Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | PTPN6, SHP1 |
| UNP ID | P29350 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
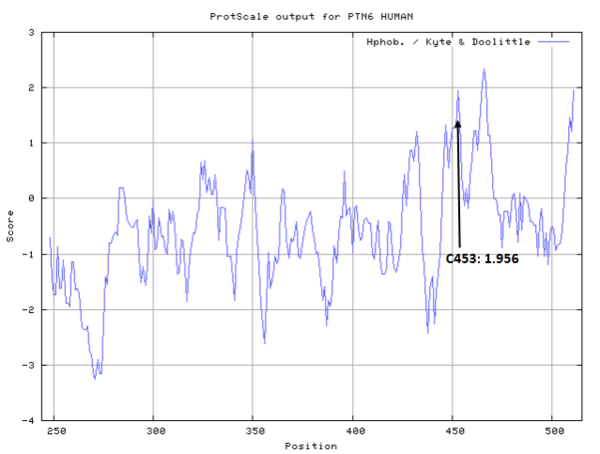
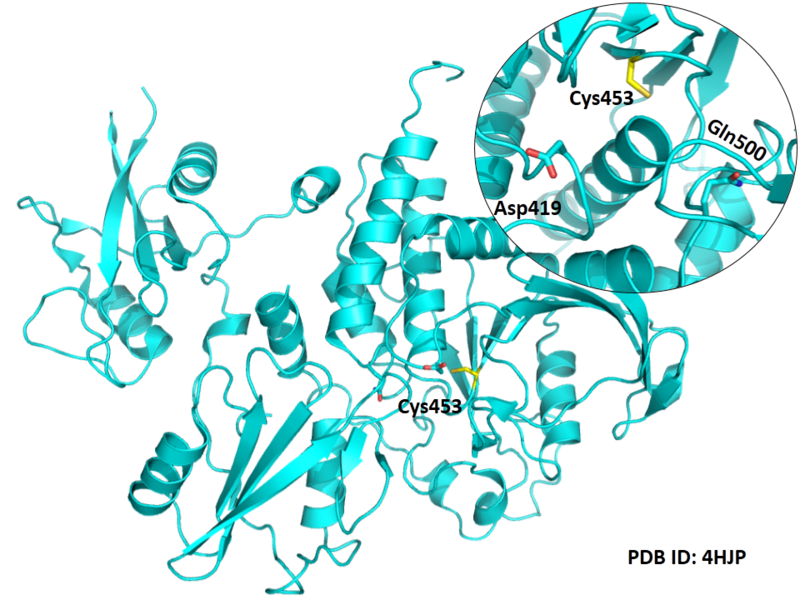
| Cys Site | Cys453 |
| Family/Domain |
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family, Non-receptor class 2 subfamily |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Post-translational Modification, Phosphatase |
Summary
Protein Function
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6, also known as Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1), is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. N-terminal part of SHP-1 contains two tandem Src homolog (SH2) domains, which act as protein phospho-tyrosine binding domains, and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. SHP-1 is expressed primarily in hematopoietic cells, and functions as an important regulator of multiple signaling pathways in hematopoietic cells. This PTP has been shown to interact with, and dephosphorylate a wide spectrum of phospho-proteins involved in hematopoietic cell signaling, (e.g., the LYN-CD22-SHP-1 pathway). (From Wikipedia)
Modulates signaling by tyrosine phosphorylated cell surface receptors such as KIT and the EGF receptor/EGFR. The SH2 regions may interact with other cellular components to modulate its own phosphatase activity against interacting substrates. Together with MTUS1, induces UBE2V2 expression upon angiotensin II stimulation. Plays a key role in hematopoiesis. (From Uniprot)
Cys Function & Property
Cys453 is one the active residues of PTPN6, which act as a phosphocysteine intermediate in catalytic process.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Cys453: 3.3 A^2
Protein Sequence
MVRWFHRDLS GLDAETLLKG RGVHGSFLAR PSRKNQGDFS LSVRVGDQVT
HIRIQNSGDF YDLYGGEKFA TLTELVEYYT QQQGVLQDRD GTIIHLKYPL
NCSDPTSERW YHGHMSGGQA ETLLQAKGEP WTFLVRESLS QPGDFVLSVL
SDQPKAGPGS PLRVTHIKVM CEGGRYTVGG LETFDSLTDL VEHFKKTGIE
EASGAFVYLR QPYYATRVNA ADIENRVLEL NKKQESEDTA KAGFWEEFES
LQKQEVKNLH QRLEGQRPEN KGKNRYKNIL PFDHSRVILQ GRDSNIPGSD
YINANYIKNQ LLGPDENAKT YIASQGCLEA TVNDFWQMAW QENSRVIVMT
TREVEKGRNK CVPYWPEVGM QRAYGPYSVT NCGEHDTTEY KLRTLQVSPL
DNGDLIREIW HYQYLSWPDH GVPSEPGGVL SFLDQINQRQ ESLPHAGPII
VHCSAGIGRT GTIIVIDMLM ENISTKGLDC DIDIQKTIQM VRAQRSGMVQ
TEAQYKFIYV AIAQFIETTK KKLEVLQSQK GQESEYGNIT YPPAMKNAHA
KASRTSSKHK EDVYENLHTK NKREEKVKKQ RSADKEKSKG SLKRK
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
Related Pathway
- Adherens junction
- Jak-STAT signaling pathway
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- Leishmaniasis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation
Reference
- Barrett D M, Black S M, Todor H, et al. Inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatases by mild oxidative stresses is dependent on S-nitrosylation[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005, 280(15): 14453-14461. 15684422
- Targets
- Homo sapiens
- Post-translational Modification
- Phosphatase
- Protein-tyrosine phosphatase family
- Non-receptor class 2 subfamily
- Adherens junction
- Jak-STAT signaling pathway
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- Leishmaniasis
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer