Difference between revisions of "Sodium/bile acid cotransporter"
(→Summary) |
(→Summary) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Protein Function === | ===Protein Function === | ||
The Na<sup>+</sup>-dependent taurocholate (TC) cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP/Ntcp) is the major sinusoidal bile salt transporter of hepatocytes. Ntcp mediates the transport of conjugated bile salts such as TC and taurochenodeoxycholate in a Na<sup>+</sup>-dependent fashion using the Na<sup>+</sup> gradient produced by the Na<sup>+</sup>-K<sup>+</sup>-ATPase. (PMID: 23886862) <br/> | The Na<sup>+</sup>-dependent taurocholate (TC) cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP/Ntcp) is the major sinusoidal bile salt transporter of hepatocytes. Ntcp mediates the transport of conjugated bile salts such as TC and taurochenodeoxycholate in a Na<sup>+</sup>-dependent fashion using the Na<sup>+</sup> gradient produced by the Na<sup>+</sup>-K<sup>+</sup>-ATPase. (PMID: 23886862) <br/> | ||
| − | + | [[File:583-function.png|center|400px]] | |
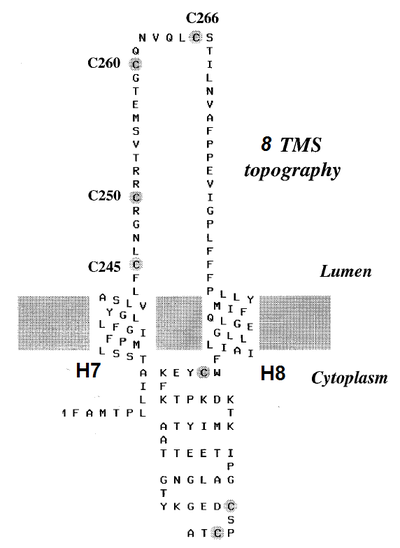
<div align="center">Distribution of cysteine residues</div> | <div align="center">Distribution of cysteine residues</div> | ||
===Cys Function & Property=== | ===Cys Function & Property=== | ||
| − | Ntcp has 8 cysteines, and one of these, Cys266, is highly conserved not only across several species but also with the NTCP/Ntcp homolog, apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter (Asbt). <br/> | + | Ntcp has 8 cysteines, and one of these, Cys266, is highly conserved not only across several species but also with the NTCP/Ntcp homolog, apical Na<sup>+</sup>-dependent bile acid transporter (Asbt). <br/> |
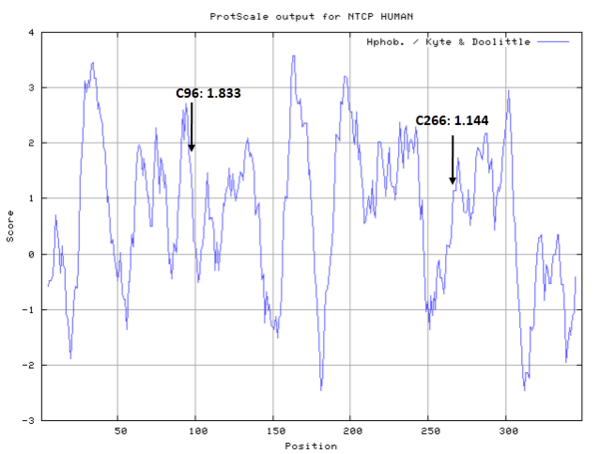
Some three-dimensional homology model for human NTCP predicts that Cys96 lies in a possible permeation pathway for Na<sup>+</sup>. And S-nitrosylation of Cys96 may result in steric hindrance that blocks the permeation pathway for Na<sup>+</sup> and thereby inhibits Ntcp function. <br/> | Some three-dimensional homology model for human NTCP predicts that Cys96 lies in a possible permeation pathway for Na<sup>+</sup>. And S-nitrosylation of Cys96 may result in steric hindrance that blocks the permeation pathway for Na<sup>+</sup> and thereby inhibits Ntcp function. <br/> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:43, 22 August 2019
| Basic Information | |
|---|---|
| Short Name | SLC10A1 |
| UNP ID | Q14973 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Cys Site | Cys96, Cys266 |
| Family/Domain | Bile acid:sodium symporter family |
| Known Ligand | Ligand list |
| Function Type | Transporter |
Summary
Protein Function
The Na+-dependent taurocholate (TC) cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP/Ntcp) is the major sinusoidal bile salt transporter of hepatocytes. Ntcp mediates the transport of conjugated bile salts such as TC and taurochenodeoxycholate in a Na+-dependent fashion using the Na+ gradient produced by the Na+-K+-ATPase. (PMID: 23886862)
Cys Function & Property
Ntcp has 8 cysteines, and one of these, Cys266, is highly conserved not only across several species but also with the NTCP/Ntcp homolog, apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter (Asbt).
Some three-dimensional homology model for human NTCP predicts that Cys96 lies in a possible permeation pathway for Na+. And S-nitrosylation of Cys96 may result in steric hindrance that blocks the permeation pathway for Na+ and thereby inhibits Ntcp function.
- Hydrophobic property:
- SASA:
- Unknown
Protein Sequence
MEAHNASAPF NFTLPPNFGK RPTDLALSVI LVFMLFFIML SLGCTMEFSK
IKAHLWKPKG LAIALVAQYG IMPLTAFVLG KVFRLKNIEA LAILVCGCSP
GGNLSNVFSL AMKGDMNLSI VMTTCSTFCA LGMMPLLLYI YSRGIYDGDL
KDKVPYKGIV ISLVLVLIPC TIGIVLKSKR PQYMRYVIKG GMIIILLCSV
AVTVLSAINV GKSIMFAMTP LLIATSSLMP FIGFLLGYVL SALFCLNGRC
RRTVSMETGC QNVQLCSTIL NVAFPPEVIG PLFFFPLLYM IFQLGEGLLL
IAIFWCYEKF KTPKDKTKMI YTAATTEETI PGALGNGTYK GEDCSPCTA
Structural Information
- Known structure with covalent ligand:
- Unknown
- Protein structure:
- Unknown
Related Pathway
Experimental Evidence
- Cys-directed Mutation, Homology Modeling
Reference
- Ramasamy U, Anwer M S, Schonhoff C M. Cysteine 96 of Ntcp is responsible for NO-mediated inhibition of taurocholate uptake[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 2013, 305(7): G513-G519. 23886862