPN ITGVEAENLL LTRGVDGSFL ARPSKSNPGD FTLSVRRNGA
VTHIKIQNTG DYYDLYGGEK FATLAELVQY YMEHHGQLKE KNGDVIELKY
PLNCADPTSE RWFHGHLSGK EAEKLLTEKG KHGSFLVRES QSHPGDFVLS
VRTGDDKGES NDGKSKVTHV MIRCQELKYD VGGGERFDSL TDLVEHYKKN
PMVETLGTVL QLKQPLNTTR INAAEIESRV RELSKLAETT DKVKQGFWEE
FETLQQQECK LLYSRKEGQR QENKNKNRYK NILPFDHTRV VLHDGDPNEP
VSDYINANII MPEFETKCNN SKPKKSYIAT QGCLQNTVND FWRMVFQENS
RVIVMTTKEV ERGKSKCVKY WPDEYALKEY GVMRVRNVKE SAAHDYTLRE
LKLSKVGQAL LQGNTERTVW QYHFRTWPDH GVPSDPGGVL DFLEEVHHKQ
ESIMDAGPVV VHCSAGIGRT GTFIVIDILI DIIREKGVDC DIDVPKTIQM
VRSQRSGMVQ TEAQYRFIYM AVQHYIETLQ RRIEEEQKSK RKGHEYTNIK
YSLADQTSGD QSPLPPCTPT PPCAEMREDS ARVYENVGLM QQQKSFR
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Ras signaling pathway
- Phospholipase D signaling pathway
- Axon guidance
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- Jak-STAT signaling pathway
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- Leukocyte transendothelial migration
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- Adipocytokine signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Shi Z Q, Sunico C R, McKercher S R, et al. S-nitrosylated SHP-2 contributes to NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in acute ischemic stroke[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(8): 3137-3142. 23382182
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Post-translational Modification
- Phosphatase
- Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family
- Non-receptor class 2 subfamily
- Ras signaling pathway
- Phospholipase D signaling pathway
- Axon guidance
- C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- Jak-STAT signaling pathway
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- Leukocyte transendothelial migration
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- Adipocytokine signaling pathway
- Insulin resistance
- Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer